Get the free Native budworm trap and net data record form
Get, Create, Make and Sign native budworm trap and



How to edit native budworm trap and online
Uncompromising security for your PDF editing and eSignature needs
How to fill out native budworm trap and

How to fill out native budworm trap and
Who needs native budworm trap and?
Native Budworm Trap and Form: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding native budworms
Native budworms, specifically the helicoverpa punctigera species, are a significant pest for various crops across Australia, particularly canola. These budworm caterpillars feed on the vegetative parts of plants, leading to considerable crop damage. Farmers need to be vigilant as these pests can proliferate rapidly during favorable weather conditions, especially in agricultural zones like Geraldton and the broader western Australia region.
These pests are primarily active during the warmer months, aligning with peak crop growth periods. Understanding their life cycle and seasonal patterns is crucial for effective pest management strategies, as populations can explode quickly if left unchecked.
Importance of monitoring native budworms
Monitoring native budworms is vital for preserving crop yields and economic stability for farmers. With an average infestation leading to a reduction in crop harvests by up to 30%, proactive measures are critical. Volunteer farmers and agronomists must work cooperatively to track pest populations and potentially avoid severe economic losses before they occur.
Furthermore, early detection through monitoring allows for the implementation of pest control measures before infestations escalate, ensuring that the crops remain healthy and productive.
Introduction to native budworm traps
Native budworm traps are specialized devices designed to capture and monitor the presence of budworms in the field. These traps consist of various components that work together to attract and capture moths, which are the adult stage of the budworms. By targeting these moths, farmers can gain insights into the impending budworm populations.
Typically, traps utilize pheromone-based lures, which are chemically formulated substances that mimic the natural scents emitted by female moths to attract males. This method of trapping provides a more effective way to gauge the potential risk of budworm infestations.
Why use native budworm traps?
Employing native budworm traps offers a range of benefits for agricultural practices. Firstly, these traps enable early detection of budworm activity, allowing farmers to take swift action against potential infestations. By identifying infestation trends, decisions on pesticide application or other interventions can be made more judiciously, ultimately reducing costs and environmental impact.
Moreover, using these traps contributes to data collection that supports informed pest management decisions. The type of trapping strategy utilized can be tailored to specific crops such as canola, based on regional pest population dynamics and environmental conditions.
Setting up your native budworm trap
Setting up a native budworm trap requires careful planning and execution to ensure its effectiveness. Start by gathering necessary materials: a trap, lures, a string or pole for hanging, and perhaps a notebook for observations. The ideal location will often be on the edge of fields where budworm activity tends to be high, avoiding areas that are too shaded by trees or other structures.
When it comes to installation, follow these steps: 1. Select an appropriate location in your field. 2. Assemble the trap components according to the manufacturer's instructions. 3. Secure the trap in your chosen position, ensuring it's stable. 4. Deploy the attractants to maximize effectiveness. Taking note of environmental factors, such as wind direction, can also influence the trap's performance.
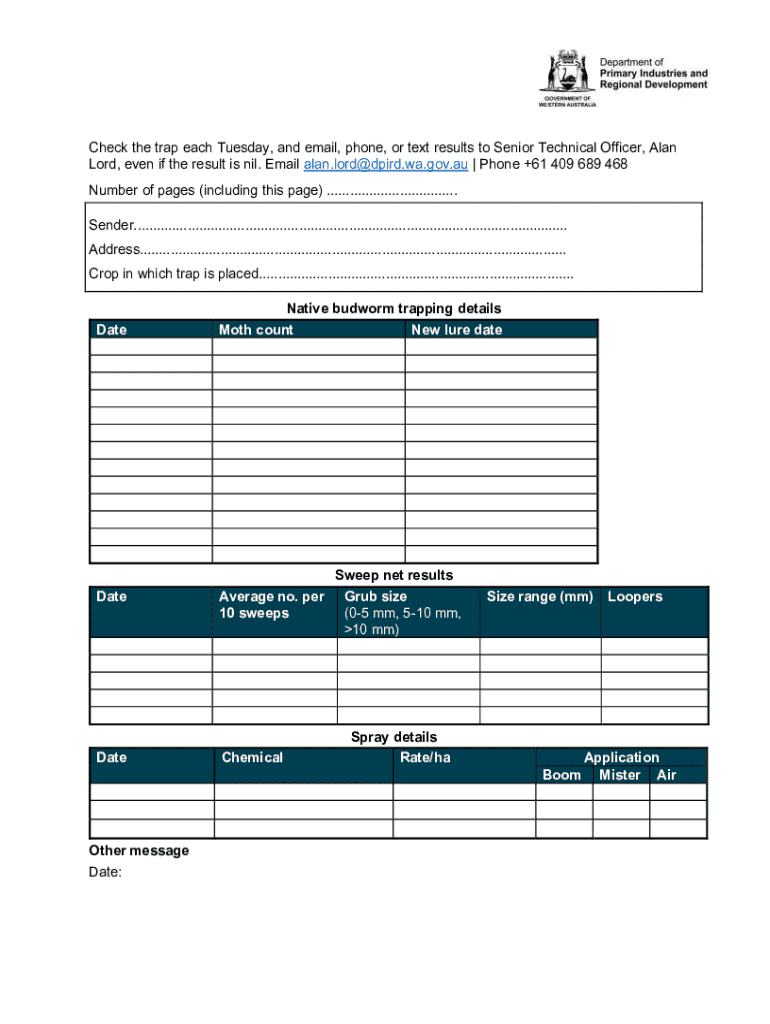
Using the native budworm trap form
Completing the native budworm trap form is essential for tracking and managing pest populations. This form records vital data that helps in analysis and eventual pest control measures. It's designed to log specific information such as the date of the trap setup, location, weather conditions, and the number of moths captured during inspections.
Filling out the form accurately can be broken down into several key sections: 1. Date and Location – noting when and where the trap was set. 2. Environmental Conditions – including temperature, humidity, and any recent weather patterns. 3. Trap Results – recording the number of captured moths to identify trends over time.
Common mistakes can diminish the effectiveness of your monitoring. Ensure data accuracy by double-checking entries, avoiding assumptions about conditions, and regularly updating the form after every inspection. This diligence in record-keeping supports better pest management practices.
Monitoring and reporting results
Regularly checking and recording trap results is fundamental in managing native budworm populations. Schedule consistent intervals for inspections—daily or weekly, depending on the activity level. The results should be noted meticulously, highlighting any significant captures that could alert you to rising pest concerns.
Looking ahead, farmers can benefit from understanding historical data trends. For example, expectations for the year 2025 should be aligned with previous seasons, allowing for proactive adjustments. Reports summarizing these findings can be shared with local agricultural bodies, ensuring that broader community efforts against pests are well-coordinated.
Integrating findings with pest management practices
Data from trapping directly influences pest control strategies. For instance, a rise in moth capture rates might necessitate more aggressive intervention tactics, including targeted pesticide use. Farmers should maintain constant communication with agricultural professionals or agronomists to validate their findings and reinforce decisions based on localized insights, particularly when managing crops like canola.
By collaborating, growers can enhance integrated pest management approaches, utilizing trapped data to justify shifting cultivation practices or introducing biological controls, which can mitigate risks effectively.
Additional actions post-analysis
Once analysis of pest monitoring has been completed, it is critical to document netting outcomes and any subsequent spraying activities. Keeping organized records ensures compliance with agricultural regulations and sets a foundation for future planning. Data should be linked to specific traps and timings to create a comprehensive understanding of how interventions have altered pest populations.
Equally important is evaluating the effectiveness of interventions employed after trapping. Farmers should assess metrics such as changes in capture rates and crop health post-treatment, forming a feedback loop that strengthens future pest control strategies and improves overall agricultural health.
Frequently asked questions (FAQs)
Farmers often have questions regarding the efficiency and practicalities of using native budworm traps. Common questions revolve around the best types of lures to use, optimal trap placement, and what to do upon detecting significant capture numbers. Understanding these nuances is key to maximizing the effectiveness of the trapping process.
Experts recommend ensuring that traps are checked regularly and that records are meticulously kept. This allows for meaningful comparisons and informed adjustments to pest management approaches as needed. Seeking advice from local agricultural specialists can also clarify operational best practices.
Conclusion: enhancing your pest management strategy
Employing a native budworm trap and maintaining an accurate trap form is invaluable for effective pest management. The systematic approach of monitoring, documenting, and analyzing pest captures directly contribute to proactive farming strategies. By applying best practices and staying informed about budworm trends, farmers can significantly improve their ability to keep crops safe from this troublesome pest.
Continuous learning through resources provided on platforms like pdfFiller enhances the overall understanding of pest management, ensuring farmers can adapt to evolving challenges in their agricultural practices successfully.






For pdfFiller’s FAQs
Below is a list of the most common customer questions. If you can’t find an answer to your question, please don’t hesitate to reach out to us.
How can I send native budworm trap and for eSignature?
How do I edit native budworm trap and straight from my smartphone?
How do I edit native budworm trap and on an Android device?
What is native budworm trap?
Who is required to file native budworm trap?
How to fill out native budworm trap?
What is the purpose of native budworm trap?
What information must be reported on native budworm trap?
pdfFiller is an end-to-end solution for managing, creating, and editing documents and forms in the cloud. Save time and hassle by preparing your tax forms online.















