Separation Equation Pdf मुफ़्त में
Drop document here to upload
Up to 100 MB for PDF and up to 25 MB for DOC, DOCX, RTF, PPT, PPTX, JPEG, PNG, JFIF, XLS, XLSX or TXT
Note: Integration described on this webpage may temporarily not be available.
0
Forms filled
0
Forms signed
0
Forms sent
Discover the simplicity of processing PDFs online

Upload your document in seconds

Fill out, edit, or eSign your PDF hassle-free

Download, export, or share your edited file instantly
Top-rated PDF software recognized for its ease of use, powerful features, and impeccable support






Every PDF tool you need to get documents done paper-free
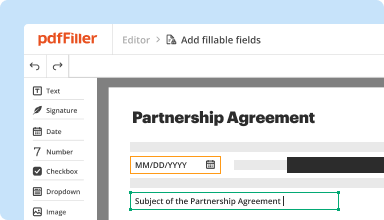
Create & edit PDFs
Generate new PDFs from scratch or transform existing documents into reusable templates. Type anywhere on a PDF, rewrite original PDF content, insert images or graphics, redact sensitive details, and highlight important information using an intuitive online editor.
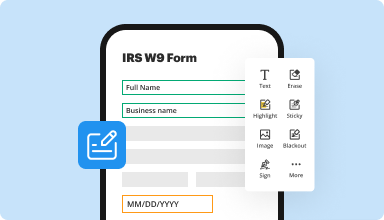
Fill out & sign PDF forms
Say goodbye to error-prone manual hassles. Complete any PDF document electronically – even while on the go. Pre-fill multiple PDFs simultaneously or extract responses from completed forms with ease.
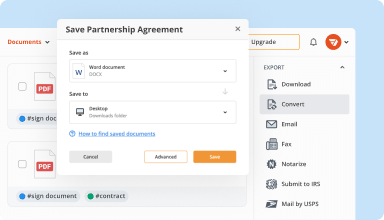
Organize & convert PDFs
Add, remove, or rearrange pages inside your PDFs in seconds. Create new documents by merging or splitting PDFs. Instantly convert edited files to various formats when you download or export them.
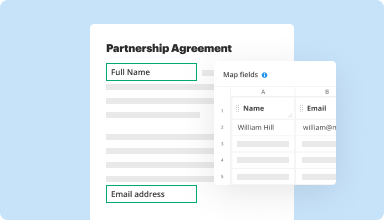
Collect data and approvals
Transform static documents into interactive fillable forms by dragging and dropping various types of fillable fields on your PDFs. Publish these forms on websites or share them via a direct link to capture data, collect signatures, and request payments.
Export documents with ease
Share, email, print, fax, or download edited documents in just a few clicks. Quickly export and import documents from popular cloud storage services like Google Drive, Box, and Dropbox.
Store documents safely
Store an unlimited number of documents and templates securely in the cloud and access them from any location or device. Add an extra level of protection to documents by locking them with a password, placing them in encrypted folders, or requesting user authentication.
Customer trust by the numbers
64M+
users worldwide
4.6/5
average user rating
4M
PDFs edited per month
9 min
average to create and edit a PDF
Join 64+ million people using paperless workflows to drive productivity and cut costs
Why choose our PDF solution?
Cloud-native PDF editor
Access powerful PDF tools, as well as your documents and templates, from anywhere. No installation needed.
Top-rated for ease of use
Create, edit, and fill out PDF documents faster with an intuitive UI that only takes minutes to master.
Industry-leading customer service
Enjoy peace of mind with an award-winning customer support team always within reach.
What our customers say about pdfFiller
See for yourself by reading reviews on the most popular resources:
Hard to find the erase button. But after I asked, I found it buried in the "tools" --seems like it should be more visible. Love the tool's simplicity otherwise.
2015-07-15
Directions to find the form to be edited could be more simple and spelled out. Through trial and error, I was able to edit the form to my satisfaction. Thanks.
2016-12-15
Everything works great, however when you send a document to sign, it would be more helpful if there was a brief explanation of instructions, so the receiving end understands how to actually go in and sign the document.
2018-10-29
What do you like best?
being able to access a document that I use every month and just make the few changes
What do you dislike?
I have not found any thing yet that I dislike about PDF filler. I tried to think and I just cannot think of anything that I don't like. It works for my needs.
Recommendations to others considering the product:
Try it you will love it and it will change the way you work.
What problems are you solving with the product? What benefits have you realized?
Time saver is the biggest. It no longer takes me 30 minutes to complete a form handwritten. I just download it to pdf filler and go in and type in the answers. I use it every single day and it saves so much of my time and my time is valuable so it is also saving our company money.
being able to access a document that I use every month and just make the few changes
What do you dislike?
I have not found any thing yet that I dislike about PDF filler. I tried to think and I just cannot think of anything that I don't like. It works for my needs.
Recommendations to others considering the product:
Try it you will love it and it will change the way you work.
What problems are you solving with the product? What benefits have you realized?
Time saver is the biggest. It no longer takes me 30 minutes to complete a form handwritten. I just download it to pdf filler and go in and type in the answers. I use it every single day and it saves so much of my time and my time is valuable so it is also saving our company money.
2019-05-21
I needed to urgently get some documents compressed and I found this online and went on basic plan . The team support was very helpful . This is a very effective tool for all documentation work
2023-09-11
I would like to become more familiar…
I would like to become more familiar with the PDF-filler tools before I provide a final Review but up to now I am happy with the program
Thanks
Chuck
2022-03-14
pdfFiller has really made editing and…
pdfFiller has really made editing and signing pdf easier for me. It has really made my work much more accessible and easy.
2021-10-29
Could be worse!
Cheap, handy, available on all my devices. Billing department works very fast and efficient.
Glitches and crashes while I am doing offline editing.
What do you think about this review?
2021-03-19
Great customer service
Great customer service, and the software allowed me to edit documents that I needed to sign and scan without access to anpronter
2021-02-22
Separation Equation PDF Feature
The Separation Equation PDF feature provides users with a straightforward way to generate, manage, and share separation equations in a convenient PDF format. With this feature, you can streamline your work and ensure that your information is well-organized and easily accessible.
Key Features
Easy generation of separation equations in PDF format
Customizable templates to suit your needs
High-quality, print-ready output
Compatibility with various devices and platforms
User-friendly interface for beginners and experts
Potential Use Cases and Benefits
Use in academic settings for assignments and presentations
Share with colleagues during meetings for clear communication
Maintain organized records for future reference
Enhance professional reports with visually appealing documents
Access anywhere, anytime for flexible working
This feature effectively addresses your need for a reliable way to create and share equations. By simplifying the process, you save time and reduce errors, allowing you to focus on your core tasks. Whether you are a student, a teacher, or a professional, the Separation Equation PDF feature empowers you to present your work clearly and efficiently.
For pdfFiller’s FAQs
Below is a list of the most common customer questions. If you can’t find an answer to your question, please don’t hesitate to reach out to us.
What if I have more questions?
Contact Support
How do you separate XY?
Multiply both sides by DX:Dy = (1/y) DX. Multiply both sides by y: y Dy = DX. Put the integral sign in front: y Dy = DX. Integrate each side: (y2)/2 = x + C. Multiply both sides by 2: y2 = 2(x + C)
How do you separate a differential equation?
The method for solving separable equations can therefore be summarized as follows: Separate the variables and integrate. Example 1: Solve the equation 2 y Dy = (x 2 + 1) DX. Example 4: Find all solutions of the differential equation (x 2 1) y 3 DX + x 2 Dy = 0.
When can you separate variables?
Separation of variables. In mathematics, separation of variables (also known as the Fourier method) is any of several methods for solving ordinary and partial differential equations, in which algebra allows one to rewrite an equation so that each of two variables occurs on a different side of the equation.
What is a differential equation example?
Differential Equations. A Differential Equation is an equation with a function and one or more of its derivatives: Example: an equation with the function y and its derivative Dy DX.
Why is a separable differential equation always exact?
For example, separable equations are always exact, since by definition they are of the form: M(y)y + N(t)=0, and then if A(y), B(t) are antiderivative of M and N (resp.), this is the same as: (A(y) + B(t)) = 0, so (t, y) = A(y) + B(t) is a conserved quantity.
When can you not use separation of variables?
Short answer: For equations that have constant coefficient, live in a nice domain, with some appropriate boundary condition, we can solve it by separation of variables. If we change one of above three conditions, then most of the time we can't solve it by separation of variables.
Does separation of variables always work?
The method of Separation of Variables cannot always be used and even when it can be used it will not always be possible to get much past the first step in the method.
Can this differential equation be solved using separation of variables?
”Separation of variables” allows us to rewrite differential equations, so we obtain an equality between two integrals we can evaluate. Separable equations are the class of differential equations that can be solved using this method.
#1 usability according to G2
Try the PDF solution that respects your time.






