Get the free Geospatial Information Systems - Farm Service Agency
Get, Create, Make and Sign geospatial information systems

How to edit geospatial information systems online
Uncompromising security for your PDF editing and eSignature needs
How to fill out geospatial information systems
How to fill out geospatial information systems
Who needs geospatial information systems?
Understanding Geospatial Information Systems Form
Understanding geospatial information systems (GIS)
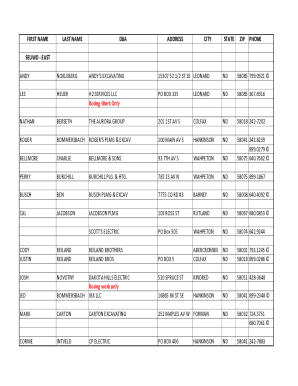
Geospatial Information Systems (GIS) encompass a framework that captures, stores, analyzes, and manages spatial data linked to specific geographic locations. These systems allow users to map and analyze data through advanced visualization techniques, enabling better decision-making across various fields.
The origins of GIS can be traced back to the 1960s, with early systems primarily focused on managing land resources. Over decades, advancements in computing technology and data processing have led to the emergence of sophisticated GIS applications that serve a vast array of sectors including transportation, urban planning, and environmental conservation. GIS enables organizations to visualize data trends over time and space, contributing to more informed decision-making.
In today’s increasingly digital world, the importance of GIS has skyrocketed. From urban planners leveraging spatial data for land use to scientists modeling climate change impacts, GIS is integral to data-driven decision-making processes. As technology continues to evolve, GIS remains a critical tool for effectively addressing complex spatial challenges.
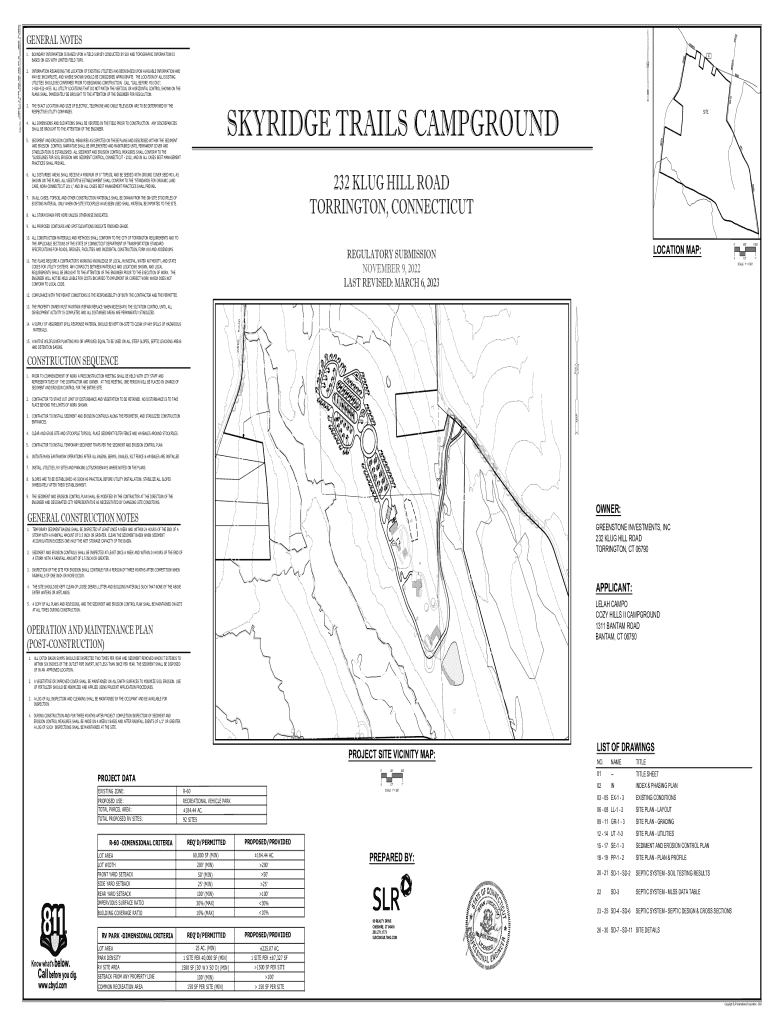
Components of a geospatial information system
A comprehensive GIS is made up of several fundamental components: hardware, software, geospatial data, and database management systems. Each of these elements plays a critical role in ensuring the efficient functioning of a GIS.
The hardware for GIS typically includes computers, GPS systems, and servers designed to handle large datasets. Software applications like ArcGIS and QGIS offer extensive tools for data analysis and visualization, catering to different user needs. Geospatial data itself can be classified into two primary types: raster data, made up of pixels (such as satellite images), and vector data, consisting of points, lines, and polygons (such as boundaries and roads).
Common uses of GIS
GIS applications are diverse and impactful across many sectors. In urban planning, for instance, GIS aids city planners in effectively managing land use, zoning, and resource allocation. Environmental organizations utilize GIS for monitoring wildlife habitats and assessing the impact of climate change, while government agencies rely on it for disaster response by assessing risk zones and planning evacuation routes.
Transportation networks also benefit from GIS, which optimizes routes and enhances logistics for freight and public transport systems. Additionally, researchers in fields such as public health use GIS to track disease outbreaks and assess population health trends. This multi-faceted approach highlights how integral GIS has become across various industries.
Filling out the geospatial information systems form
Accessing and completing the geospatial information systems form is crucial for efficient data capturing and project planning. To get started, users can find the form on pdfFiller, which provides a straightforward interface for document management.
When filling out the form, pay close attention to the key fields. These include personal information such as name and contact details, specific geographic data requirements regarding the area of study, and clearly defined project objectives and scope to ensure that all data is relevant and appropriately classified.
For optimal data accuracy, ensure that all geographic details are up-to-date, and consider collaboration with team members for verification.
Editing and collaborating on GIS forms
Once the geospatial information systems form is filled out, pdfFiller offers robust editing tools. Users can add comments and notes directly onto the document, offering insights or clarifications for colleagues. This feature enhances collaboration, enabling real-time feedback and adjustments, which is essential for project accuracy.
To streamline teamwork, organize regular review sessions where members can discuss edits in person or via video call while using the pdfFiller platform. This shared space fosters connectivity and transparency in the collaborative work process.
Signing and managing GIS documents
E-signing the geospatial information systems form is a straightforward process on pdfFiller. Users can quickly add their signatures using various available methods, including typing, drawing, or uploading an image of their signature. This seamless capability ensures that documents are signed, stored, and shared without unnecessary delays.
In addition to signing, pdfFiller provides essential document management features. Users can categorize GIS files, track the status of documents, and manage revisions. This organization is crucial for maintaining comprehensive records of projects and ensuring that all team members have access to the most current information.
Advanced functions in geospatial information systems
Beyond basic functions, GIS offers a variety of advanced analytical techniques. Spatial analysis, for example, facilitates the identification of relationships between different geographic features, which greatly enhances the understanding of spatial patterns. This could include everything from analyzing demographic changes in urban development to understanding environmental impacts on wildlife.
Cartography methods within GIS are equally impressive, as they allow users to create detailed and visually appealing maps that can be used in presentations or publications. The ongoing trends in GIS technology, such as the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning, promise further advancements in how geospatial data is processed and utilized.
Addressing GIS challenges
While GIS holds significant advantages, various challenges can arise during geospatial data collection and management. Common pitfalls include data redundancy, which can inflate costs and processing time, and issues related to data accuracy, which jeopardize the reliability of analyses. As geospatial technology becomes increasingly sophisticated, maintaining data integrity is essential.
Ethical considerations in GIS usage are also paramount, particularly regarding data privacy and the socio-political implications of mapping. GIS professionals must remain vigilant about ethical standards to ensure that data is used responsibly without infringing on individuals' rights or perpetuating inequalities.
Future of geospatial information systems
Looking ahead, the future of GIS appears poised for transformative changes driven by emerging technologies. Innovations such as augmented reality (AR) and the Internet of Things (IoT) are beginning to integrate with GIS, enhancing capabilities and opening new avenues for data collection and interaction. These advancements could revolutionize fields such as urban planning and emergency management, as they allow for real-time data analysis and visualization.
Moreover, the role of GIS in global sustainability efforts is undeniable. As societies strive to address environmental challenges through resource management and urban adaptation, GIS will serve as a crucial tool for data-driven decision-making. Additionally, public participation in geospatial data collection is gaining traction, which empowers communities and ensures that diverse perspectives are included in planning processes.






For pdfFiller’s FAQs
Below is a list of the most common customer questions. If you can’t find an answer to your question, please don’t hesitate to reach out to us.
How can I edit geospatial information systems from Google Drive?
How do I edit geospatial information systems straight from my smartphone?
How do I edit geospatial information systems on an Android device?
What is geospatial information systems?
Who is required to file geospatial information systems?
How to fill out geospatial information systems?
What is the purpose of geospatial information systems?
What information must be reported on geospatial information systems?
pdfFiller is an end-to-end solution for managing, creating, and editing documents and forms in the cloud. Save time and hassle by preparing your tax forms online.