Tag Limited Field Resolution For Free
Drop document here to upload
Up to 100 MB for PDF and up to 25 MB for DOC, DOCX, RTF, PPT, PPTX, JPEG, PNG, JFIF, XLS, XLSX or TXT
Note: Integration described on this webpage may temporarily not be available.
0
Forms filled
0
Forms signed
0
Forms sent
Discover the simplicity of processing PDFs online

Upload your document in seconds

Fill out, edit, or eSign your PDF hassle-free

Download, export, or share your edited file instantly
Top-rated PDF software recognized for its ease of use, powerful features, and impeccable support






Every PDF tool you need to get documents done paper-free
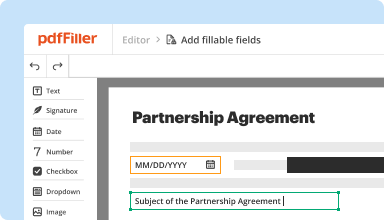
Create & edit PDFs
Generate new PDFs from scratch or transform existing documents into reusable templates. Type anywhere on a PDF, rewrite original PDF content, insert images or graphics, redact sensitive details, and highlight important information using an intuitive online editor.
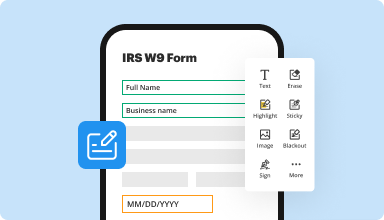
Fill out & sign PDF forms
Say goodbye to error-prone manual hassles. Complete any PDF document electronically – even while on the go. Pre-fill multiple PDFs simultaneously or extract responses from completed forms with ease.
Organize & convert PDFs
Add, remove, or rearrange pages inside your PDFs in seconds. Create new documents by merging or splitting PDFs. Instantly convert edited files to various formats when you download or export them.
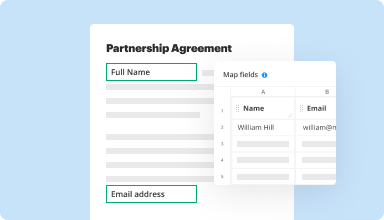
Collect data and approvals
Transform static documents into interactive fillable forms by dragging and dropping various types of fillable fields on your PDFs. Publish these forms on websites or share them via a direct link to capture data, collect signatures, and request payments.
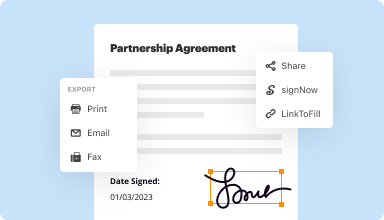
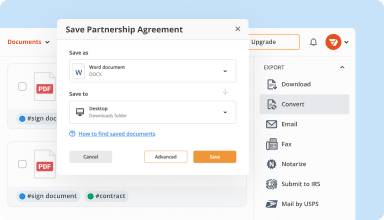
Export documents with ease
Share, email, print, fax, or download edited documents in just a few clicks. Quickly export and import documents from popular cloud storage services like Google Drive, Box, and Dropbox.
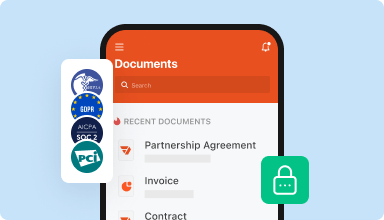
Store documents safely
Store an unlimited number of documents and templates securely in the cloud and access them from any location or device. Add an extra level of protection to documents by locking them with a password, placing them in encrypted folders, or requesting user authentication.
Customer trust by the numbers
64M+
users worldwide
4.6/5
average user rating
4M
PDFs edited per month
9 min
average to create and edit a PDF
Join 64+ million people using paperless workflows to drive productivity and cut costs
Why choose our PDF solution?
Cloud-native PDF editor
Access powerful PDF tools, as well as your documents and templates, from anywhere. No installation needed.
Top-rated for ease of use
Create, edit, and fill out PDF documents faster with an intuitive UI that only takes minutes to master.
Industry-leading customer service
Enjoy peace of mind with an award-winning customer support team always within reach.
What our customers say about pdfFiller
See for yourself by reading reviews on the most popular resources:
It takes awhile to get use to but now I think I have it.
Thanks! This should make life easier if I can figure out how to continue using the PDFfiller.
Virginia James-Diehl
2014-09-08
thumbs up! the customer care and the support are on top level!quick response and great desire to solve an issue! about the pdf filler ..easy to use ,awesome features like send to sign button!!
2014-10-19
I live in Philadelphia SEPTA is not running because of contract issues but my military ask that I complete a form and send it to them within five days or I would be subject to pay large amount. Since I could use PDF Filler that lets me fax , signed update all at once I made the deadline without leaving my home ... I sent this out to many of my friends we all need a choice to fax and complete forms ASAP
2016-11-03
Quite good!Only after I finished, did I see that the date next to my signature at the bottom was misaligned and printing over some text on the form. So, I had to go back to edit that. Very helpful tool, though!
2020-02-19
The support team are the BEST!
The support team are the BEST!I didn’t understand that I was signing up a yearly subscription. I wanted to use the pdf only once. I notice in my account they charge me for a yearly subscription. I contacted the support group, explained my problem within minutes they solved my problem and refund my money.Thanks again for a Great job!!
2019-05-16
It is an awesome program... I do so little on it I have to start over every year trying to figure it out... Thanks so much for your help.. I was lost ... You guys are the best...
2022-02-09
PDFfiller is a great tool for having documents signed on PDFs!
Overall, I am super satisfied with PDFfiller and will continue to use.
What I like most about PDFfiller is how easy it is for myself and clients to sign documents. This is one of the best tools I have found to edit.
I do not have any complaints at this time regarding PDFfiller. It has been a lifesaver for myself when I need things signed!!
2021-01-05
I really appreciate being able to transform a regular,...
I really appreciate being able to transform a regular, annoying PDF into an easily accessible document my clients can sign from any device and be sent by almost any app or service. This will definitely make going paperless a reality for our business
2020-04-30
I signed up for a trial. I'm so happy to purchase it. I love it and it has made my business processes move much quicker than printing a form, completing, scanning, send it back, and storing a copy. Excellent!
2025-02-28
Tag Limited Field Resolution Feature
The Tag Limited Field Resolution feature offers precise control over the spatial resolution of your tagging system. This functionality allows you to improve accuracy in your data collection processes.
Key Features
Adjustable field resolution settings for specific tagging needs
Seamless integration with existing tagging infrastructure
User-friendly interface for easy configuration
Potential Use Cases and Benefits
Improved data accuracy in crowded environments
Enhanced performance for inventory management systems
Streamlined operations in logistics and supply chain
By implementing the Tag Limited Field Resolution feature, you can solve common issues related to data overlap and inaccuracies. This feature helps you focus on the most relevant data points, allowing for improved decision-making and operational efficiency.
For pdfFiller’s FAQs
Below is a list of the most common customer questions. If you can’t find an answer to your question, please don’t hesitate to reach out to us.
What if I have more questions?
Contact Support
What is the resolution of a fluorescence microscope?
Spatio-temporal visualization of cellular structures by fluorescence microscopy has become indispensable in biology. However, the resolution of conventional fluorescence microscopy is limited by diffraction to about 180 nm in the focal plane and to about 500 nm along the optic axis.
What is resolution of a microscope?
In microscopy, the term 'resolution' is used to describe the ability of a microscope to distinguish detail. In other words, this is the minimum distance at which two distinct points of a specimen can still be seen — either by the observer or the microscope camera — as separate entities.
What is resolution in terms of a microscope?
In microscopy, the term 'resolution' is used to describe the ability of a microscope to distinguish detail. In other words, this is the minimum distance at which two distinct points of a specimen can still be seen — either by the observer or the microscope camera — as separate entities.
What is magnification and resolution of a microscope?
Key Points. Magnification is the ability to make small objects seem larger, such as making a microscopic organism visible. Resolution is the ability to distinguish two objects from each other. Light microscopy has limits to both its resolution and its magnification.
What is the resolution or resolving power of a microscope?
The limit of resolution (or resolving power) is a measure of the ability of the objective lens to separate in the image adjacent details that are present in the object. It is the distance between two points in the object that are just resolved in the image.
What factors affect resolution of a microscope?
The primary factor in determining resolution is the objective numerical aperture, but resolution is also dependent upon the type of specimen, coherence of illumination, degree of aberration correction, and other factors such as contrast-enhancing methodology either in the optical system of the microscope or in the
What kind of microscope is used for fluorescence imaging?
Most fluorescence microscopes in use are fluorescence microscopes, where excitation of the fluoroscope and detection of the fluorescence are done through the same light path (i.e. through the objective).
What is fluorescent imaging?
Fluorescence imaging is a type of non-invasive imaging technique that can help visualize biological processes taking place in a living organism. Fluorescence itself, is a form of luminescence that results from matter emitting light of a certain wavelength after absorbing electromagnetic radiation.
#1 usability according to G2
Try the PDF solution that respects your time.






