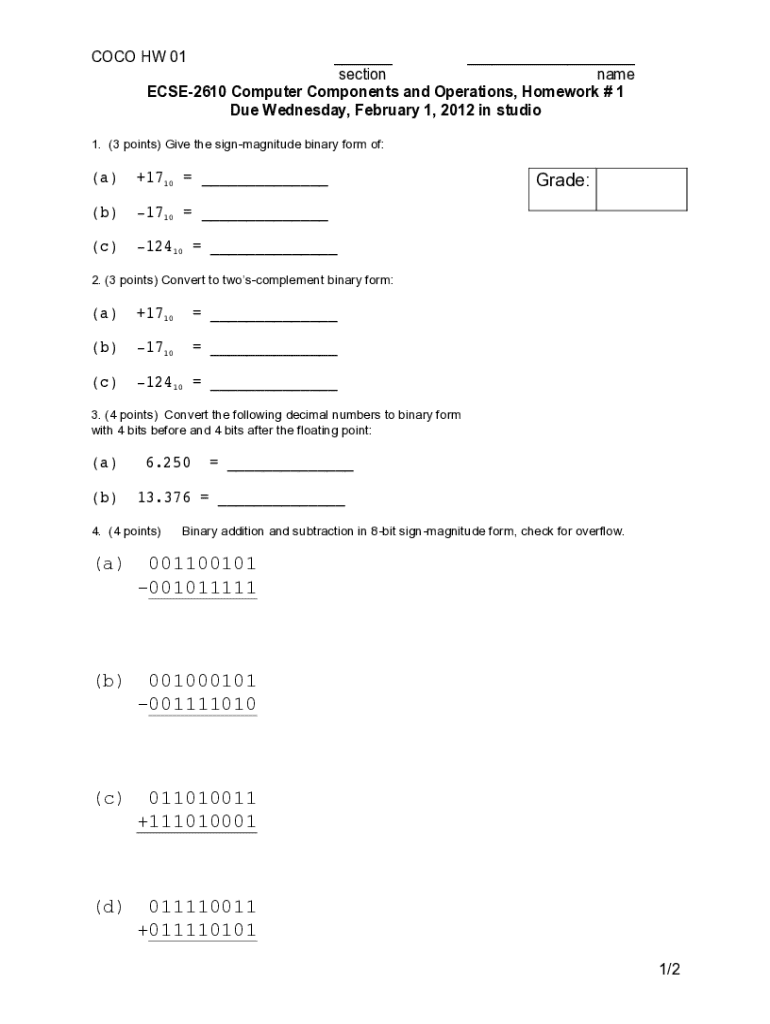
Get the free Binary Arithmetic: Logic Diagrams, Sign-Magnitude, Two's
Get, Create, Make and Sign binary arithmetic logic diagrams

How to edit binary arithmetic logic diagrams online
Uncompromising security for your PDF editing and eSignature needs
How to fill out binary arithmetic logic diagrams
How to fill out binary arithmetic logic diagrams
Who needs binary arithmetic logic diagrams?
Understanding Binary Arithmetic Logic Diagrams Form
1. Understanding binary arithmetic logic
Binary arithmetic is a system that deals with numbers expressed in binary notation, which is a base-2 numeral system. It employs just two symbols, 0 and 1, to represent all values. The significance of binary arithmetic in digital electronics cannot be overstated; it's the underlying framework upon which all digital systems operate, leading to complex operations in computers and communication devices.
In essence, binary arithmetic operates on the principles of binary numbers, allowing for calculations that are fundamental to computing. Logic diagrams visually represent these mathematical operations, offering engineers and programmers a clear way to see how data flows through digital circuits.
2. Core concepts in binary arithmetic
Understanding the concepts of number systems is crucial for grasping binary arithmetic. At its core is the binary system which uses only two states – on (1) and off (0) – making it highly suitable for electronic circuits. Other numeric systems such as decimal or hexadecimal, although widely used by humans, do not align as neatly with electronic states.
Basic operations in binary arithmetic include addition, subtraction, and the manipulation of binary representations. Binary addition, for example, works differently than decimal addition. Carrying over occurs when the sum of two binary bits exceeds one. The aforementioned logical operations play a vital role in computing as logic gates like AND, OR, and NOT process binary data to perform these calculations effectively.
3. Building blocks of binary logic
Logic gates serve as the foundation of binary arithmetic, forming the essential components that process input signals to produce a desired output. Gates like AND, OR, and NOT serve different functions but are incredibly effective when combined. The ability of these gates to manipulate binary values lies at the heart of binary arithmetic logic diagrams.
In digital computing, the Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) is pivotal for performing mathematical and logical operations. It acts as a core component within the CPU, integrating several logic gates to execute operations quickly. Understanding the ALU's inner workings allows engineers and developers to refine their coding practices.
4. Binary adder circuits
Binary adders are essential for arithmetic operations in digital circuits. The half adder, full adder, and parallel adders are key kinds that showcase different levels of complexity in performing binary addition. A half adder can add two binary digits and provide an output of sum and carry; however, it cannot take into account carry-in from previous additions.
The full adder expands on the half adder concept by adding a carry input, allowing for the addition of three binary bits. This addition builds complexity and efficiency in binary calculations tailored for digital computing. By combining multiple full adders, larger binary numbers can be added in parallel, enhancing computational speed.
Parallel adders, such as 4-bit parallel adders, utilize multiple full adders to add binary numbers efficiently. They streamlines the arithmetic operations significantly compared to serial addition and are widely used in digital circuits for rapid processing.
5. Advanced topics in binary arithmetic
Carry Look Ahead Adders (CLA) are advanced techniques designed to resolve the limitations of basic adders by evolving their carry computation. By predicting carry outputs based on the input values, CLA can significantly enhance the speed of arithmetic operations, a vital requirement in high-performance calculations.
Moreover, the need for multiple-precision arithmetic grows with demand for greater computation accuracy. Techniques like the utilization of arrays and registers to manage larger binary numbers allow programmers to bypass limits of standard processors, driving innovative solutions in software and hardware development.
6. Practical applications of binary arithmetic logic
Binary arithmetic logic finds its application in numerous digital systems, making it indispensable in programming and computing. From basic calculators to advanced processors, understanding how binary arithmetic is applied can benefit both budding programmers and seasoned engineers.
In real-world scenarios, industries leverage binary arithmetic logic to optimize performance and enhance efficiency. Case studies reveal how companies implement effective designs leading to significant improvements in processing times and capabilities. These innovations, driven by binary arithmetic logic, showcase how foundational knowledge can lead to industry breakthroughs.
7. Creating your own binary arithmetic logic diagram
Creating binary arithmetic logic diagrams not only aids in understanding how data flows through systems but also is a vital skill in designing effective circuits. Numerous tools and platforms, such as pdfFiller, can streamline this process, offering interactive capabilities to visualize and create complex logic diagrams easily.
To draw effective logic diagrams, it is crucial first to choose the right components. Once the initial building blocks are laid out, structuring the logic flow visually becomes essential. Clarity and precision in design can significantly impact the usability and effectiveness of the diagram in real-world applications.
8. Troubleshooting common issues in binary arithmetic
Errors in binary logic can severely impact calculations and functionality. Identifying and resolving these issues is critical for maintaining the integrity of systems that rely on binary arithmetic. A systematic approach helps engineers detect discrepancies and address them promptly.
9. Engaging with interactive learning
Interactive learning is an effective way to master complex subjects like binary arithmetic. pdfFiller offers numerous templates and forms designed to enhance understanding through practical application and exploration of concepts. By actively engaging with the content, learners can solidify their grasp on binary arithmetic logic.
10. Exploring further learning opportunities
For those interested in deepening their understanding of binary arithmetic, structured learning paths can be immensely beneficial. By utilizing platforms that focus on digital electronics and binary systems, users can acquire knowledge that translates directly into practical skills in computing and hardware design.






For pdfFiller’s FAQs
Below is a list of the most common customer questions. If you can’t find an answer to your question, please don’t hesitate to reach out to us.
How can I edit binary arithmetic logic diagrams from Google Drive?
How do I execute binary arithmetic logic diagrams online?
How do I edit binary arithmetic logic diagrams online?
What is binary arithmetic logic diagrams?
Who is required to file binary arithmetic logic diagrams?
How to fill out binary arithmetic logic diagrams?
What is the purpose of binary arithmetic logic diagrams?
What information must be reported on binary arithmetic logic diagrams?
pdfFiller is an end-to-end solution for managing, creating, and editing documents and forms in the cloud. Save time and hassle by preparing your tax forms online.















