Aws Electronic Signature For Free




Join the world’s largest companies
How to Aws Electronic Signature - video instructions
Watch the video guide to learn more about pdfFiller's online Signature feature









Why choose pdfFiller for eSignature and PDF editing?

Cross-platform solution

Unlimited document storage

Widely recognized ease of use

Reusable templates & forms library
The benefits of electronic signatures

Efficiency

Accessibility

Cost savings

Security

Legality

Sustainability
Enjoy straightforward eSignature workflows without compromising data security

GDPR compliance

SOC 2 Type II Certified

PCI DSS certification

HIPAA compliance

CCPA compliance
AWS Electronic Signature Feature
AWS Electronic Signature feature simplifies the process of signing and managing documents. With this solution, you can accelerate workflows, enhance security, and improve compliance. It offers a reliable, user-friendly interface for capturing electronic signatures digitally.
Key Features
Potential Use Cases and Benefits
By implementing AWS Electronic Signature, you can resolve common challenges related to document signing. It eliminates the need for physical paperwork, reduces delays in processes, and enhances security through encryption. Use this feature to improve efficiency in your organization while maintaining compliance and security.
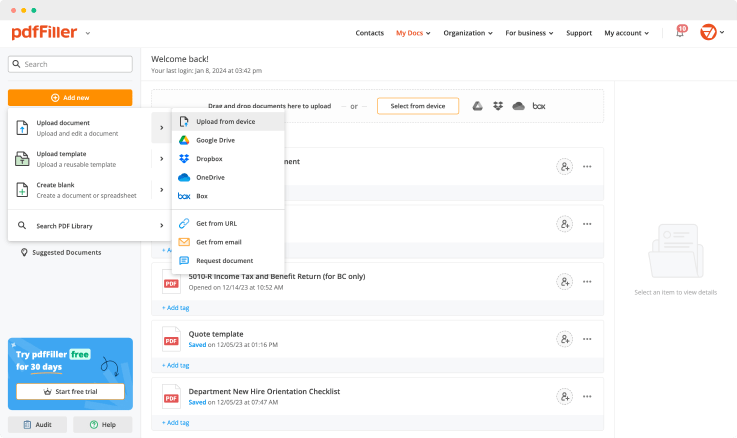
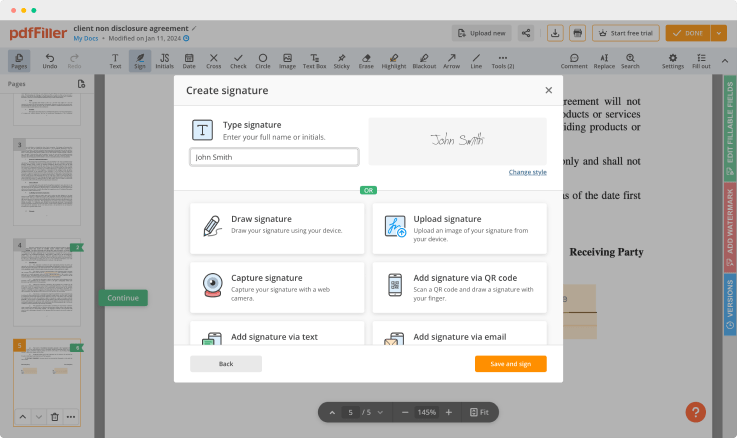
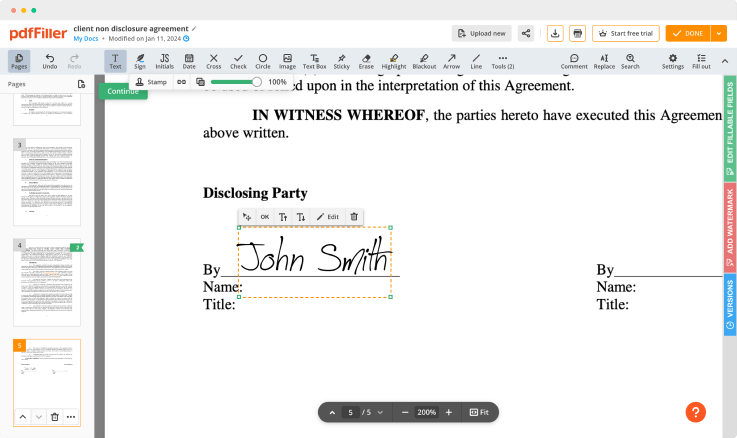
How to AWS Electronic Signature
Stuck working with numerous applications for managing documents? Try this all-in-one solution instead. Use our document management tool for the fast and efficient process. Create forms, contracts, make document templates, integrate cloud services and utilize other features within one browser tab. Plus, the opportunity to use Aws Electronic Signature and add more features like orders signing, alerts, attachment and payment requests, easier than ever. Have the value of full featured program, for the cost of a lightweight basic app. The key is flexibility, usability and customer satisfaction. We deliver on all three.
How-to Guide
How to edit a PDF document using the pdfFiller editor:
For pdfFiller’s FAQs
Ready to try pdfFiller's? Aws Electronic Signature