Get the free Cheat Sheets - Python Crash Course, Third Edition
Get, Create, Make and Sign cheat sheets - python



Editing cheat sheets - python online
Uncompromising security for your PDF editing and eSignature needs
How to fill out cheat sheets - python

How to fill out cheat sheets - python
Who needs cheat sheets - python?
Cheat Sheets - Python Form: Your Comprehensive Guide
Understanding Python cheat sheets
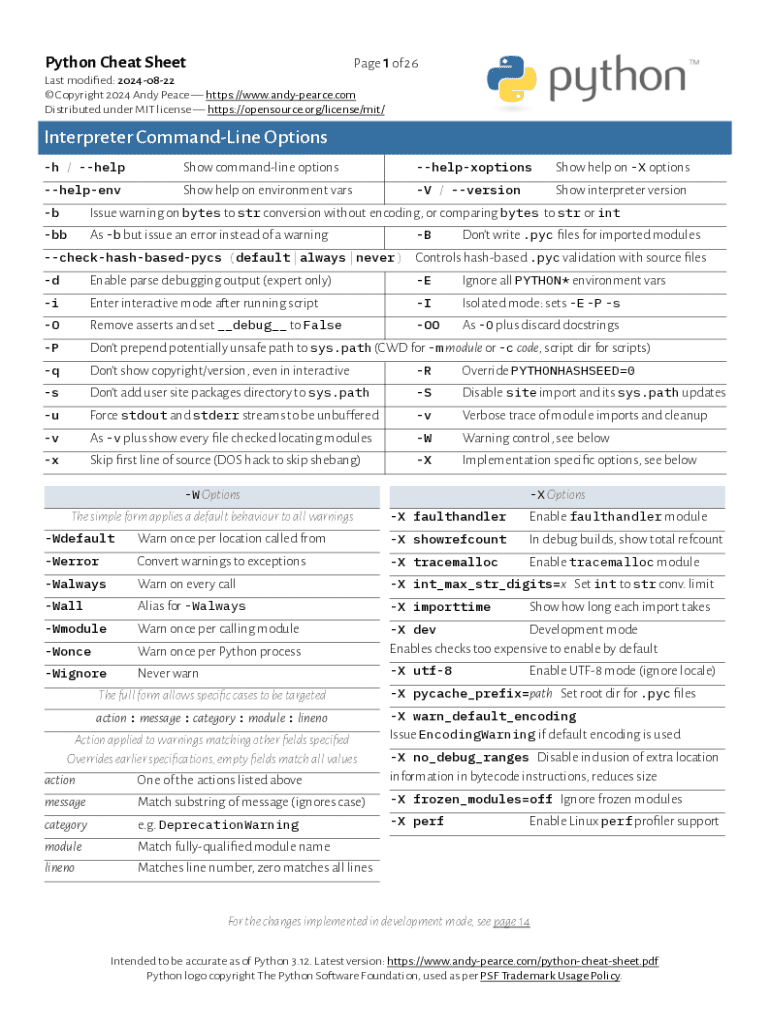
A cheat sheet in programming is a concise set of notes used for quick reference. In the context of Python, these cheat sheets serve as valuable tools that compile essential concepts, syntax, and functions in one place, allowing programmers—from beginners to experienced professionals—to access critical information swiftly. The importance of cheat sheets cannot be overstated as they not only streamline the coding process but also significantly reduce the time spent searching for details in extensive documentation.
Using Python cheat sheets offers various benefits. They enhance productivity by providing immediate access to vital information like syntax rules, data types, and built-in functions. For developers tackling Python programming tasks or preparing for interviews, having a cheat sheet on hand can mean the difference between smooth coding sessions and frustrating setbacks due to forgotten syntax. Furthermore, they facilitate the learning process by allowing users to reinforce their knowledge through a hands-on approach.
Getting started with Python
Python is a high-level, interpreted programming language known for its readability and simplicity. Its versatility makes it a popular choice for various applications, including web development, data analysis, artificial intelligence, and more. To leverage Python effectively, you must first install Python and set up a suitable development environment.
To install Python, follow these steps: 1. Visit the official Python website at python.org. 2. Download the latest version suitable for your operating system (Windows, macOS, or Linux). 3. Run the installer, ensuring you check the box to 'Add Python to PATH'. 4. Verify the installation by opening the command line and typing 'python --version'. After installing, you can set up your Python environment by choosing an Integrated Development Environment (IDE) such as PyCharm, Visual Studio Code, or Jupyter Notebook, which can enhance your coding experience.
Python basics cheat sheet
Understanding the fundamental building blocks of Python is crucial. Python includes several data types, the most commonly used ones are: Numeric types (int, float, complex), text type (str), sequence types (list, tuple), mapping type (dict), and set types (set, frozenset). Learning how to manipulate these data types allows you to handle data efficiently and perform operations essential for your programming tasks.
Declaring variables in Python is straightforward—simply assign a value to a name. For instance, 'age = 30' is a valid declaration. To maintain code clarity, follow naming conventions such as using lowercase letters, avoiding reserved words, and using underscores for multi-word variable names. It's also a best practice to use constants in uppercase to distinguish them from regular variables, enhancing readability.
Control flow in Python
Control flow statements manage the order of execution of code blocks. Conditional statements like 'if', 'else', and 'elif' allow programmers to execute different blocks of code based on certain conditions. For example: if (x > 0): print('Positive') else: print('Negative or Zero'). Another essential feature is the ternary operator, which offers a compact syntax: result = true_value if condition else false_value.
For looping, 'for' and 'while' loops provide powerful structures for iterating over data. The 'for' loop iterates over items of a list or collection, while the 'while' loop continues until a specified condition is no longer met. Control flow statements like 'break', 'continue', and 'pass' allow finer control over loop execution: 'break' exits a loop, 'continue' skips the current iteration, and 'pass' serves as a placeholder for future code.
Functions in Python
Functions are reusable code blocks that streamline programming in Python. To define a function, use the 'def' keyword followed by the function name and parentheses. For example: def greet(name): print(f'Hello, {name}!'). Function arguments can be passed within the parentheses, and a return statement can send back output from the function. Understanding how to effectively use functions, including built-in functions such as 'len()', 'max()', and 'sum()', is critical for optimizing your code.
Additionally, Python supports default and keyword arguments, giving you flexibility in function calls. For instance, def multiply(x, y=1): return x * y allows the second argument to default to 1 if not provided, simplifying function calls for common cases.
Data structures in Python
Data structures allow you to organize and store data efficiently in Python. Lists are one of the most versatile structures. You can create a list using square brackets: fruits = ['apple', 'banana', 'cherry']. Modifying lists is straightforward with methods like append() to add items, remove() to delete, or sort() to arrange. Being familiar with these functionalities is essential for effective data manipulation.
Dictionaries, defined using curly braces, map keys to values: user = {'name': 'Alice', 'age': 30}. Accessing and updating dictionary items is quick, utilizing methods such as keys(), values(), and items() to retrieve and manipulate data. Tuples, defined with parentheses, are immutable, meaning once created, they cannot be modified. Lastly, sets provide a collection of unique items, with operations like union, intersection, and difference to help manage the data effectively.
Object-oriented programming in Python
Object-oriented programming (OOP) is a programming paradigm that uses 'objects' to represent data. In Python, a class serves as a blueprint for creating objects, encapsulating data attributes and behaviors through methods. The key concepts of OOP—encapsulation, inheritance, and polymorphism—are fundamental to designing efficient and maintainable code. For example, a class can inherit properties from another class, allowing for code reuse and reducing redundancy.
Encapsulation involves bundling data and methods into a single unit or class, which promotes data hiding and separation of interface and implementation. Polymorphism allows objects to be treated as instances of their parent class, providing flexibility in how functions and methods are applied. Mastering these concepts enables programmers to build robust applications structured for future expansion and maintenance.
Handling exceptions
Error handling is an integral aspect of writing reliable code. Python's exception handling system enables developers to manage runtime errors gracefully. The 'try' block establishes a section of code to test, while the 'except' block defines how to respond in case of an error. You can also use 'else' to execute code when no exceptions occur and 'finally' to ensure that certain actions happen regardless of whether an exception was raised, making your programs robust.
Common exceptions include ValueError, IndexError, and KeyError, each indicating specific types of problems that may occur. By understanding how to anticipate and handle these exceptions, you can greatly enhance the resilience of your Python applications and reduce unexpected crashes during execution.
Reading and writing files
File I/O (input/output) operations are fundamental for data persistence. Python makes file management simple. You can open a file with the 'open()' function, specifying the file path and mode ('r' for reading, 'w' for writing, or 'a' for appending). Always remember to close the file using 'close()' to free system resources. For reading, methods like read(), readline(), and readlines() help you extract content from files efficiently.
When writing to files, use methods such as write() or writelines() to save strings or lists. Opting for 'with' statements ensures proper resource management, as it automatically handles closing the file once the operations are complete. Understanding how to perform these operations can facilitate effective data management for applications ranging from simple scripts to complex systems.
Key Python libraries and modules
Python's rich ecosystem is bolstered by its extensive libraries and modules. Standard libraries, such as os for operating system interactions, sys for system-specific parameters, and datetime for date manipulation, provide essential utilities that streamline development. Additionally, the math library offers mathematical functions, while NumPy and Pandas are powerful tools for data analysis and manipulation, making them indispensable for those working in data science.
For web development, frameworks like Flask and Django introduce abstraction layers to simplify server-side coding. As you progress, familiarizing yourself with these libraries is vital, as they not only enhance productivity but also allow you to leverage pre-existing solutions to complex problems, optimizing your workflow in Python programming.
Practical Python examples
Real-world applications of Python showcase its versatility across different domains. For example, in web development, building a simple REST API using Flask can provide insights into server-client interactions. Similarly, using Pandas for data manipulation on CSV files allows data scientists to process significant datasets efficiently without compromising performance. Sample code for an API could look like this: app = Flask(__name__); methods=['GET']) def get_data(): return jsonify(data).
In addition, Python's popularity in automation is evident in scripts that automate repetitive tasks, enhancing productivity. Incorporating best practices, such as writing clean and efficient code, is essential. such practices include using meaningful variable names, modularizing your code into functions, and incorporating comments or docstrings for documentation purposes. By focusing on these details, you not only create effective solutions but also ensure that they are maintainable for future needs.
Optimizing your Python code
Writing optimized Python code is crucial for improving performance and reducing resource consumption. Common pitfalls include using inefficient algorithms or unnecessarily deep nesting of loops. To enhance performance, prioritize algorithm selection based on time and space complexity. Tools like timeit can help measure the execution time of code snippets, guiding optimization efforts.
Additionally, using built-in functions and list comprehensions can lead to more compact and efficient code. Directly utilizing Python libraries for specific tasks will reduce the amount of code you must write and maintain. By implementing strategic optimizations, you not only improve application performance but also enhance user experience by providing faster, more responsive applications.
Preparing for Python interviews
Being well-prepared for Python interviews often involves mastering a variety of topics. Commonly asked questions revolve around fundamental Python concepts such as data structures, control flow, and OOP principles. Interviewers might also assess your understanding of exception handling and file I/O operations through practical coding exercises.
To excel in technical interviews, it's advantageous to articulate your thought process while coding. Practice solving problems on platforms like LeetCode or HackerRank, focusing on Python syntax and idiomatic solutions. Additionally, preparing explanations for key concepts will enhance your confidence and demonstrate your proficiency to potential employers.
Best practices for using Python cheat sheets
To maximize the effectiveness of Python cheat sheets, it's essential to approach them strategically. First, customize your cheat sheet to suit your specific needs and frequently used functions. Categorize sections based on personal usage patterns to create a logical flow that reflects your coding behavior.
Stay updated with new Python features by regularly revising and enhancing your cheat sheet. As Python evolves, keeping your notes aligned with the latest syntax and suggestions streamlines your programming experience. Ultimately, a well-curated cheat sheet not only serves as a quick reference but also reinforces your understanding, acting as an effective learning tool.
Interactive tools and resources
The availability of interactive tools enhances the Python learning experience. Online compilers such as Replit and Jupyter Notebook serve as platforms where developers can write, test, and share Python code easily. These tools provide instant feedback, enabling rapid prototyping and experimentation with coding concepts without needing extensive local setup.
Furthermore, community platforms like Stack Overflow and GitHub foster collaboration and discussion among Python programmers, providing access to a wealth of resources and shared code repositories. Engaging with these communities also opens doors to networking opportunities in the tech industry, expanding your knowledge base and offering insights into contemporary best practices in Python programming.
Engaging with the Python community
Participating in the Python community can greatly enhance your programming journey. Various forums and discussion groups are dedicated to Python, including the official Python subreddit and local meetups. Engaging in discussions, asking questions, and sharing your projects not only refines your coding skills but also provides valuable feedback and learning opportunities.
Another significant way to engage is by contributing to open-source projects. These initiatives not only allow you to practice coding with real-world applications but also enhance your visibility within the developer community. Such contributions can lead to professional opportunities and help you build a rich portfolio that showcases your skills.
Future of Python and emerging trends
The future of Python continues to look bright, with significant innovations and trends continuously shaping its landscape. Recent advancements in data science and machine learning highlight Python's versatility and applicability in fields that actively demand efficient and scalable solutions. The growing integration of Python with other technologies like AI and web development frameworks solidifies its position as a critical tool in modern programming.
Additionally, the rise of Python in IoT and automation signifies its adaptability across diverse sectors. As more developers adopt Python for complex applications, investing time in understanding its evolving ecosystem will serve you well. Keeping abreast of these trends allows programmers not only to harness the power of Python but also to stay relevant and competitive in the rapidly changing tech landscape.






For pdfFiller’s FAQs
Below is a list of the most common customer questions. If you can’t find an answer to your question, please don’t hesitate to reach out to us.
How can I edit cheat sheets - python on a smartphone?
How do I edit cheat sheets - python on an Android device?
How do I fill out cheat sheets - python on an Android device?
What is cheat sheets - python?
Who is required to file cheat sheets - python?
How to fill out cheat sheets - python?
What is the purpose of cheat sheets - python?
What information must be reported on cheat sheets - python?
pdfFiller is an end-to-end solution for managing, creating, and editing documents and forms in the cloud. Save time and hassle by preparing your tax forms online.















