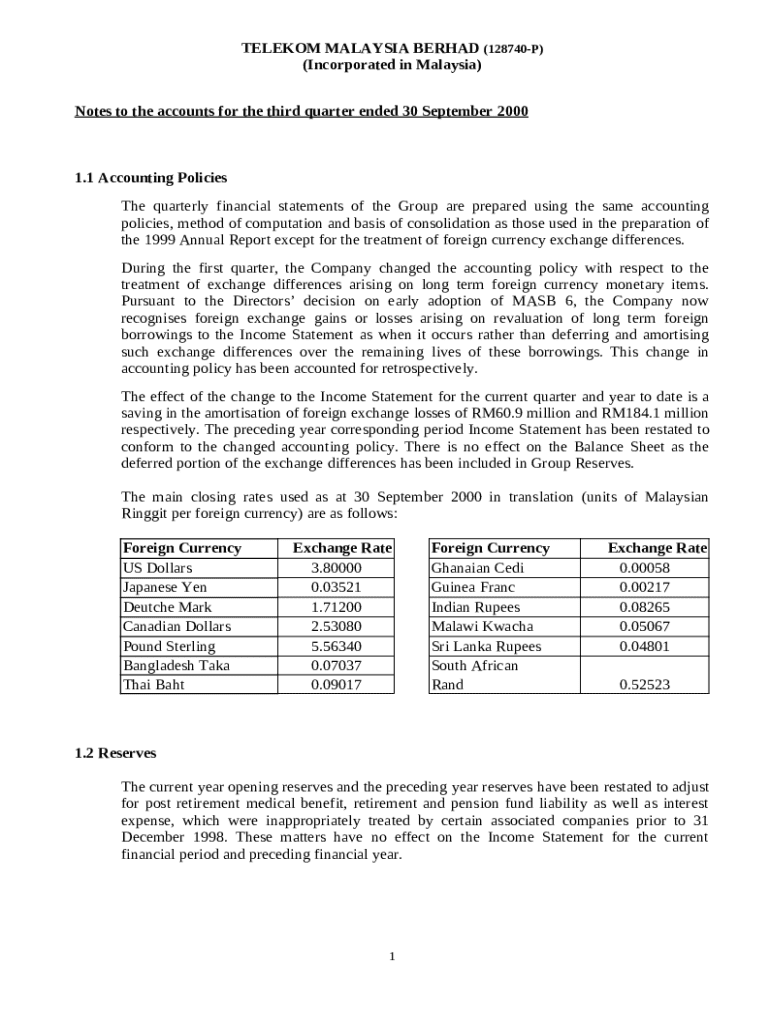
Consolidated Financial Statements for Form: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding financial statements: The basics
Financial statements are formal records that outline the financial activities and position of a business, organization, or individual. They play a critical role in communicating the financial health of an entity to various stakeholders, including investors, creditors, and management. Financial statements are not just mere numbers; they tell the story of a company's performance and its ability to generate profit, manage expenses, and sustain growth.
The importance of financial statements cannot be overstated. They serve as a tool for decision-making, allowing stakeholders to assess the profitability and viability of an entity. By offering an overview of financial activities, they can aid in compliance with regulations, facilitate funding opportunities, and inform strategic planning. Generally, there are three primary types of financial statements: income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements.
What are consolidated financial statements?
Consolidated financial statements combine the financial information of a parent company and its subsidiaries into a single set of reports. This consolidation provides a holistic view of the overall financial position and performance of the entire corporate group, rather than just individual entities. The primary purpose is to provide stakeholders with relevant and comprehensive insights into the organization's financial dynamics.
It's important to differentiate consolidated financial statements from combined financial statements. The latter simply aggregate the figures of multiple entities without eliminating intercompany transactions. This means that the financial results can be inflated, failing to accurately reflect the true economic reality. Consolidated statements, on the other hand, promote clarity and prevent duplication of revenues or expenses across subsidiary lines.
Provides a comprehensive view of financial performance by integrating all subsidiaries' results.
Enhances comparability for stakeholders, allowing them to make better-informed investment decisions.
Simplifies financial reporting for multi-entity organizations, presenting a clearer overall financial picture.
The components of consolidated financial statements
Consolidated financial statements consist of three main components: the consolidated income statement, the consolidated balance sheet, and the consolidated cash flow statement, each providing unique insights into the company's fiscal health.
Consolidated income statement
The consolidated income statement summarizes the revenues, expenses, and net income of the entire group. Revenues are derived from all subsidiaries but must be adjusted to eliminate any intercompany sales. Expenses include all costs incurred during the reporting period, leading to the net income, which reflects the profit or loss attributed to the parent company's stakeholders.
Consolidated balance sheet
The consolidated balance sheet provides a snapshot of the group's assets, liabilities, and equity at a specific point in time. Assets include everything owned by the companies, while liabilities represent the obligations owed to creditors. Equity reflects the residual interest in the assets after subtracting liabilities, giving insight into the company's financial stability and health.
Consolidated cash flow statement
The consolidated cash flow statement outlines the cash generated and used throughout the reporting period across three activities: operating, investing, and financing. This statement reveals how well the company manages its cash inflows and outflows, providing crucial information on liquidity and solvency.
Who needs consolidated financial statements?
Consolidated financial statements are essential for businesses with multiple entities or subsidiaries. These statements are not merely optional; they are often required for regulatory compliance, particularly for publicly traded companies and larger organizations with complex structures. Stakeholders such as investors, creditors, and management rely on these consolidated reports to assess overall corporate performance and risk.
Investors looking for insights on company profitability and potential return on investment.
Creditors assessing the creditworthiness of the company and its ability to meet obligations.
Management needing a complete understanding of financial performance across all subsidiaries to inform decision-making.
How to prepare consolidated financial statements
Preparing consolidated financial statements is a structured process that requires careful attention to detail. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help ensure accuracy and compliance with relevant accounting standards.
Gather financial data from subsidiaries, including their individual income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements.
Eliminate any intercompany transactions to avoid double counting, which ensures an accurate reflection of financial performance.
Combine individual financial statements, ensuring that revenues, expenses, assets, liabilities, and equity are appropriately aggregated.
Adjust for minority interests, if applicable, to accurately represent the ownership stake of the parent company.
Ensure compliance with accounting standards such as IFRS or GAAP to maintain transparency and adherence to regulations.
Accurate reporting and thorough auditing are paramount in this process. Companies should establish internal controls and practices to prevent errors and ensure compliance with applicable laws. Engaging with external auditors can also validate the integrity of the statements.
Tools and resources to simplify the process
Utilizing advanced tools such as pdfFiller can significantly streamline the creation and management of consolidated financial statements. This platform empowers users to edit PDFs, obtain electronic signatures, and collaborate efficiently in real time.
Seamless editing of PDF financial documents allows for quick adjustments and renaming, thus simplifying version control.
The eSignature capability ensures that financial statements can be signed off easily, expediting the approval process.
Interactive templates specifically designed for consolidated financial statements aid teams in filling out necessary forms correctly.
Collaboration features make team reviews and adjustments far more efficient, reducing turnaround times.
Common challenges when dealing with consolidated financial statements
Organizing consolidated financial statements presents several challenges, particularly for companies with multiple entities across various jurisdictions. A primary complexity arises from the need to accurately report the financial results from multiple subsidiaries, each potentially adhering to different accounting practices and currencies.
Currency conversions are often required when dealing with international subsidiaries, introducing additional layers of calculation. Furthermore, addressing audit and compliance issues can be daunting, especially when navigating distinct tax regulations across different regions. Companies must remain vigilant and deliberate in addressing any discrepancies that may arise during consolidation.
Frequently asked questions (FAQs)
Understanding consolidated financial statements can raise various questions among financial professionals and stakeholders. Here are some frequently asked questions that may clarify common concerns.
What is the difference between consolidated and unconsolidated financial statements? Consolidated statements include financial results from all subsidiaries, while unconsolidated statements only reflect the financial results of the parent company.
How often do companies need to prepare consolidated financial statements? Most companies are required to prepare them quarterly and annually, particularly if they are publicly traded or meet specific regulatory requirements.
What accounting implications arise from consolidating financial statements? Consolidation may affect financial ratios, tax obligations, and reporting methods, so it is crucial to ensure compliance with appropriate accounting standards.
Best practices for maintaining accurate consolidated financial statements
To ensure the reliability and accuracy of consolidated financial statements, organizations should adhere to best practices. These practices foster integrity in financial reporting and build trust among stakeholders.
Conduct regular internal reviews and audits to identify discrepancies and ensure compliance with accounting standards.
Maintain detailed records of subsidiary transactions, as thorough documentation promotes transparency and supporting evidence during audits.
Stay updated with regulatory changes that may affect consolidation practices, ensuring that the company remains compliant with local and international laws.
Next steps for aspiring financial professionals
For individuals interested in advancing their careers in financial reporting, several steps can enhance their expertise and marketability. Pursuing relevant certifications, such as CPA or CMA, can provide foundational and advanced knowledge in financial reporting, including the nuances of consolidated financial statements.
Consider certification programs focused on financial management and reporting.
Engage in networking opportunities, such as joining professional organizations or attending industry conferences to connect with experienced professionals.
Utilize online resources, webinars, and courses for ongoing learning and development in accounting standards and reporting best practices.