Combine Equation Accreditation For Free
Drop document here to upload
Up to 100 MB for PDF and up to 25 MB for DOC, DOCX, RTF, PPT, PPTX, JPEG, PNG, JFIF, XLS, XLSX or TXT
Note: Integration described on this webpage may temporarily not be available.
0
Forms filled
0
Forms signed
0
Forms sent
Discover the simplicity of processing PDFs online

Upload your document in seconds

Fill out, edit, or eSign your PDF hassle-free

Download, export, or share your edited file instantly
Top-rated PDF software recognized for its ease of use, powerful features, and impeccable support






Every PDF tool you need to get documents done paper-free
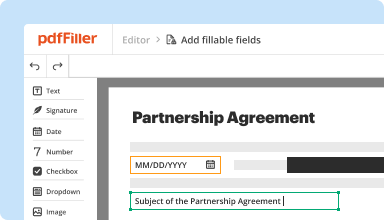
Create & edit PDFs
Generate new PDFs from scratch or transform existing documents into reusable templates. Type anywhere on a PDF, rewrite original PDF content, insert images or graphics, redact sensitive details, and highlight important information using an intuitive online editor.
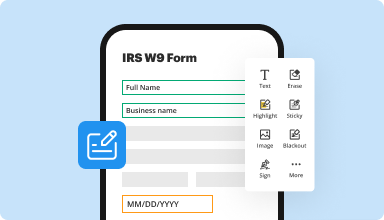
Fill out & sign PDF forms
Say goodbye to error-prone manual hassles. Complete any PDF document electronically – even while on the go. Pre-fill multiple PDFs simultaneously or extract responses from completed forms with ease.
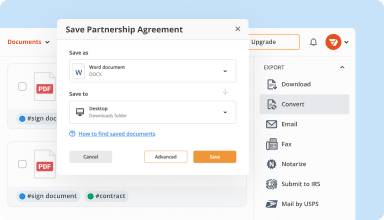
Organize & convert PDFs
Add, remove, or rearrange pages inside your PDFs in seconds. Create new documents by merging or splitting PDFs. Instantly convert edited files to various formats when you download or export them.
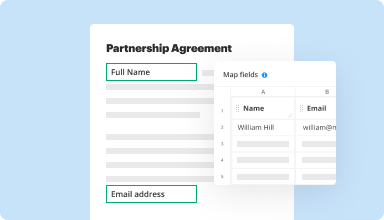
Collect data and approvals
Transform static documents into interactive fillable forms by dragging and dropping various types of fillable fields on your PDFs. Publish these forms on websites or share them via a direct link to capture data, collect signatures, and request payments.
Export documents with ease
Share, email, print, fax, or download edited documents in just a few clicks. Quickly export and import documents from popular cloud storage services like Google Drive, Box, and Dropbox.
Store documents safely
Store an unlimited number of documents and templates securely in the cloud and access them from any location or device. Add an extra level of protection to documents by locking them with a password, placing them in encrypted folders, or requesting user authentication.
Customer trust by the numbers
64M+
users worldwide
4.6/5
average user rating
4M
PDFs edited per month
9 min
average to create and edit a PDF
Join 64+ million people using paperless workflows to drive productivity and cut costs
Why choose our PDF solution?
Cloud-native PDF editor
Access powerful PDF tools, as well as your documents and templates, from anywhere. No installation needed.
Top-rated for ease of use
Create, edit, and fill out PDF documents faster with an intuitive UI that only takes minutes to master.
Industry-leading customer service
Enjoy peace of mind with an award-winning customer support team always within reach.
What our customers say about pdfFiller
See for yourself by reading reviews on the most popular resources:
I wish it wasn't so expensive...I'm still on the free trial right now but this app is great. Maybe offer like a college student pricing? I know us kids in college cant pay $40 a month for it
2019-02-18
Fill it out!
Overall, I love when this is available to use for forms I need to fax or email.
I love the feature of being able to fill the form out online. Very easy to use and beats having to fill in by hand, scan and send.
I am not quite sure how to do this myself and have to ask IT to assist in making the form fillable for me.
2019-12-04
Time Saver!
Helps me with quickly signing contracts without printing, filling out many forms that I used to hand write. keeps me organized.
Saves time and easy to understand, not to complex.
I could not find a way to merge multiple PDFs unto one PDF.
2019-05-16
Efficient way to fill out forms online.
You can setup default information to be populated online in any type of form.
Ensure to select which user being utilized as if you use for multiple people on one machine, you can mix up information if you are not paying attention.
2018-08-13
Great to use especially working from home
I have been working from home and Sarah PDF has been trying amazing. It is very easy to use and the way I am able to merge my documents and download them is great.
2024-01-17
Great application! I was able to edit some incorrect dates sent to me by a reference who could not access the document for an extended period of time. I was able to get my document corrected and resubmitted without issue
2022-08-15
Its a little bit hard to email the…
Its a little bit hard to email the documents back to yourself after the conversion - otherwise, this is a great website for document alterations and conversions. Easy to use, great variation of different tools and mediums.
2021-07-29
It would be beneficial to be able to…
It would be beneficial to be able to download or email document prior to signing so that it can be shared with attorneys or anyone else that will assist with reviewing the document prior to signing.
2021-01-26
Completed what I needed done
Completed what I needed done. The reason for 4 stars is because you force people to sign up for a monthly subscription versus just charging for the one time use of the feature.
2025-03-03
Combine Equation Accreditation Feature
The Combine Equation Accreditation feature empowers you to streamline your accreditation processes with greater ease and efficiency. It offers a comprehensive solution for organizations seeking to maintain high standards in their operations.
Key Features
Automated accreditation tracking to monitor progress easily
User-friendly dashboard for quick access to important information
Customizable templates for various accreditation standards
Secure document storage to keep all necessary files organized
Real-time notifications to keep you updated on deadlines
Potential Use Cases and Benefits
Educational institutions aiming for program accreditation
Non-profits ensuring compliance with industry standards
Corporate sectors looking to maintain certification validity
Consultants providing guidance on accreditation processes
Government agencies in charge of public service standards
By using the Combine Equation Accreditation feature, you can solve the common challenge of managing accreditation requirements. This tool helps you track deadlines, organize documents, and ensure compliance. With these capabilities, you can focus on your core operations while maintaining the quality and standards necessary for success.
For pdfFiller’s FAQs
Below is a list of the most common customer questions. If you can’t find an answer to your question, please don’t hesitate to reach out to us.
What if I have more questions?
Contact Support
How do you combine uncertainty?
The simplest case is where the result is the sum of a series of measured values (either added together or subtracted). The combined standard uncertainty is found by squaring the uncertainties, adding them all together, and then taking the square root of the total.
What is combined standard uncertainty?
Combined Uncertainty is the square-root of the linear sum of squared standard uncertainty components. ... Each component is the product (i.e. result of multiplication) of the standard uncertainty and its associated sensitivity coefficient.
How do you combine absolute uncertainty?
If you're adding or subtracting quantities with uncertainties, you add the absolute uncertainties. If you're multiplying or dividing, you add the relative uncertainties. If you're multiplying by a constant factor, you multiply absolute uncertainties by the same factor, or do nothing to relative uncertainties.
What is uncertainty in statistics?
Uncertainty in statistics is measured by the amount of error in an estimate of the mean or average value of a population.
What is uncertainty in calibration?
Purpose. The purpose is to quantify the uncertainty of a 'future' result that has been corrected by the calibration curve. In principle, the uncertainty quantifies any possible difference between the calibrated value and its reference base (which normally depends on reference standards).
What is expanded uncertainty?
Expanded Uncertainty. Expanded uncertainty is the last calculation when estimating uncertainty in measurement. Typically, it is very easy and only requires you to multiply the combined uncertainty by a desired coverage factor.
How do I calculate uncertainty?
To calculate uncertainty, you will use the formula: best estimate ± uncertainty, where the uncertainty is the possibility for error or the standard deviation. You should always round your experimental measurement to the same decimal place as the uncertainty.
How do you calculate uncertainty in chemistry?
7:12
8:29
Suggested clip
11.1 Determine the uncertainties in results [SL IB Chemistry ... YouTubeStart of suggested client of suggested clip
11.1 Determine the uncertainties in results [SL IB Chemistry ...
How do you calculate absolute uncertainty?
2:00
2:22
Suggested clip
11.1 State uncertainties as absolute and percentage uncertainties ... YouTubeStart of suggested client of suggested clip
11.1 State uncertainties as absolute and percentage uncertainties ...
What does uncertainty in measurement mean?
In metrology, measurement uncertainty is the expression of the statistical dispersion of the values attributed to a measured quantity. ... Thus, the relative measurement uncertainty is the measurement uncertainty divided by the absolute value of the measured value, when the measured value is not zero.
#1 usability according to G2
Try the PDF solution that respects your time.






