Classify Equation Accreditation For Free
Drop document here to upload
Up to 100 MB for PDF and up to 25 MB for DOC, DOCX, RTF, PPT, PPTX, JPEG, PNG, JFIF, XLS, XLSX or TXT
Note: Integration described on this webpage may temporarily not be available.
0
Forms filled
0
Forms signed
0
Forms sent
Discover the simplicity of processing PDFs online

Upload your document in seconds

Fill out, edit, or eSign your PDF hassle-free

Download, export, or share your edited file instantly
Top-rated PDF software recognized for its ease of use, powerful features, and impeccable support






Every PDF tool you need to get documents done paper-free
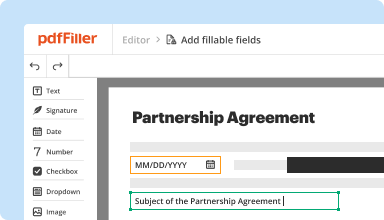
Create & edit PDFs
Generate new PDFs from scratch or transform existing documents into reusable templates. Type anywhere on a PDF, rewrite original PDF content, insert images or graphics, redact sensitive details, and highlight important information using an intuitive online editor.
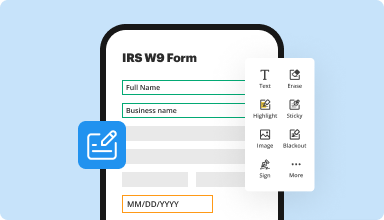
Fill out & sign PDF forms
Say goodbye to error-prone manual hassles. Complete any PDF document electronically – even while on the go. Pre-fill multiple PDFs simultaneously or extract responses from completed forms with ease.
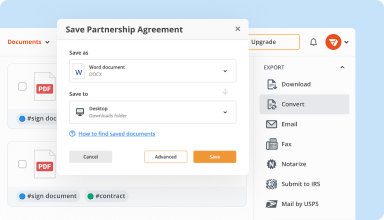
Organize & convert PDFs
Add, remove, or rearrange pages inside your PDFs in seconds. Create new documents by merging or splitting PDFs. Instantly convert edited files to various formats when you download or export them.
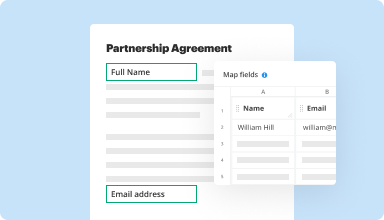
Collect data and approvals
Transform static documents into interactive fillable forms by dragging and dropping various types of fillable fields on your PDFs. Publish these forms on websites or share them via a direct link to capture data, collect signatures, and request payments.
Export documents with ease
Share, email, print, fax, or download edited documents in just a few clicks. Quickly export and import documents from popular cloud storage services like Google Drive, Box, and Dropbox.
Store documents safely
Store an unlimited number of documents and templates securely in the cloud and access them from any location or device. Add an extra level of protection to documents by locking them with a password, placing them in encrypted folders, or requesting user authentication.
Customer trust by the numbers
64M+
users worldwide
4.6/5
average user rating
4M
PDFs edited per month
9 min
average to create and edit a PDF
Join 64+ million people using paperless workflows to drive productivity and cut costs
Why choose our PDF solution?
Cloud-native PDF editor
Access powerful PDF tools, as well as your documents and templates, from anywhere. No installation needed.
Top-rated for ease of use
Create, edit, and fill out PDF documents faster with an intuitive UI that only takes minutes to master.
Industry-leading customer service
Enjoy peace of mind with an award-winning customer support team always within reach.
What our customers say about pdfFiller
See for yourself by reading reviews on the most popular resources:
I'm so glad that I can fill in all the forms and documents easily with PDF filler. Before it was so frustrating not to be able to sign my name, PDF Filler is great!
2018-01-30
I think your site is well designed and has substantial potential. But being unfamiliar with all the choices, my initial effort at using your site took a little longer that I had hoped it would. But that is a minor critique. i'll do more exploring at a later date.
2018-09-26
Getting to put 3 people on the account has been great. All of the features are exactly what I needed, and the editor is easy to use. I was a little wary if it would be worth the money, but I'm very happy with my purchase.
2019-08-12
Easy to use
Easy to use. Only one downside - can't bring in any other types of fonts. That would be helpful. Other than that it's good for my needs.
2020-01-14
I have been using the services for a…
I have been using the services for a few years know and i can honestly say they have updated and made it very user friendly.
2024-06-30
RECOMMENDED
This app/website is really good. It is easier and it has some features that is really useful if you're dealing with pdf files all day long. The downside tho, it is quite pricey for me. But if you're okay with the price, consider subscribe to their service, very recommended.
2022-12-14
Thank you so much for the opportunity…
Thank you so much for the opportunity to use pdfFiller it was useful but due to difficulty of internet connection in our place and seldom I use the application, I have decided to cancel. Rest assured that I would also recommend it to my officemates.
2022-10-17
Extremely user friendly and extremely…
Extremely user friendly and extremely helpful. Especially when there isn't a printer and scanner handy and you're in a hurry to fill out a form.
2022-05-05
I am using pdf filler for doing ongoing reports and also for tax documents. It is good to have a way to complete these documents and have a digital record.
2021-08-07
Classify Equation Accreditation Feature
The Classify Equation Accreditation feature offers a reliable way to validate and enhance your organization's processes. With this feature, you can ensure that your operations meet high standards and are recognized within your industry.
Key Features
Streamlined accreditation process
Comprehensive reporting tools
User-friendly interface for easy navigation
Real-time tracking of accreditation status
Customizable templates for tailored documentation
Potential Use Cases and Benefits
Organizations seeking industry recognition
Educational institutions needing program accreditation
Businesses aiming for compliance with regulations
Nonprofits looking to enhance credibility
Consultants who help clients achieve standards
By implementing the Classify Equation Accreditation feature, you can address the challenge of maintaining industry standards. This solution simplifies the accreditation journey, making it easier for you to demonstrate your commitment to quality. With improved credibility, you can attract more clients and build trust within your community.
For pdfFiller’s FAQs
Below is a list of the most common customer questions. If you can’t find an answer to your question, please don’t hesitate to reach out to us.
What if I have more questions?
Contact Support
What are the classification of equation?
While differential equations have three basic types ordinary (Odes), partial (Pies), or differential-algebraic (DAE's), they can be further described by attributes such as order, linearity, and degree.
What are the two types of differential equation?
Two broad classifications of both ordinary and partial differential equations consists of distinguishing between linear and nonlinear differential equations, and between homogeneous differential equations and heterogeneous ones.
What is differential equation and its types?
A differential equation is an equation which contains one or more terms which involve the derivatives of one variable (i.e., dependent variable) with respect to the other variable (i.e., independent variable) Dy/DX = f(x) Here x is an independent variable and y is a dependent variable. For example, Dy/DX = 5x.
What are the differential equation explain?
A differential equation is a mathematical equation that relates some function with its derivatives. In applications, the functions usually represent physical quantities, the derivatives represent their rates of change, and the differential equation defines a relationship between the two.
What are the applications of differential equations?
Differential equations have a remarkable ability to predict the world around us. They are used in a wide variety of disciplines, from biology, economics, physics, chemistry and engineering. They can describe exponential growth and decay, the population growth of species or the change in investment return over time.
How do you tell what order a differential equation is?
The number of the highest derivative in a differential equation. A differential equation of order 1 is called first order, order 2 second order, etc. Example: The differential equation y” + XY' x3y = sin x is second order since the highest derivative is y” or the second derivative.
What is ordinary and partial differential equations?
An ordinary differential equation (ODE) has only derivatives of one variable that is, it has no partial derivatives. Here are a few examples of Odes: In contrast, a partial differential equation (PIE) has at least one partial derivative. ... First-order Odes contain only first derivatives.
What is the difference between an ordinary differential equation and a partial differential equation?
An Ordinary Differential Equation is a differential equation that depends on only one independent variable. A Partial Differential Equation is differential equation in which the dependent variable depends on two or more independent variables.
What is partial differential equations used for?
Partial differential equations are used to mathematically formulate, and thus aid the solution of, physical and other problems involving functions of several variables, such as the propagation of heat or sound, fluid flow, elasticity, electrostatics, electrodynamics, etc.
What is meant by ordinary differential equation?
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. In mathematics, an ordinary differential equation (ODE) is a differential equation containing one or more functions of one independent variable and the derivatives of those functions.
#1 usability according to G2
Try the PDF solution that respects your time.






