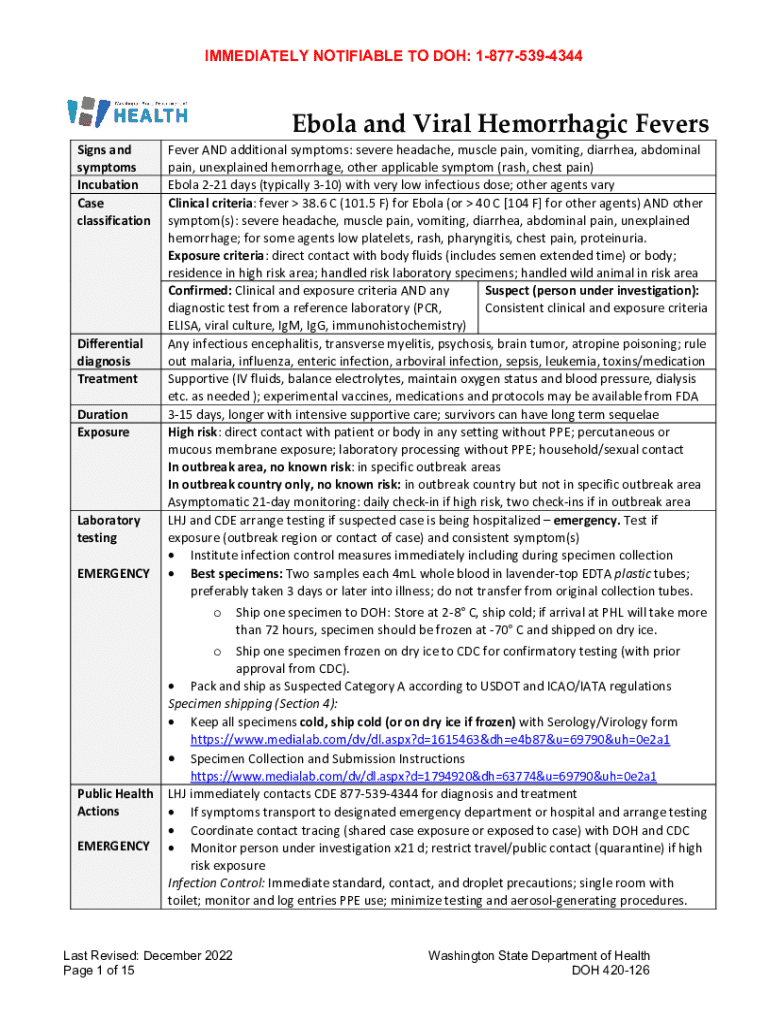
Get the free Ebola and Viral Hemorrhagic Fevers Reporting Guidelines
Get, Create, Make and Sign ebola and viral hemorrhagic



How to edit ebola and viral hemorrhagic online
Uncompromising security for your PDF editing and eSignature needs
How to fill out ebola and viral hemorrhagic

How to fill out ebola and viral hemorrhagic
Who needs ebola and viral hemorrhagic?
Ebola and Viral Hemorrhagic Form: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding Ebola and viral hemorrhagic fever
Viral Hemorrhagic Fevers (VHFs) represent a group of diseases caused by several distinct viruses. These include highly pathogenic agents that can lead to outbreaks and significant mortality. Characterized by fever, bleeding, and multi-organ dysfunction, VHFs often require rapid response and containment strategies to prevent widespread transmission.
Ebola virus disease (EVD) is one of the best-known forms of VHFs. First identified in 1976 near the Ebola River in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, this disease has since caused several severe outbreaks primarily in Central and West Africa. The Ebola virus naturally resides in non-human primates and fruit bats, regarded as key hosts in the transmission cycle to humans.
Transmission pathways for the Ebola virus typically include direct contact with bodily fluids of infected individuals or animals. Primary methods of transmission involve blood, secretions, and organ fluids. The capacity for human-to-human transmission in healthcare settings underscores the importance of strict protocols during outbreaks.
Symptoms and diagnosis of Ebola
Recognizing the symptoms of Ebola is crucial for timely intervention. Initial symptoms usually arise 2 to 21 days after exposure and include abrupt fever, fatigue, muscle pain, and sore throat. As the disease progresses, more severe symptoms manifest, such as vomiting, diarrhea, and hemorrhagic manifestations including bleeding from gums and in urine.
In the advanced stages, multiorgan failure can occur, often leading to death. Diagnosis is conducted through various laboratory tests, including PCR assays to identify the viral RNA, serological testing to detect antibodies, and antigen capture enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA). Accurate and prompt diagnosis is fundamental to differentiate Ebola from other VHFs, such as Marburg or Lassa fever, which share overlapping symptoms.
Prevention strategies for Ebola
Prevention of Ebola virus transmission hinges on understanding risk factors, primarily geographic areas where outbreaks are frequent. Regions in Central and West Africa are notably at higher risk due to frequent human-wildlife interactions and insufficient healthcare infrastructure. Community behaviors, such as contact with infected individuals or improper burial practices, significantly contribute to the risk of spread.
Key preventative measures focus on vaccination, safe burial practices, and strict use of personal protective equipment (PPE). The landscape of Ebola vaccination has advanced significantly with products like the rVSV-ZEBOV vaccine showing high efficacy in preventing infection. Communities must engage in educating the population about behaviors that mitigate risk, such as avoiding contact with sick individuals and using designated burial teams.
Management of Ebola cases
Managing Ebola cases requires a multi-faceted approach that prioritizes supportive care. Patients suffering from EVD are commonly treated through hydration, administering intravenous fluids, and managing complications as they arise. This supportive care is crucial as there is currently no specific antiviral treatment available, hence the reliance on experimental therapies like monoclonal antibodies or antiviral treatments in clinical trials.
Protocols in healthcare facilities emphasize infection control procedures. It is imperative for healthcare personnel to undergo rigorous training on managing patients suspected of EVD. Proper disposal of medical waste, adherence to strict hand hygiene protocols, and isolation of symptomatic patients play pivotal roles in curbing the spread within medical environments.
Community engagement in Ebola response
Community engagement is fundamental in tackling Ebola outbreaks. Risk communication plays a critical role in educating the community about symptoms, transmission routes, and the significance of early healthcare access. Building trust in health messaging is essential; community leaders and healthcare workers should collaborate to distribute health information through workshops, meetings, and media campaigns.
Collaborative response planning with local organizations can help foster a sense of ownership in outbreak management. Involving the community in designing prevention strategies tailored to local customs or behaviors increases compliance and effectiveness. Approaching health behaviors culturally and socially allows for a more robust community response.
Resources for documenting and managing Ebola-related information
Effective documentation and management of Ebola-related information are crucial for a successful outbreak response. Utilizing interactive tools for tracking and reporting cases allows for real-time updates and responsive action. Documentation not only aids in outbreak management but can also inform future strategies based on historical data analysis.
Cloud-based solutions like pdfFiller offer comprehensive document management capabilities for teams involved in outbreak response. Users can create and edit various documents necessary for tracking cases, utilizing step-by-step templates that enhance collaborative efforts. The platform allows for the integration of eSignatures and collaborative features, ensuring that teams stay connected and informed.
Current research and developments
Research continues to evolve our understanding of the Ebola virus. Recent publications have focused on breakthrough studies related to vaccine efficacy and novel treatment modalities that may improve patient outcomes. The commitment to ongoing research remains essential for preventing future outbreaks by allowing scientists to stay ahead of the virus's mutations and transmission dynamics.
Future directions in Ebola treatment and prevention involve global health policy implications and enhancing preparedness strategies. The pursuit of effective vaccines such as the rVSV-ZEBOV and improved palliative care options showcases the need for sustained investment in health research and infrastructure, particularly in regions disproportionately affected by the virus.
Case studies and infographics
Historical case studies of Ebola outbreaks offer invaluable lessons for future endeavors. Analyzing previous responses to outbreaks can yield insights that refine current practices. Each outbreak presents unique challenges and opportunities and understanding them aids in tailoring responses effectively, such as the 2 West Africa outbreak, which highlighted both the shortcomings and successes of global health systems.
Visual data representations, including infographics, can disseminate critical information on infection rates and highlight effective prevention strategies. Tools for comparative analysis of Ebola against other VHFs enable better understanding, empowering communities and health professionals alike to contextualize their approaches to disease control.
Videos and multimedia learning tools
Educational videos on Ebola are valuable resources for understanding the virus and its implications. Documentary-style overviews of outbreaks provide context and breadth, while expert interviews offer insights from frontline workers. These platforms are vital for disseminating knowledge and enhancing public awareness.
Interactive learning modules can engage individuals and communities, often featuring simulations of outbreak scenarios. These tools are not only instructional but provide an avenue for reinforcing knowledge. Engaging activities serve as vital reinforcement, allowing learners to apply their understanding in practical scenarios.
Related health topics
Exploring other Viral Hemorrhagic Fevers (VHFs) widens the understanding of similar pathogens, such as Marburg and Lassa fever. These diseases exhibit symptoms similar to Ebola and share complexities in treatment and outbreak management strategies. Analyzing their differences and similarities informs better preparedness and response across the board.
The implications of ebola and other VHFs extend beyond immediate health concerns, spotlighting the importance of global health frameworks. Insights from the G7 and other collaborative efforts highlight international preparedness for health crises and strategies to foster cooperation for quick responses, which are critical in the global fight against emerging infectious diseases.






For pdfFiller’s FAQs
Below is a list of the most common customer questions. If you can’t find an answer to your question, please don’t hesitate to reach out to us.
How can I edit ebola and viral hemorrhagic from Google Drive?
Where do I find ebola and viral hemorrhagic?
Can I sign the ebola and viral hemorrhagic electronically in Chrome?
What is ebola and viral hemorrhagic?
Who is required to file ebola and viral hemorrhagic?
How to fill out ebola and viral hemorrhagic?
What is the purpose of ebola and viral hemorrhagic?
What information must be reported on ebola and viral hemorrhagic?
pdfFiller is an end-to-end solution for managing, creating, and editing documents and forms in the cloud. Save time and hassle by preparing your tax forms online.

























