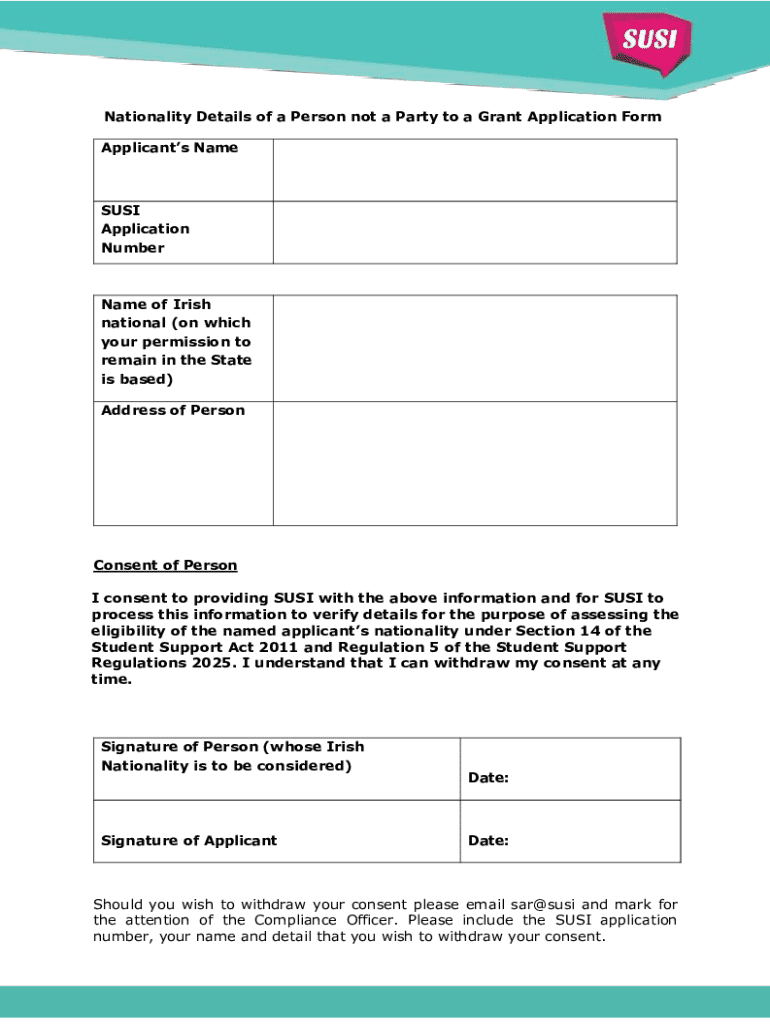
Get the free Nationality Details of a Person Not a Party to a Grant Application Form
Get, Create, Make and Sign nationality details of a



Editing nationality details of a online
Uncompromising security for your PDF editing and eSignature needs
How to fill out nationality details of a

How to fill out nationality details of a
Who needs nationality details of a?
Nationality details of a form: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding nationality
Nationality is a legal relationship between an individual and a state. It signifies a person's membership within a nation and often determines the rights and responsibilities that person holds. A clear understanding of nationality is essential for navigating legal systems, as it affects everything from voting rights to inheritance.
It's crucial to distinguish between nationality and citizenship, although the terms are often used interchangeably. While nationality refers to the affiliation with a specific nation, citizenship encompasses a broader scope that includes a set of legal rights and duties afforded to an individual within that nation. This distinction highlights the complexities involved in various legal frameworks globally.
The importance of nationality within legal systems cannot be overstated. It functions as a basis for national laws that regulate issues like immigration, work rights, and taxation. For those filling out nationality-related forms, understanding these nuances is vital to avoid legal pitfalls.
Nationality in international law
International laws governing nationality revolve around frameworks designed to protect individuals' rights as members of a state. These laws aim to prevent statelessness and ensure that individuals have access to their nationality rights, no matter where they reside.
Key treaties and conventions, like the 1961 Convention on the Reduction of Statelessness, articulate the responsibilities of states to grant nationality to individuals born within their territory. The role of international organizations, such as the United Nations, is crucial in monitoring compliance with these treaties and promoting awareness of nationality issues.
Determining factors of nationality
Several factors play a pivotal role in determining nationality. Place of birth is one of the most significant. Many countries follow the principle of jus soli, allowing individuals born on their territory automatic nationality regardless of their parent's nationality.
Parental nationality is another influential element, particularly in systems where jus sanguinis (right of blood) prevails. In such cases, a child's nationality may derive from their parents' citizenship, even if they are born abroad. Additionally, naturalization processes enable foreigners to acquire nationality after meeting specific criteria, such as residency duration, language proficiency, and understanding of local customs.
Legal protections related to nationality
Nationality grants individuals a spectrum of rights and protections under the law. These rights can include access to education, healthcare, and legal assistance, which vary significantly from one nation to another. Understanding the specific legal protections available in each country is crucial for individuals seeking nationality.
Moreover, the principle of non-discrimination ensures that individuals cannot be denied nationality based on race, gender, or religion. While this principle is upheld in many international laws, enforcement can vary, creating disparities in how nationality rights are realized.
Nationality versus citizenship: A closer look
Citizenship signifies a full set of rights granted to individuals, including voting, running for office, and receiving protection from the state. Nationality, on the other hand, may not confer all these rights, particularly in cases where individuals are nationals but not citizens due to their legal status.
Understanding the legal implications of different statuses is essential, especially when completing nationality details of a form. For instance, an individual may have to navigate different pathways or fulfill distinct obligations based on whether they are applying from citizenship or just nationality.
Nationality in context
Historically, nationality has evolved dramatically, reflecting changes in political landscapes and power dynamics over time. Today, nationality shapes cultural identity, influencing not just individual lives but also the collective ethos of societies. It plays a critical role in the context of globalization, where people frequently migrate, leading to complex questions about multiculturalism and national identity.
As globalization progresses, the meaning of nationality is being redefined, challenging traditional notions and opening discussions around inclusivity and belonging.
Nationality versus ethnicity: Unpacking the terms
While nationality relates to the legal affiliation with a state, ethnicity pertains to cultural identity, including shared language, traditions, and history. Understanding this distinction is vital, especially in discussions about national rights and representation.
Ethnic nationalism promotes the idea of a nation defined by a shared ethnicity, whereas civic nationalism advocates for a political construct based on citizenship. These differing perspectives affect how national rights are approached in various countries.
Nationality versus national identity
National identity encompasses the shared values, beliefs, and experiences of individuals in a nation. While nationality is a formal status, national identity entails deeper connections and emotional ties to a nation's land and people. This interplay shapes societal impacts, influencing policies and community engagement.
As individuals navigate nationality-related forms, understanding this relationship can provide insights into the personal significance of obtaining a national status and the responsibilities that come with it.
Dual nationality: Opportunities and challenges
Dual nationality, where individuals hold citizenship in two countries, is increasingly recognized in today's interconnected world. This status offers numerous benefits, such as access to two labor markets, educational opportunities, and the ability to travel freely between countries.
However, it comes with challenges, including legal obligations such as taxation and potential conflict of laws. Individuals exploring dual nationality should understand their rights and responsibilities to navigate their unique legal landscapes effectively.
Statelessness and its implications
Statelessness occurs when an individual is not considered a national by any state. This condition, often resulting from conflict, discrimination, or administrative oversight, has severe repercussions. Stateless individuals lack access to basic rights, including education, healthcare, and legal protection, leaving them vulnerable.
Global efforts to combat statelessness include international treaties and advocacy programs aimed at ensuring everyone has a nationality. Raising awareness about this issue is vital as it encourages nations to create inclusive policies that promote the right to nationality.
Conferment of nationality
The process of granting or conferring nationality involves specific procedures and documentation requirements that vary by country. Common steps include applications, interviews, and proof of residency or familial connections. Understanding these processes is essential when filling out nationality details of a form.
Challenges such as bureaucratic delays, legal ambiguities, or financial costs can hinder the conferment process. Ensuring that individuals have access to comprehensive information can assist in overcoming these obstacles.
Regional perspectives on nationality
Nationality laws differ significantly across regions. In Africa, for example, some countries base nationality on ethnic affiliation, leading to complex legal challenges. In contrast, in the Americas, nationality laws are often more straightforward, rooted in jus soli principles.
Asian countries may have restrictions on dual nationality and extensive requirements for naturalization. In Europe, nationality laws are increasingly adopting inclusive policies to accommodate migration. Oceania reflects a mix of practices, often shaped by both Indigenous rights and colonial histories. Understanding these regional nuances can be beneficial when completing nationality-related forms.
Practical steps for completing nationality-related forms
When filling out nationality forms, several key sections typically require attention. These include personal information, proof of identity, and documentation related to the applicant’s birthplace or parental nationality. Each section must be completed with accuracy to avoid delays in processing.
Crucial documentations often required include birth certificates, passports, and proof of residency. It's advisable to double-check each document for completeness. Tips for ensuring accuracy include thorough reviews of completed forms and consulting available guidelines.
Tools for managing nationality documentation
In today’s digital age, managing nationality forms has become more streamlined thanks to technological solutions. Services like pdfFiller provide powerful tools for editing, signing, and managing documents smoothly from a single platform. Users can conveniently create, fill out, and share forms online, ensuring their nationality documentation is always accessible.
Cloud-based solutions enhance document management efficiency, allowing users to store and retrieve necessary forms effortlessly. Using features like electronic signatures or collaboration tools can facilitate smoother processes for teams navigating nationality-related paperwork.
FAQs about nationality forms
Individuals dealing with nationality forms often have several questions, such as 'What documents do I need?' or 'How long does the process take?' These inquiries reflect common concerns about the complexities involved in nationality applications.
Additionally, misconceptions about nationality rights may arise, such as the belief that only children of citizens can claim nationality. Resources are available to clarify these misconceptions and help individuals navigate their nationality journey more effectively.






For pdfFiller’s FAQs
Below is a list of the most common customer questions. If you can’t find an answer to your question, please don’t hesitate to reach out to us.
How do I execute nationality details of a online?
Can I create an eSignature for the nationality details of a in Gmail?
Can I edit nationality details of a on an Android device?
What is nationality details of a?
Who is required to file nationality details of a?
How to fill out nationality details of a?
What is the purpose of nationality details of a?
What information must be reported on nationality details of a?
pdfFiller is an end-to-end solution for managing, creating, and editing documents and forms in the cloud. Save time and hassle by preparing your tax forms online.















