Update Sum Statement Of Work For Free
Drop document here to upload
Up to 100 MB for PDF and up to 25 MB for DOC, DOCX, RTF, PPT, PPTX, JPEG, PNG, JFIF, XLS, XLSX or TXT
Note: Integration described on this webpage may temporarily not be available.
0
Forms filled
0
Forms signed
0
Forms sent
Discover the simplicity of processing PDFs online

Upload your document in seconds

Fill out, edit, or eSign your PDF hassle-free

Download, export, or share your edited file instantly
Top-rated PDF software recognized for its ease of use, powerful features, and impeccable support






Every PDF tool you need to get documents done paper-free
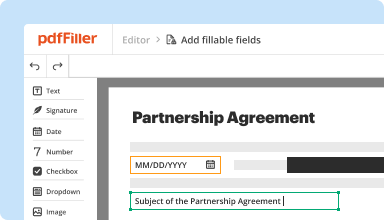
Create & edit PDFs
Generate new PDFs from scratch or transform existing documents into reusable templates. Type anywhere on a PDF, rewrite original PDF content, insert images or graphics, redact sensitive details, and highlight important information using an intuitive online editor.
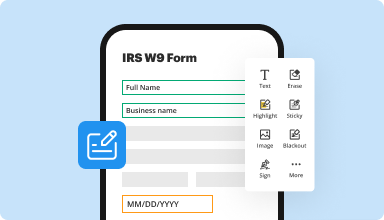
Fill out & sign PDF forms
Say goodbye to error-prone manual hassles. Complete any PDF document electronically – even while on the go. Pre-fill multiple PDFs simultaneously or extract responses from completed forms with ease.
Organize & convert PDFs
Add, remove, or rearrange pages inside your PDFs in seconds. Create new documents by merging or splitting PDFs. Instantly convert edited files to various formats when you download or export them.
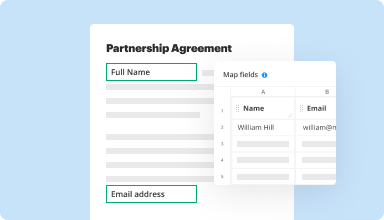
Collect data and approvals
Transform static documents into interactive fillable forms by dragging and dropping various types of fillable fields on your PDFs. Publish these forms on websites or share them via a direct link to capture data, collect signatures, and request payments.
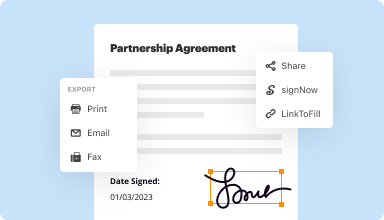
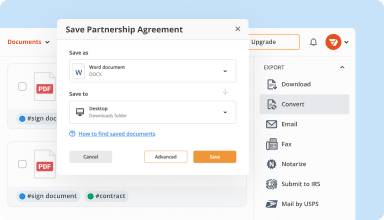
Export documents with ease
Share, email, print, fax, or download edited documents in just a few clicks. Quickly export and import documents from popular cloud storage services like Google Drive, Box, and Dropbox.
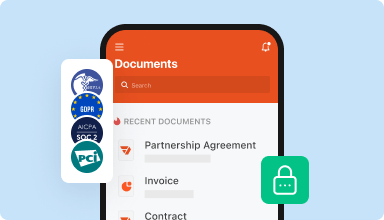
Store documents safely
Store an unlimited number of documents and templates securely in the cloud and access them from any location or device. Add an extra level of protection to documents by locking them with a password, placing them in encrypted folders, or requesting user authentication.
Customer trust by the numbers
64M+
users worldwide
4.6/5
average user rating
4M
PDFs edited per month
9 min
average to create and edit a PDF
Join 64+ million people using paperless workflows to drive productivity and cut costs
Why choose our PDF solution?
Cloud-native PDF editor
Access powerful PDF tools, as well as your documents and templates, from anywhere. No installation needed.
Top-rated for ease of use
Create, edit, and fill out PDF documents faster with an intuitive UI that only takes minutes to master.
Industry-leading customer service
Enjoy peace of mind with an award-winning customer support team always within reach.
What our customers say about pdfFiller
See for yourself by reading reviews on the most popular resources:
It is convenient, ensures legibility and a professional appearance, and is easy to use. I have used it only for basic functions - i.e. filling in blank lines. I still need to explore what else it can do.
2017-12-10
This is a very handy program to have access to when you need employee signatures, but they work in different locations throughout the country. It eliminates the need for faxes or snail mail.
2019-12-26
Love the ease of use.
I would highly recommednd this product to any business person.
Initially, I was hesistant because learning new software is always my dread. However, once I signed on it was so easy. Makes daily document updates and creations easy. I can always find an Accord form I needed with this as well. And edit of pdfs are no longer an avoidance.
Sometimes there is a delay from screen to screen. But nothing to really complain about.
2019-01-22
I have had a great experience thus far…
I have had a great experience thus far in my free trial. I have been able to merge documents to create a continuous flow, create signature stamps and fill out fillable pdfs' for my work. This is a great product!
2024-10-30
Excellent Product
Makes nonstop-filling-out-documents projects go by quickly. Rare online product that not only works as intended, but includes most of the features you wouldn't expect it to have. The interface and options are also shockingly seamless. It's easy to print, save, share, download, etc pretty much any document from any screen.
2021-07-13
This app is just what I needed to class…Senior Softball brackets
This app is just what I needed to class up my brackets for Senior Softball Tournaments. Easy to understand, very user friendly even for an old guy. I highly recommend it. A very good value,
2021-05-18
Excellent application but not sure if…
Excellent application but not sure if its worth $9 a month for an individual user working on domestic household forms. Definitely worth it if using for a small business.
2020-10-01
Easy to fill
I have always been able to fill out my documents without any frustrations, and the paperwork prints out seamlessly. Thank you for such an amazing program.
2020-07-02
I wish it was a little easier to type things into my...
I wish it was a little easier to type things into my papers however I am getting the hang of it, I dont like that sometimes I will click in an area and the typing bar doesnt appear where I clicked on, but near the area, sometimes thats in the middle of a line on the page and thats annoying.
2020-05-22
Update Sum Statement Of Work Feature
The Update Sum Statement Of Work feature simplifies project management by providing clarity and flexibility in tracking work progress. This tool is designed to help teams better manage their projects, ensuring they stay on the right path.
Key Features
Conveniently track workload and progress
Easily update project metrics in real-time
Support for collaborative work environments
Visualize project updates and changes
Integrate seamlessly with existing project management tools
Potential Use Cases and Benefits
Adjust project details during team meetings for immediate implementation
Keep stakeholders informed with up-to-date summaries
Support remote teams by providing clear updates from anywhere
Facilitate efficient decision-making with accessible data
Enhance accountability through transparent tracking of tasks
This feature addresses common challenges by providing an easy way to update project statuses. It eliminates misunderstandings and ensures everyone is on the same page. By using the Update Sum Statement Of Work feature, you empower your team to make informed decisions and maintain momentum in their projects.
For pdfFiller’s FAQs
Below is a list of the most common customer questions. If you can’t find an answer to your question, please don’t hesitate to reach out to us.
What if I have more questions?
Contact Support
How do you get the sum in SQL?
COUNT() Syntax. SELECT COUNT(column_name) FROM table_name. WHERE condition. AVG() Syntax. SELECT AVG(column_name) FROM table_name. WHERE condition. SUM() Syntax. SELECT SUM(column_name) FROM table_name. WHERE condition.
How do I sum two columns in SQL?
If you want to add two columns together, all you have to do is add them. Then you will get the sum of those two columns for each row returned by the query. What your code is doing is adding the two columns together and then getting a sum of the sums.
How do I sum a query in MySQL?
If you use the SUM() function in a SELECT statement that returns no row, the SUM() function returns NULL, not zero. The DISTINCT option instructs the SUM() function to calculate the sum of only distinct values in a set. The SUM() function ignores the NULL values in the calculation.
How do I sum by group in SQL?
SUM is used with a GROUP BY clause. The aggregate functions summarize the table data. Once the rows are divided into groups, the aggregate functions are applied in order to return just one value per group. It is better to identify each summary row by including the GROUP BY clause in the query result.
How do you use sum and count together in SQL?
SELECT COUNT returns a count of the number of data values. SELECT SUM returns the sum of the data values. SELECT AVG returns the average of the data values.
How do you sum a count in SQL?
COUNT() Syntax. SELECT COUNT(column_name) FROM table_name. WHERE condition. AVG() Syntax. SELECT AVG(column_name) FROM table_name. WHERE condition. SUM() Syntax. SELECT SUM(column_name) FROM table_name. WHERE condition.
How do I use sum by Group function in SQL?
SUM is used with a GROUP BY clause. The aggregate functions summarize the table data. Once the rows are divided into groups, the aggregate functions are applied in order to return just one value per group. It is better to identify each summary row by including the GROUP BY clause in the query result.
What is difference between Count and Sum?
Sum is doing the mathematical sum, whereas count simply counts any value as 1 regardless of what data type.
#1 usability according to G2
Try the PDF solution that respects your time.






