Get the free Microprocessor Design & Organisation HCA2102 - RHH
Get, Create, Make and Sign microprocessor design amp organisation



How to edit microprocessor design amp organisation online
Uncompromising security for your PDF editing and eSignature needs
How to fill out microprocessor design amp organisation

How to fill out microprocessor design amp organisation
Who needs microprocessor design amp organisation?
Microprocessor Design and Organization Form
Understanding microprocessor design and organization
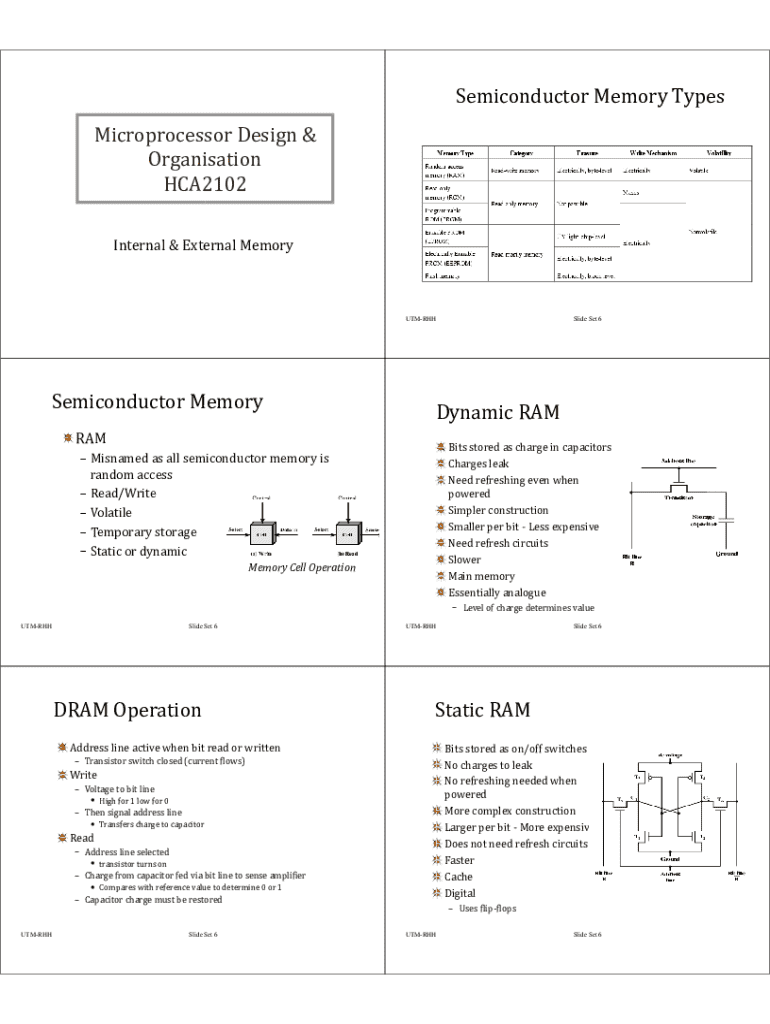
Microprocessor design refers to the architectural and functional framework that determines how a microprocessor operates. It involves creating the circuitry and layout that integrates various components within the chip to execute instructions critical for computing tasks.
The concept of organization delves into the internal structure and the way microprocessor components interact to process data. This includes understanding how different units work together to perform calculations, communicate with memory, and execute commands.
Key elements in microprocessor design
Architectural concepts are fundamental to understanding microprocessors. The two primary architectures are Von Neumann and Harvard. Von Neumann architecture utilizes a single memory space for both instructions and data, making it simpler but often slower. In contrast, Harvard architecture has separate memory spaces for instructions and data, enhancing performance but increasing complexity.
Additionally, the debate between RISC (Reduced Instruction Set Computing) and CISC (Complex Instruction Set Computing) shapes microprocessor design. RISC focuses on a small set of simple instructions which can be executed quickly, whereas CISC supports a larger set of instructions, allowing for more complex operations within a single cycle.
Types of microprocessors
The Central Processing Unit (CPU) is the heart of computing, executing instructions and managing data flow. It comprises various components like the Control Unit (CU), which directs operations, the Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) for calculations, and registers that hold data temporarily.
Graphics Processing Units (GPUs) are specialized microprocessors designed for parallel processing, vital for high-performance graphics rendering. Digital Signal Processors (DSPs), on the other hand, are optimized for signal processing tasks, such as audio and video compression.
Designing microprocessors: Steps and best practices
Designing a microprocessor begins with gathering specifications and requirements. Understanding user needs and market trends helps define the capabilities and performance levels the microprocessor must achieve.
Architectural design considerations follow, where choosing between RISC and CISC architectures impacts performance and cost. The Register Transfer Level (RTL) design phase involves detailed planning of data flow and operations at the level of registers and operations.
Emerging trends in microprocessor design
The development of multicore processors allows simultaneous execution of multiple processes, greatly enhancing performance for multitasking environments. Heterogeneous computing platforms further optimize workload distribution among different processing units, improving efficiency.
Low power and energy-efficient designs are becoming critical as mobile devices and IoT applications proliferate. Techniques such as dynamic voltage scaling help reduce energy consumption without sacrificing performance.
Real-world applications of microprocessors
Microprocessors are integral components in various consumer electronics, including smartphones and laptops. They manage applications, processes, and user interfaces, ensuring smooth and efficient operation.
In the automotive sector, microprocessors control systems from navigation to engine management, enhancing safety and performance. Likewise, in industrial automation, microcontrollers enable precise control of machinery, leading to greater efficiency and reduced downtime.
FAQs about microprocessor design and organization
What are the key differences between RISC and CISC architectures? RISC focuses on a small set of simple instructions for quick execution, while CISC offers a wider array of complex instructions, catering to sophisticated operations.
How does a microprocessor communicate with other components? Microprocessors utilize buses—internal pathways that transmit data, addresses, and control signals to facilitate communication between the CPU, memory, and peripheral devices.






For pdfFiller’s FAQs
Below is a list of the most common customer questions. If you can’t find an answer to your question, please don’t hesitate to reach out to us.
How can I edit microprocessor design amp organisation from Google Drive?
How do I edit microprocessor design amp organisation online?
How do I edit microprocessor design amp organisation on an Android device?
What is microprocessor design & organisation?
Who is required to file microprocessor design & organisation?
How to fill out microprocessor design & organisation?
What is the purpose of microprocessor design & organisation?
What information must be reported on microprocessor design & organisation?
pdfFiller is an end-to-end solution for managing, creating, and editing documents and forms in the cloud. Save time and hassle by preparing your tax forms online.






















