Your Comprehensive Guide to Non-Disclosure Agreement Template Form
Understanding non-disclosure agreements (NDAs)
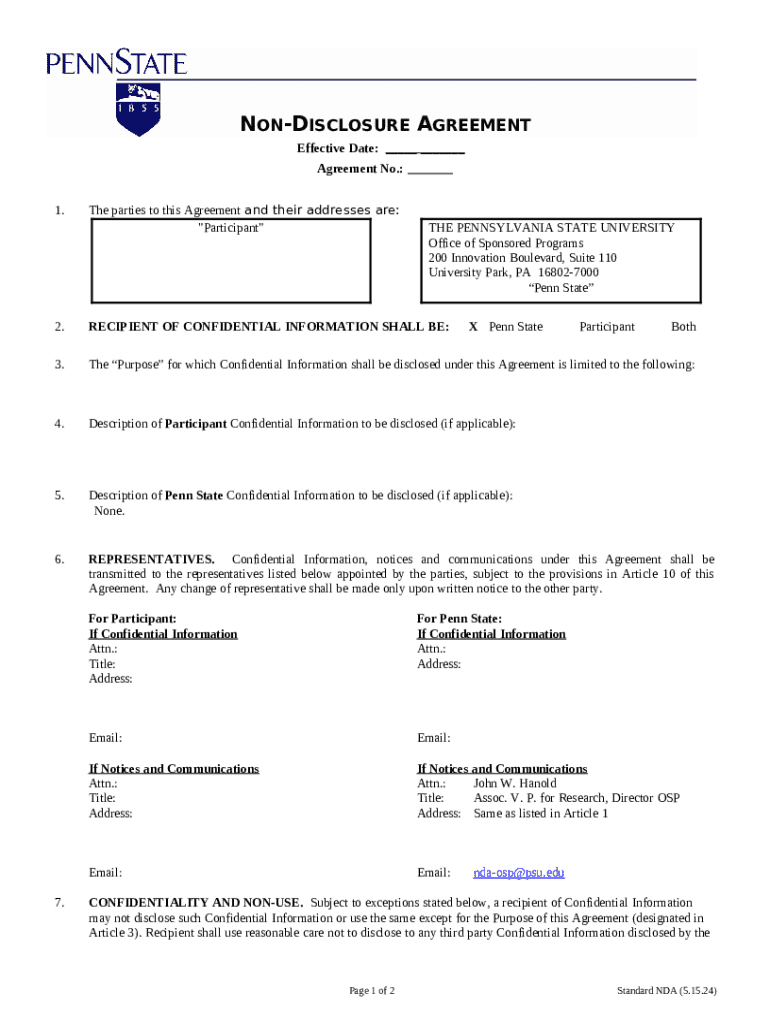
A non-disclosure agreement (NDA) is a legally binding contract that outlines the terms under which confidential information can be shared between parties while ensuring that such information remains protected. The primary purpose of an NDA is to safeguard sensitive information from unauthorized disclosure, which can be crucial in various business settings.
NDAs play an essential role in business transactions by fostering trust between parties. They allow businesses to share proprietary information, trade secrets, or project details that are vital for collaboration without the fear of leaking valuable trade information to competitors.
Protecting trade secrets when discussing potential partnerships.
Preserving confidentiality during the hiring process for freelancers and contractors.
Safeguarding sensitive product development information from competitors.
Types of non-disclosure agreements
There are primarily two types of NDAs: mutual and one-way. A mutual non-disclosure agreement involves two parties who share confidential information with each other and both agree to protect that information. This type is frequently used in situations where both parties will exchange sensitive information.
On the other hand, a one-way non-disclosure agreement is appropriate when only one party discloses confidential information, while the other party is obligated to keep it confidential. This setup is commonly used when a business needs to share proprietary information with potential investors or buyers.
Mutual Non-Disclosure Agreement: Ideal when both parties are sharing sensitive information.
One-way Non-Disclosure Agreement: Best when only one side is providing confidential data.
Unilateral vs. Bilateral NDAs: Unilateral obligations on one side versus bilateral obligations on both.
Components of an NDA template
An effective NDA template includes several essential clauses to ensure comprehensive protection and clarity. One critical element is the definition of confidential information, which specifies what exactly is considered confidential and what is excluded, such as publicly available information.
Definition of Confidential Information: Clearly outline what the confidential information entails.
Obligations of the Receiving Party: Detail what the receiving party must do to protect the information.
Duration of Confidentiality: State how long the information must remain confidential.
Severability and Legal Compliance: Include terms that allow the NDA to remain in effect, even if one part is invalid.
Integration Clause: Ensure that the NDA constitutes the entire agreement, overriding any previous agreements.
Step-by-step guide to using the NDA template form
Using the NDA template from pdfFiller is straightforward. First, users need to download and access the NDA template directly from the pdfFiller platform. This allows for easy editing and customization.
After downloading, you can customize the template with the necessary information, like the names of the parties involved and the specifics of what is being protected. Ensuring that all key sections are accurately filled is crucial.
Download and Access the NDA Template: Access the form on pdfFiller’s platform.
Customize the NDA Template: Fill in specific details relevant to your situation.
Review the NDA: Double-check for any incomplete sections and ensure compliance.
Signing the NDA: Consider both electronic signing through pdfFiller and traditional methods.
Managing and Storing Your NDA: Utilize cloud services for secure document management.
Practical tips for drafting effective NDAs
When drafting NDAs, there are several dos and don'ts to consider. For instance, do be clear and concise in your language; avoid ambiguous terms that could lead to misinterpretation. Another essential tip is to tailor the NDA to the specific circumstances, which can reduce the chances of disputes later.
Do use precise language: Clarity reduces ambiguity in legal agreements.
Don't overreach: Avoid overly broad definitions that may not hold up in court.
Do consult legal professionals: When in doubt, seek legal advice to ensure compliance.
Don't forget about jurisdiction: Specify governing law in case disputes arise.
Special considerations in specific industries
Different industries have unique needs regarding NDAs. For instance, in the tech sector, businesses often must protect their intellectual property, making NDAs critical when collaborating on software development or hardware design.
For startups, NDAs not only protect new ideas but also help secure investors by creating a safe space for discussion. Academia typically requires NDAs to protect sensitive research data shared during collaborative projects, ensuring that research integrity remains intact.
Confidentiality in the Tech Sector: Essential for protecting proprietary technologies.
NDAs for Startups: Crucial for securing funding and protecting innovative ideas.
University Research and NDAs: Vital for protecting sensitive data and research findings.
Case studies and examples
Examining real-world applications of NDAs can provide valuable insights. For instance, company A and company B entered into a mutual non-disclosure agreement before discussing a potential merger. This NDA allowed both parties to share sensitive financial documents without fear of regulatory issues or competitive disadvantage.
Standard Bilateral NDA: A common agreement between two parties to protect shared information.
One-way NDA Template Example: Used by company A when discussing trade secrets with potential partners.
Analysis of Effective NDA Terms: Keys to enforceability and compliance.
Glossary of key terms
Understanding the terminology surrounding NDAs is essential for effective use. Key terms include 'Confidential Information,' which refers to all proprietary data shared under an NDA, and 'Severability,' which ensures that if one part of the NDA is found invalid, the remainder still holds.
Confidential Information: Any proprietary or sensitive data shared through an NDA.
Severability: A clause ensuring the remainder of the contract remains effective if part is void.
Integration Clause: Asserts that the NDA represents the complete understanding between parties.
FAQs about non-disclosure agreements
Frequently asked questions can clarify common concerns related to NDAs. A typical question is about the binding nature of an NDA—yes, NDAs are enforceable contracts that can result in legal action if violated. Another concern is about the implications of violation; a breach can lead to legal consequences, including damages payout.
How binding is an NDA?: They are legally enforceable and protect confidential data.
What happens if an NDA is violated?: Breach can lead to legal repercussions.
Can NDAs be modified after signing?: Yes, but both parties must agree to the modifications.
User testimonials and experiences
Feedback from businesses using NDAs reflects their positive impact. Startups report successfully negotiating funding rounds while utilizing NDA templates that safeguard sensitive business plans. Established companies often share success stories about partnering with new businesses facilitated by well-structured NDAs.
Success Stories of Businesses Using NDAs: Increased trust and faster negotiations.
Feedback from Users of the NDA Template Form: Users appreciate the clarity and ease of customization.
Interactive tools for enhanced NDA management
pdfFiller offers a range of interactive tools that streamline the NDA management process. Users can compare documents to ensure compliance and consistency through built-in features, making collaborative NDA drafting more effective.
Document Comparison and Reporting Features: Easily identify changes between document versions.
Collaborating with Team Members on NDA Drafts: Facilitates seamless teamwork and feedback.
Tracking Changes and Versions: Maintain a clear record of all alterations for accountability.