Understanding PSYC 300: Statistics in Form
Understanding the importance of statistics in psychology
Statistics play a pivotal role in the field of psychology, acting as the backbone of research studies and data analysis. In this context, statistics can be defined as the systematic collection, analysis, interpretation, presentation, and organization of data. They are integral in providing clarity and insight, allowing psychologists to make informed decisions based on empirical evidence.
In research, statistics enable psychologists to analyze behavioral data and evaluate the effectiveness of different therapeutic approaches. They provide tools to quantify results and translate intangible human thoughts and behaviors into quantifiable data—critical for validating or challenging psychological theories.
Improved Decision-Making: Statistical analysis helps psychologists make reasoned decisions based on evidence.
Enhanced Research Validity: Accurate statistical methods uphold the integrity of research findings.
Practical Application: Statistics inform brain-behavior relationships and help develop interventions.
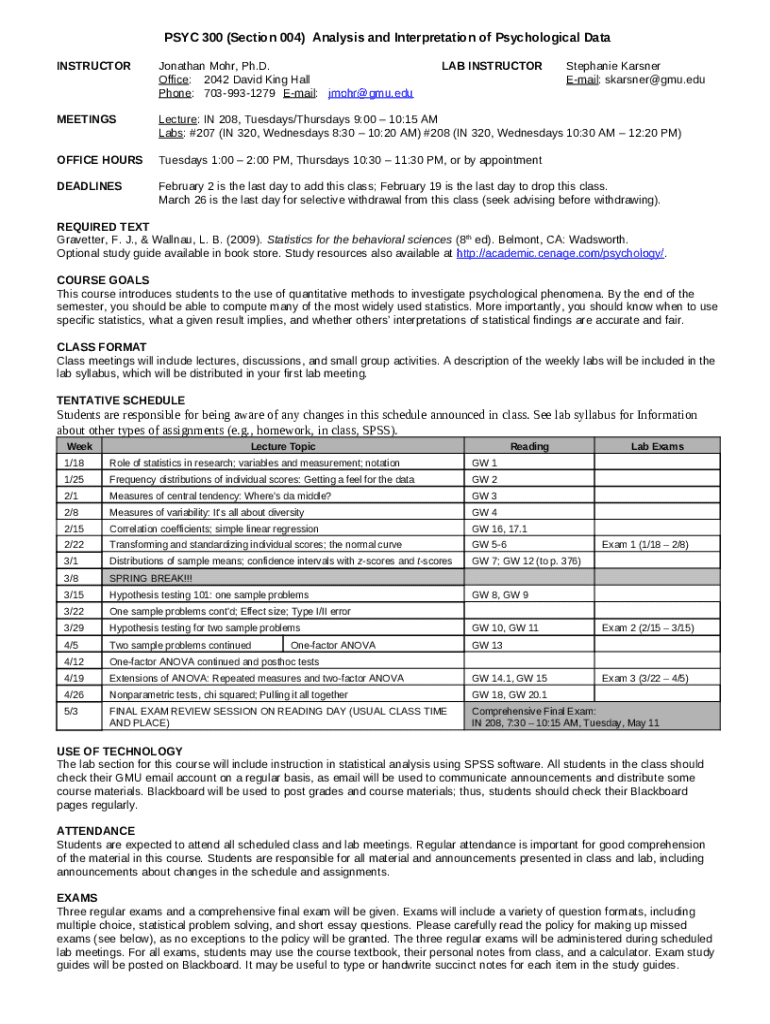
Overview of PSYC 300: Course objectives and expectations
PSYC 300 is designed as a foundational statistics course tailored for psychology students. The curriculum covers core topics that are essential for understanding statistics in psychological research. Students will delve into the intricacies of both descriptive and inferential statistics, equipping them with the skills needed to analyze various data sets. This course aims to bridge the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application, ensuring students can seamlessly transition their statistics knowledge into real-world scenarios.
Learning outcomes for PSYC 300 include the ability to conduct statistical analysis, interpret research data accurately, and apply appropriate statistical tests in diverse psychological contexts. Additionally, students will engage in collaborative learning environments, emphasizing the importance of teamwork in statistical discovery and application. Such experiences enhance critical thinking and foster a supportive academic community.
Understanding Descriptive Statistics: Students learn how to summarize and interpret data.
Inferential Statistics Proficiency: Skills in hypothesis testing and infer comprehensive analysis.
Team Dynamics: Engagement in group projects to enhance collaborative learning.
Essential statistics concepts for psychology students
To excel in PSYC 300 and the larger field of psychology, students must grasp foundational statistical concepts. Descriptive statistics serve as the starting point, with measures of central tendency and variability being crucial. The mean, median, and mode help summarize data, while range, variance, and standard deviation assess data distribution and spread. Understanding these measures allows psychologists to convey their findings effectively.
Moving beyond descriptive statistics, inferential statistics provides tools for making predictions about a population based on sample data. These concepts include hypothesis testing, which involves null and alternative hypotheses, and the awareness of Type I and Type II errors. Furthermore, differentiating correlation from causation is critical; just because two variables correlate, it does not imply one causes the other. Recognizing this distinction is crucial for ethical and accurate psychological practice.
Descriptive Statistics: Mean, median, mode, range, variance, and standard deviation.
Inferential Statistics: Understanding hypothesis testing and errors in statistical conclusions.
Correlation vs. Causation: Recognizing the nuances of data relationships.
Key statistical methods used in psychological research
Psychological research employs various statistical methods to draw meaningful conclusions from data. One of the primary tools is the t-test, which allows researchers to compare the means between two different groups to determine if they differ significantly. This can be vital in evaluating the effectiveness of a new psychological intervention compared to a control group.
Another essential method is ANOVA (Analysis of Variance), which helps analyze differences among group means when more than two groups are present. Regression analysis allows psychologists to predict outcomes based on independent variables, while the Chi-square test assesses relationships in categorical data. Mastery of these methods equips students of PSYC 300 to conduct robust psychological research.
T-Tests: Compare group means to assess significant differences.
ANOVA: Analyze variance among three or more groups.
Regression Analysis: Predict outcomes based on variable relationships.
Chi-Square Tests: Assess relationships in categorical data.
The role of statistical software in PSYC 300
In the digital age, statistical software has become indispensable in the realm of psychology. Students in PSYC 300 can expect to use popular tools such as SPSS and R to conduct data analyses. These platforms provide user-friendly interfaces and powerful capabilities that simplify complex statistical calculations, making it easier to focus on interpreting results rather than getting lost in computations.
By using statistical software, students can conduct illustrative analyses to comprehend data trends better and visualize results. An interactive demonstration of software functionalities can be highly beneficial. This familiarity with technology enhances their statistical learning and prepares them for future research endeavors, whether in academia or applied settings.
SPSS: A widely used tool for statistical analysis in psychology.
R: A powerful programming language for statistical computing.
Hands-on experience: Utilizing software to understand and interpret data effectively.
Practical application: Filling out statistical forms in your studies
Filling out statistical forms can be a daunting but crucial task for psychology students. To streamline this process, understanding the structure of the form is essential. Key information to include typically involves your data set summary, statistical tests applied, significance levels, and interpretations of the findings. Accuracy in reporting these elements prevents miscommunication, ensuring your results are credible.
Common mistakes often arise from mislabeling data, errors in statistical computations, or overlooking critical components of the analysis report. By reviewing examples of completed statistical forms, students can gain insights into effective formatting and reporting styles. These practical skills are invaluable not only in academia but also in future professional endeavors.
Form Structure: Familiarize yourself with the components of the statistical form.
Key Information: Include necessary details like data set summary and significance levels.
Avoid Common Mistakes: Double-check for errors in computations and labels.
Collaborating on group projects: Managing statistical data
Group projects in PSYC 300 can enhance learning, but managing statistical data collectively requires efficient communication and organizational tools. Collaborative document editing platforms facilitate teamwork, making it easier to compile data, share findings, and co-author reports efficiently. Technologies such as Google Docs or specialized eSigning tools ensure that all team members can contribute effectively, regardless of their physical location.
Real-time data sharing also streamlines the collaboration process. Teams can analyze data together while ensuring that everyone is on the same page. Employing best practices in communication—such as regular check-ins and task delegation—ensures that projects remain organized and productive, leading to more successful outcomes.
Collaborative Tools: Use platforms for editing and sharing statistical documents.
Effective Communication: Foster open dialogue to track project progress.
Real-Time Sharing: Utilize cloud services to concurrently analyze data.
Advanced topics: Moving beyond PSYC 300
Upon completion of PSYC 300, students are encouraged to continue their statistical education with advanced techniques pertinent to psychology. Topics such as multivariate statistics, structural equation modeling, and meta-analysis can greatly enhance a psychologist's toolkit. These methods offer deeper insights into complex data patterns and allow for the examination of numerous variables simultaneously.
For those considering graduate studies, solidifying statistical knowledge is vital. Graduate programs often place a strong emphasis on research methods, so students should explore additional resources like specialized online courses, workshops, and textbooks dedicated to advanced statistical methods in psychology. Building a robust understanding of these topics lays the groundwork for more sophisticated research inquiries.
Continued Learning: Engage with advanced statistical techniques in psychology.
Resources: Seek out books, online courses, and workshops for deeper insights.
Graduate Studies: Understand the importance of statistics in advanced research.
Interactive tools to enhance your learning experience
Interactive tools can significantly enrich the learning experience in PSYC 300. Platforms like pdfFiller offer features that allow students to edit, manage, and eSign statistical forms seamlessly. Utilizing these tools can streamline the completion of assignments, fostering a more engaging and organized workflow. Students can quickly adapt form templates to their specific needs, enabling effective communication of their analytical findings.
Moreover, participating in interactive case studies enables students to apply theoretical knowledge in real-world scenarios. These applications reinforce learning, illustrating the practical consequences of statistical methodology in psychological research.
pdfFiller: Tools for editing, signing, and managing statistical forms.
Case Studies: Engage with real-world applications of psychology statistics.
Interactive Learning: Enhance understanding through active participation.
Real-life implications of statistics in psychology
The implications of statistics in psychology extend beyond academic realms, influencing real-life outcomes in therapeutic practices, policy formulation, and community interventions. Case studies highlight how statistical analysis has led to groundbreaking findings in areas like mental health treatment efficacy and the development of psychological theories grounded in empirical evidence. Such insights underscore the necessity for evidence-based practices in psychology.
Moreover, as the psychological field evolves, the future of statistics in psychological science appears promising, with advancements in data analytics and computational psychology shifting paradigms in research methodologies. There are ethical considerations to navigate; responsible data reporting and analysis uphold the integrity and credibility of psychological research. Future psychologists must prioritize ethical standards to ensure that their statistical practices contribute positively to society.
Case Studies: Examine the influence of statistics in psychological research outcomes.
Future Advances: Explore how data analytics and computational methods evolve research.
Ethical Standards: Commit to responsible reporting in psychological statistics.
User testimonials and success stories
Feedback from PSYC 300 alumni highlights the transformative powers that effective use of statistics can have on research endeavors. Many students report gaining confidence in their statistical skills, expressing that they feel more equipped to tackle real-world psychological problems after mastering these analytical techniques. This boost in confidence has translated into successful project submissions and even higher academic performance across the board.
Case highlights showcase innovations driven by a robust understanding of statistics, ranging from clinical trials to neuropsychological research. Such insights not only validate the significance of statistical education in psychology but also inspire future generations of psychologists to embrace statistical rigor in their work.
Transformative Impact: Alumni share how statistics improved their research outcomes.
Enhanced Confidence: Increased skill levels in statistical analysis among graduates.
Innovations in Psychology: Showcase how statistics drive progress in the field.