What is 2 sample t test formula?
The 2 sample t test formula is a statistical method used to determine if there is a significant difference between the means of two independent groups. It is commonly used in hypothesis testing to assess whether the means of two populations are statistically different from each other. The formula calculates a t-value, which represents the difference between the sample means divided by the variability within the samples. By comparing the t-value to a critical value, we can determine if the difference is statistically significant.
What are the types of 2 sample t test formula?
There are three common types of 2 sample t test formula:
Independent samples t-test: This is used when the two groups being compared are completely independent of each other, meaning there is no relationship or pairing between the observations in the two groups.
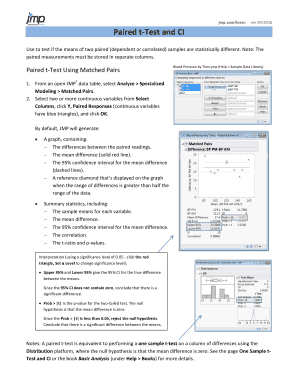
Paired samples t-test: This is used when the two groups being compared are related or paired in some way. For example, the same group of subjects is measured before and after an intervention.
Equal variance t-test: This is used when the assumption of equal variances between the two groups is met. It allows for the comparison of means when the variances are assumed to be equal.
How to complete 2 sample t test formula
To complete the 2 sample t test formula, follow these steps:
01
Specify the null hypothesis and alternative hypothesis based on the research question.
02
Collect data from the two independent groups.
03
Calculate the sample means, standard deviations, and sample sizes for each group.
04
Calculate the t-value using the formula: t = (mean1 - mean/ sqrt((s1^2 / n+ (s2^2 / n2)), where mean1 and mean2 are the sample means, s1 and s2 are the sample standard deviations, and n1 and n2 are the sample sizes.
05
Determine the degrees of freedom, typically calculated as (n1 - + (n2 - 1).
06
Find the critical value for the desired significance level and degrees of freedom in the t-distribution table.
07
Compare the calculated t-value with the critical value to determine if the null hypothesis should be rejected or not.
08
Interpret the results and draw conclusions based on the analysis.
pdfFiller empowers users to create, edit, and share documents online. Offering unlimited fillable templates and powerful editing tools, pdfFiller is the only PDF editor users need to get their documents done.