Get the free Audiology Pure-Tone Testing: Overview, Indications, ...
Get, Create, Make and Sign audiology pure-tone testing overview

Editing audiology pure-tone testing overview online
Uncompromising security for your PDF editing and eSignature needs
How to fill out audiology pure-tone testing overview
How to fill out audiology pure-tone testing overview
Who needs audiology pure-tone testing overview?
Audiology Pure-Tone Testing Overview Form
Understanding pure-tone testing
Pure-tone audiometry is a cornerstone of audiological assessments used extensively to evaluate hearing ability. This specific form of testing measures a person’s ability to hear various pure tones at different frequencies, ranging from low to high pitches. By identifying the softest sounds a person can hear at specific frequencies, audiologists can ascertain the presence and extent of hearing loss across various sound ranges. The testing process typically involves using headphones or ear inserts through which sounds are played, while the participant indicates when they hear these tones.
The significance of pure-tone testing extends beyond simple thresholds; it provides insights into an individual’s overall auditory health. This testing is not only essential for diagnosing hearing impairment but also forms the basis for recommending interventions, such as hearing aids or further medical evaluations.
Purpose of pure-tone testing
The primary purposes of pure-tone testing include identifying hearing loss and assessing the functionality of the ear. Audiologists utilize this test to determine whether a person can hear specific frequencies, which aids in understanding the nature and extent of any hearing problems. By methodically identifying these thresholds, practitioners can differentiate between various forms of hearing loss, such as conductive or sensorineural loss.
Furthermore, pure-tone testing can help evaluate ear health. Abnormal results may indicate issues such as ear obstructions or problems with the auditory nerve, pushing further investigations and specific recommendations. Overall, this straightforward yet comprehensive analysis serves as the initial step in developing a tailored treatment plan.
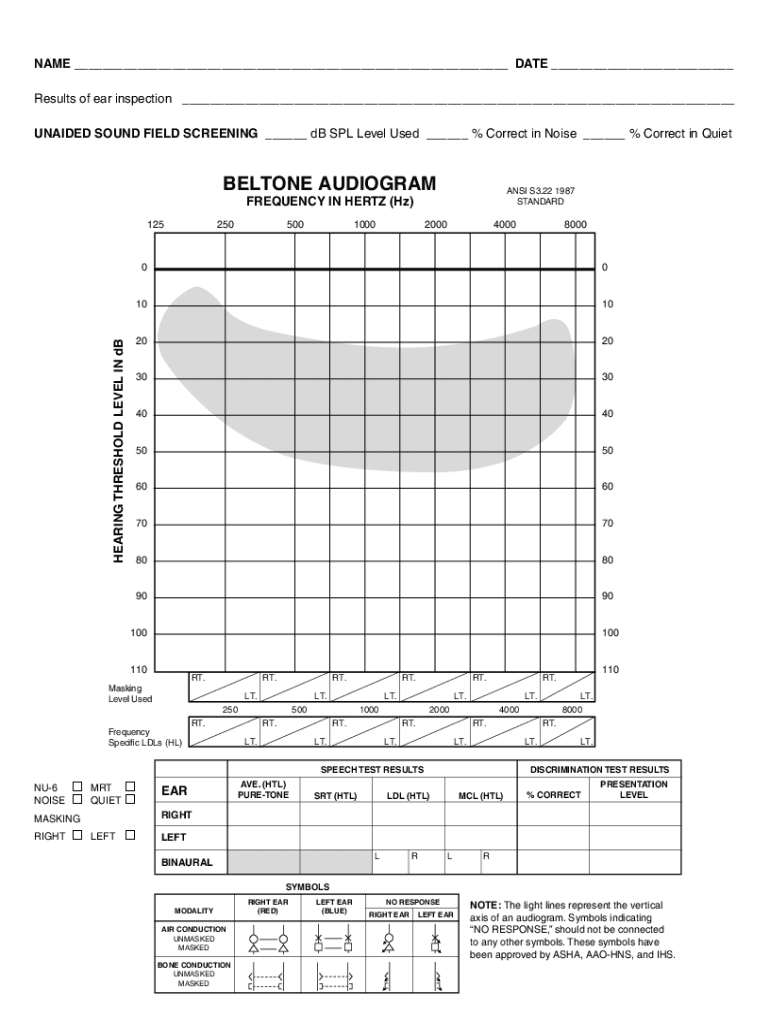
The pure-tone audiogram
A pure-tone audiogram is a graphical representation of an individual’s hearing sensitivity across various frequencies and is instrumental in conveying test results effectively. The layout typically includes frequency (measured in Hertz) displayed along the horizontal axis and hearing level (in decibels) on the vertical axis, facilitating a clear visual overview of hearing capability.
Audiologists use specific symbols to indicate the responses during testing, with circles representing right ear results and crosses indicating left ear results. Additional symbols may denote air conduction or bone conduction thresholds, providing comprehensive data that assists in clinical decision-making.
Importance of accurate audiograms
Accurate audiograms are crucial for formulating an effective intervention plan. When test results are clear and precise, audiologists can make informed recommendations regarding treatment options. Misinterpretations can lead to inappropriate treatments, highlighting the importance of detailed and careful administration of pure-tone tests. Inaccurate audiograms could drastically impact patient care, delaying crucial treatments and exacerbating hearing issues.
Equipment used in pure-tone testing
Pure-tone testing is conducted using audiometers, devices designed to produce specified sounds at controlled volumes and frequencies. Different types of audiometers, including portable models, standard diagnostic audiometers, and sound booths with advanced features, cater to varying clinical settings and needs. The choice of equipment can influence test outcomes, making it critical to select the appropriate tool for the testing environment.
Calibration and maintenance of audiometers are paramount to ensuring accurate results. Routine checks help confirm that devices are functioning as intended, with periodic professional calibrations standard in many clinical practices. Ensuring that all equipment meets the required standards not only upholds the integrity of results but also prioritizes patient safety.
Patient preparation for pure-tone testing
Proper preparation of patients prior to pure-tone testing is essential for measuring accurate auditory thresholds. Pre-test guidelines typically include ensuring the environment is quiet and free from distractions, which may affect patient responses. Audiologists need to communicate with patients about what to expect during the test, which can alleviate anxiety and enhance their cooperation.
Clear instructions are vital for facilitating the testing process. Patients should be informed on how to indicate that they have heard a tone, whether it's by raising a hand or pressing a button. Educating patients on the importance of honest feedback during testing can further ensure related results are representative of their actual hearing capabilities.
Testing methodologies
The ascending method of pure-tone testing is commonly employed, which involves presenting sounds at lower volumes and gradually increasing the intensity until the patient can hear the tone. This process ensures a more precise measurement of threshold levels. By systematically recording the lowest intensity at which a sound is perceivable, audiologists can establish reliable thresholds across different frequencies.
Bone conduction testing is another critical element, allowing audiologists to determine how sound travels through the bones of the skull to reach the inner ear, bypassing the outer and middle ear. Comparing air conduction results with bone conduction provides vital insights into the type of hearing loss present. Considerations for cross hearing and masking are also integral; when there’s a possibility that sound may travel to the non-test ear, masking techniques can be employed to ensure accurate results.
Result interpretation
Understanding the results from pure-tone testing is essential for diagnosing and articulating the nature of hearing loss. Audiologists evaluate the audiogram to determine thresholds, assessing the lowest decibel levels at which sounds are heard. Thresholds are categorized into degrees of hearing loss, such as normal, mild, moderate, severe, or profound, which guides clinical recommendations.
Interpreting the severity, laterality, and symmetry of responses plays a significant role in identifying specific auditory issues. Audiologists can conclude whether hearing loss is unilateral or bilateral and whether it exhibits symmetrical patterns, aiding in more targeted therapeutic strategies.
Common challenges in pure-tone testing
Testing in noisy environments is a common challenge that can skew pure-tone test results. Audiologists can implement several strategies to minimize external noise, such as conducting tests in soundproof booths and using noise-canceling headphones to enhance accuracy. Maintaining a controlled and quiet environment helps ensure the validity of test outcomes and builds trust with patients.
Psychological factors can also significantly impact testing outcomes. Patient anxiety, whether stemming from fear of results or unfamiliarity with the process, can lead to unreliable responses. Addressing these concerns through thorough explanations and providing reassuring communication during testing can enhance patient comfort, leading to more factual test results.
Overview of related hearing studies
Insights into age-related hearing loss underscore the importance of regular pure-tone assessments as individuals age, with studies indicating that hearing loss affects approximately one in three older adults. Audiometric trends show that frequency sensitivity often diminishes with age, emphasizing the necessity of hearing evaluations as part of aging healthcare protocols.
Additionally, understanding the effects of acoustic trauma is crucial. Exposure to loud noises can have irreversible effects on hearing, highlighting the need for protective measures in occupational and recreational environments. Audiologists play a vital role in alerting patients about safe listening practices and implementing preventive strategies derived from these studies.
Best practices for conducting pure-tone testing
Establishing and re-establishing hearing thresholds forms the foundation of effective pure-tone testing. Audiologists must follow systematic protocols to ascertain accurate thresholds, which involve providing clear instructions and ample time for patient responses. This meticulous approach is essential for developing a comprehensive audiogram.
Effective masking procedures are also critical when cross hearing is suspected. Employing masking noise ensures the test remains valid, leading to reliable results. Audiologists should be well-versed in the characteristics of masking and how to implement it where necessary, ensuring that auditory measurements accurately reflect the patient’s hearing ability.
Lastly, adhering to common rules during testing—such as presenting tones at appropriate volumes, allowing for adequate response times, and ensuring all equipment is properly set—guarantees both patient safety and the accuracy of results. By following structured best practices, healthcare professionals can uphold high standards in audiological testing.
Leveraging technology for document management
The audiology pure-tone testing overview form is an essential tool that can greatly enhance the efficiency of managing patient records. Using a platform like pdfFiller allows audiologists to streamline their document management processes, ensuring that forms are easily accessible and editable from anywhere. By digitizing this process, practitioners can save time and reduce paperwork burdens.
pdfFiller offers various features specifically designed for audiologists, including the ability to fill out, eSign, and collaborate on documents. This seamless integration enhances both communication and documentation accuracy, making it simpler to share important information with other healthcare professionals and patients alike.
The convenience of accessing documents through a cloud-based solution significantly improves workflow efficiency. Audiologists can retrieve test results, patient notes, and forms swiftly, leading to enhanced patient care and satisfaction. With tools that champion effective document management, pdfFiller truly empowers audiology professionals to focus on what matters most—their patients.






For pdfFiller’s FAQs
Below is a list of the most common customer questions. If you can’t find an answer to your question, please don’t hesitate to reach out to us.
How do I make changes in audiology pure-tone testing overview?
How can I edit audiology pure-tone testing overview on a smartphone?
How do I edit audiology pure-tone testing overview on an Android device?
What is audiology pure-tone testing overview?
Who is required to file audiology pure-tone testing overview?
How to fill out audiology pure-tone testing overview?
What is the purpose of audiology pure-tone testing overview?
What information must be reported on audiology pure-tone testing overview?
pdfFiller is an end-to-end solution for managing, creating, and editing documents and forms in the cloud. Save time and hassle by preparing your tax forms online.















