Map Formula Accreditation For Free
Drop document here to upload
Up to 100 MB for PDF and up to 25 MB for DOC, DOCX, RTF, PPT, PPTX, JPEG, PNG, JFIF, XLS, XLSX or TXT
Note: Integration described on this webpage may temporarily not be available.
0
Forms filled
0
Forms signed
0
Forms sent
Discover the simplicity of processing PDFs online

Upload your document in seconds

Fill out, edit, or eSign your PDF hassle-free

Download, export, or share your edited file instantly
Top-rated PDF software recognized for its ease of use, powerful features, and impeccable support






Every PDF tool you need to get documents done paper-free
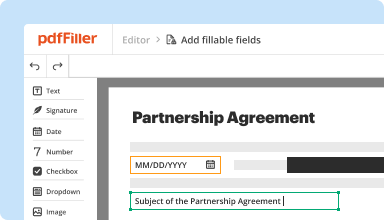
Create & edit PDFs
Generate new PDFs from scratch or transform existing documents into reusable templates. Type anywhere on a PDF, rewrite original PDF content, insert images or graphics, redact sensitive details, and highlight important information using an intuitive online editor.
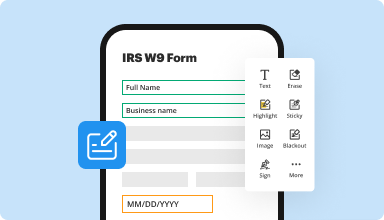
Fill out & sign PDF forms
Say goodbye to error-prone manual hassles. Complete any PDF document electronically – even while on the go. Pre-fill multiple PDFs simultaneously or extract responses from completed forms with ease.
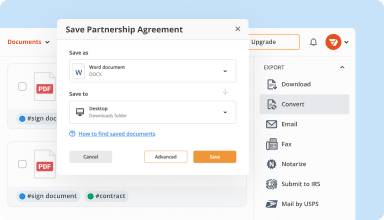
Organize & convert PDFs
Add, remove, or rearrange pages inside your PDFs in seconds. Create new documents by merging or splitting PDFs. Instantly convert edited files to various formats when you download or export them.
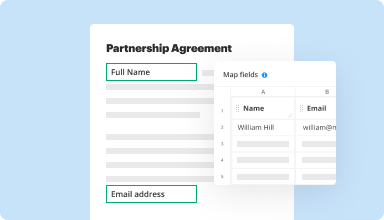
Collect data and approvals
Transform static documents into interactive fillable forms by dragging and dropping various types of fillable fields on your PDFs. Publish these forms on websites or share them via a direct link to capture data, collect signatures, and request payments.
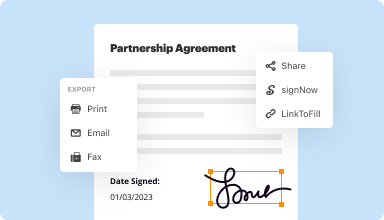
Export documents with ease
Share, email, print, fax, or download edited documents in just a few clicks. Quickly export and import documents from popular cloud storage services like Google Drive, Box, and Dropbox.
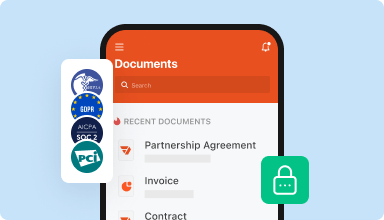
Store documents safely
Store an unlimited number of documents and templates securely in the cloud and access them from any location or device. Add an extra level of protection to documents by locking them with a password, placing them in encrypted folders, or requesting user authentication.
Customer trust by the numbers
64M+
users worldwide
4.6/5
average user rating
4M
PDFs edited per month
9 min
average to create and edit a PDF
Join 64+ million people using paperless workflows to drive productivity and cut costs
Why choose our PDF solution?
Cloud-native PDF editor
Access powerful PDF tools, as well as your documents and templates, from anywhere. No installation needed.
Top-rated for ease of use
Create, edit, and fill out PDF documents faster with an intuitive UI that only takes minutes to master.
Industry-leading customer service
Enjoy peace of mind with an award-winning customer support team always within reach.
What our customers say about pdfFiller
See for yourself by reading reviews on the most popular resources:
It is a little hard getting the text to line up on the lines just right, but I figured a few tricks that help. Would have saved me time if I had been shown/told first in a tutorial how to fill it out best.
2015-09-22
Just started using the program but have search many times before to find an easy way to access documents occasionally needed by our business. This format fits very well and will certainly increase the productivity of office hours. much thanks, Steve Rowell ( Brooks Carpet Inc. )
2017-12-05
I absolutely LOVE the convenience PDF filler provides for our patients, as well as our front desk staff. The only thing that would improve the service would be a guide that indicates to the patient that they missed a section, so they know to keep scrolling to complete all the forms.
2018-11-13
But the important thing is they indicate that it is free to use online, but they demand that we subscribe to make a charge, then we do not have the link to cancel
2019-02-02
Usefull
Very useful app you can do stuff on phone and easily move on to desktop to continue what you're doing nothing special but it definetely isn't bad
2023-06-15
PDFfiller do all the document from now on instead of MS.
1). 541 31ST St. Oakland, Ca. 94609-3203/Rental Property: so far tenants owe 4 mos. rent $8,056.00 2). The Alameda County superior court Case: Chung VS. Smith; 3). It's court request to use PDFfiller to do the Pleading, Ex-Parte and Declaration. 4). due to this instruction brought me to PDFfiller and learn how to do the legal document. 5).. From now on will use PDFfiler to do all the document: just use MS. do the preparation and copy and paste to the PDFfiler and that's all. -> From: Angel K. Chung-Gipson, 9/14/2021, 3:20 a.m.
2021-09-14
I used you to arrange a document and I…
I used you to arrange a document and I must point out that it was easy to operate and arrange. Very convenient to use and the customer service is pleasant and courteous.
2020-10-17
Honesty and integrity are not something…
Honesty and integrity are not something I align with online trial subscription. Most will hope you forget so they can charge you anyway. But PDFfilIer holds to a higher standard. I am NOT an employee forced to write a review. This for real just happened like 10 minutes ago.
I signed up for a trial to complete a job for my employer. Forgot to cancel before the trial ended. I don't make much, so $96 was a hit I wasn't expecting or able to pay. Support had already approved and completed the refund and cancelation of my subscription before I had even finished explaining my situation to the rep in chat (Aiden). The email came from "Sarah from PDFfiller" explaining that it was taken care of while I was still chatting with the rep.
I was expecting a battle. Now I expect to either sign up with PDFfiller when I have a more consistent need or get my boss to pay for the service. The platform was quick and easy to navigate. Based solely on this experience, I would recommend this platform if you are in need of creating these types of documents.
The only thing I would change is that I couldn't find my payment options in my account info to see what card was used. Nor could I find an avenue to change my payment options.
2025-06-18
Its great overall for all the services…
Its great overall for all the services but hated the part where it reveals at the end that subscription is a must.
2025-01-21
Map Formula Accreditation Feature
The Map Formula Accreditation feature streamlines your accreditation process, making it easier to manage and maintain standards. This tool is designed with your needs in mind, ensuring you have clarity and efficiency at every step.
Key Features
Automated accreditation workflows
Real-time progress tracking
Customizable accreditation standards
User-friendly dashboard for easy navigation
Integration with existing systems
Potential Use Cases and Benefits
Educational institutions seeking streamlined accreditation processes
Organizations meeting industry standards efficiently
Businesses needing to ensure compliance with minimal effort
Consultants helping clients maintain accreditation status
By implementing the Map Formula Accreditation feature, you address common challenges in the accreditation process. This tool minimizes errors, saves time, and enhances transparency. You can focus on your core activities while ensuring that your accreditation requirements are met effectively.
For pdfFiller’s FAQs
Below is a list of the most common customer questions. If you can’t find an answer to your question, please don’t hesitate to reach out to us.
What if I have more questions?
Contact Support
How do you calculate mean arterial pressure?
While MAP can only be measured directly by invasive monitoring it can be approximately estimated using a formula in which the lower (diastolic) blood pressure is doubled and added to the higher (systolic) blood pressure and that composite sum then is divided by 3 to estimate MAP.
What is the formula for mean arterial pressure?
To calculate a mean arterial pressure, double the diastolic blood pressure and add the sum to the systolic blood pressure. Then divide by 3. For example, if a patient's blood pressure is 83 mm Hg/50 mm Hg, his MAP would be 61 mm Hg. Here are the steps for this calculation: MAP = SVP + 2 (DBP)
What is the formula to calculate map?
To calculate the MAP, you need two values — you systolic and diastolic blood pressure. They are usually given in the form XX/BY, where XX is the systolic pressure, and BY — the diastolic. For example, a person with blood pressure 120/80 has SVP = 120 MMH, and DBP = 80 MMH.
What is the normal range for mean arterial pressure?
It is vital to have a MAP of at least 60 MMH to provide enough blood to the coronary arteries, kidneys, and brain. The normal MAP range is between 70 and 100 MMH. Mean arterial pressures that deviate from this range for prolonged periods of time can have drastic negative effects on the body.
What affects mean arterial pressure?
Factors Regulating Arterial Blood Pressure. Mean arterial pressure is regulated by changes in cardiac output and systemic vascular resistance. ... Cardiac output is determined by the product of stroke volume and heart rate. Stroke volume is determined by isotropy and ventricular preload.
How do you calculate Map BP?
To calculate the MAP, you need two values — you systolic and diastolic blood pressure. They are usually given in the form XX/BY, where XX is the systolic pressure, and BY — the diastolic. For example, a person with blood pressure 120/80 has SVP = 120 MMH, and DBP = 80 MMH.
What is a normal map BP?
MAP is the measurement that explains the average blood pressure in a person's blood vessels during a single cardiac cycle. ... It is vital to have a MAP of at least 60 MMH to provide enough blood to the coronary arteries, kidneys, and brain. The normal MAP range is between 70 and 100 MMH.
What is the mean arterial pressure of a blood pressure of 140 80?
The mean arterial pressure represents the average arterial pressure throughout the cardiac cycle, and is the force that drives blood through the vasculature. ... For example, the calculated mean arterial pressure is the same whether the systolic/diastolic pressure values are 120/80 mm Hg or 160/60 mm Hg.
What does a high mean arterial pressure mean?
A high MAP is anything over 100 MMH, which indicates that there's a lot of pressure in the arteries. This can eventually lead to blood clots or damage to the heart muscle, which has to work a lot harder. Many things that cause very high blood pressure can also cause a high MAP, including: heart attack.
What is a normal mean arterial pressure?
Mean arterial pressure is significant because it measures the pressure necessary for adequate perfusion of the organs of the body. ... It is vital to have a MAP of at least 60 MMH to provide enough blood to the coronary arteries, kidneys, and brain. The normal MAP range is between 70 and 100 MMH.
#1 usability according to G2
Try the PDF solution that respects your time.






