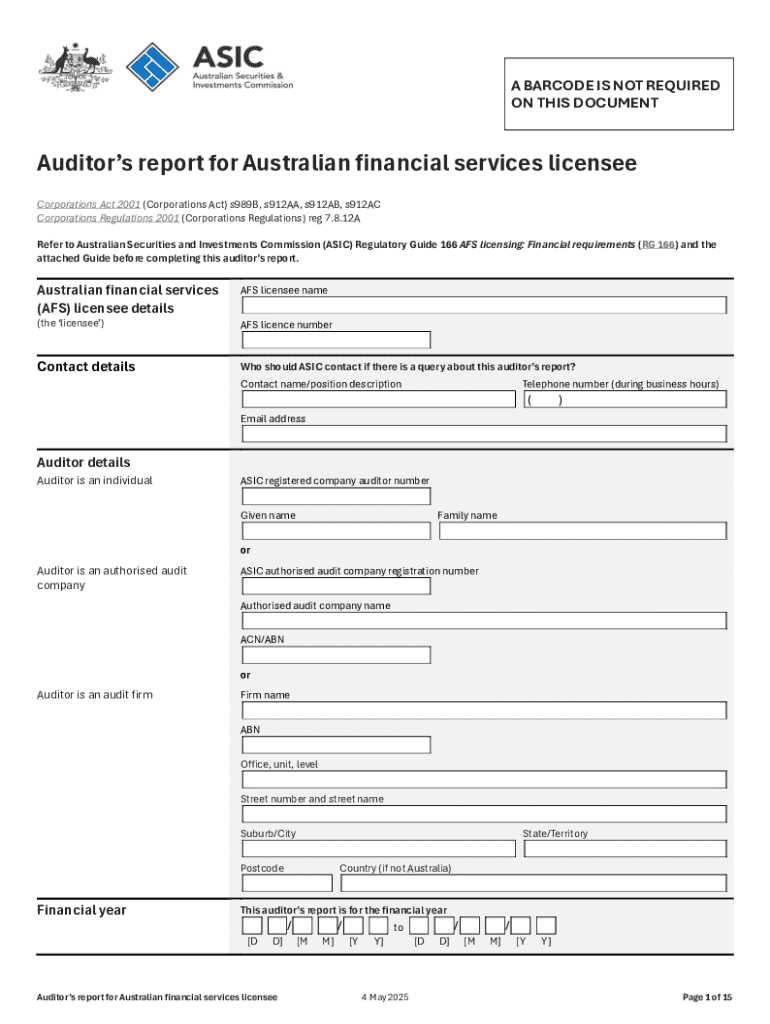
Get the free Auditor's Report for Australian Financial Services Licensee
Get, Create, Make and Sign auditors report for australian



How to edit auditors report for australian online
Uncompromising security for your PDF editing and eSignature needs
How to fill out auditors report for australian

How to fill out auditors report for australian
Who needs auditors report for australian?
Auditors report for Australian form: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the auditor's report
An auditor's report is a formal opinion or disclaimer provided by an auditor regarding the financial statements of an entity. This document is crucial as it signifies the auditor's assessment of the fairness and accuracy of financial information presented by a company. The primary purpose of an auditor’s report is to add credibility to the financial reports, enhancing stakeholders' trust in the organization's financial health. It plays a vital role in financial transparency, ensuring that stakeholders, including investors, management, and regulatory bodies, receive a reliable insight into the company's operations.
The audit process typically involves several stages: planning, execution, and reporting. During the planning phase, auditors identify key areas of risk and prepare a strategy to address these risks effectively. In the execution phase, auditors gather evidence to support their opinions, employing various techniques such as testing transactions and evaluating internal controls. Finally, the results of the audit culminate in the auditor's report, which is delivered to relevant parties.
Composition of an auditor’s report
The structure of an auditor’s report generally adheres to standard components that ensure clarity and compliance with regulations. The main elements of an auditor’s report include:
In Australia, these components are influenced by several auditing standards set forth by regulatory bodies such as the Auditing and Assurance Standards Board (AUASB), ensuring uniformity and reliability across auditor reports.
Types of auditor's reports in Australia
In the realm of auditor reports, opinions can vary significantly based on the findings of the audit. The most common types of auditor opinions in Australia include:
Understanding the context in which these opinions are delivered is crucial for stakeholders, as it shapes the financial narrative of the entity.
Key responsibilities of auditors
Auditors carry significant responsibilities throughout the audit process. Ethical considerations are paramount, demanding independence to ensure objectivity is maintained. Under the Australian Auditing Standards, auditors are accountable for assessing financial statements against established legal frameworks. Their role isn't limited to merely filling a compliance requirement; it encompasses a thorough evaluation of the internal controls and operational effectiveness of companies.
An auditor must maintain professional skepticism throughout the audit, verifying assumptions and information before rendering an opinion. This duty to remain impartial is crucial as it influences the integrity of the auditor’s report and, by extension, trust in the financial reporting process.
Understanding the Australian auditing standards
The Australian auditing landscape is governed by a series of standards designed to uphold the integrity and quality of audits. The main body overseeing these standards is the AUASB, which aligns Australian standards with international counterparts, although there are unique local requirements to consider. Key standards include those that dictate the fundamental principles of auditing, such as ASA 200 (Overall Objectives of the Independent Auditor) and ASA 315 (Identifying and Assessing the Risks of Material Misstatement).
Recent changes to these standards often respond to evolving market conditions and stakeholder expectations. For example, advancements in technology and data analysis have prompted updates on risk assessment methodologies and reporting formats. Understanding these ongoing amendments is critical for both auditors and the entities they serve to navigate the complexities of compliance effectively.
Auditing standards under the Corporations Act 2001
The Corporations Act 2001 establishes the legal framework governing financial reporting and auditing in Australia. One critical aspect is Section 336, which spells out the need for financial reports to comply with applicable accounting standards and provide a true and fair view of a corporation's financial position. This section lays the groundwork for the requirements imposed on auditors regarding what their reports must encompass.
Different types of companies, whether small or large, face varied reporting obligations under this legislation. Large entities typically require a more comprehensive audit process compared to smaller businesses, reflecting the complexity of their financial operations and the level of scrutiny they attract from regulators and the public.
Documenting the auditor’s work
A fundamental aspect of the auditing process is the documentation of the auditor’s work. This documentation must be thorough, supporting each conclusion drawn and ensuring compliance with auditing standards. Essential requirements for documentation include clarity and relevance to the financial statements being audited.
To compile solid audit evidence, auditors often utilize various techniques, including sampling, analytical procedures, and inquiries. All documentation should demonstrate the completeness of the audit process, protecting both the auditor and the entity in the face of future scrutiny or challenges. Proper documentation not only serves as a legal safeguard but also enhances the overall credibility of the audit.
Key considerations in issuing an auditor’s report
Several considerations impact the issuance of an auditor’s report. Evaluating materiality is a cornerstone of the audit process, as it helps determine the significance of specific financial information in influencing the decisions of users. The auditor’s assessment of materiality affects the scope of the audit and the nature of the testing performed.
Additionally, auditors must gauge audit risk and the effectiveness of internal controls before finalizing their opinion. Communication with governance and stakeholders is crucial, as it ensures alignment on expectations and provides insight into any concerns detected during the audit, solidifying trust and clarity in the audit process.
Challenges auditors face in reporting
In preparing auditor’s reports, auditors often encounter various challenges. Common pitfalls include misunderstanding complex regulations or failing to adequately assess risks within the financial statements. As the regulatory environment becomes increasingly intricate, auditors must continuously adapt their strategies to remain compliant.
Furthermore, the rapid advancement of technology is reshaping audit practices. While technology offers powerful tools for efficiency and analysis, it also introduces new challenges related to data security and transparency. Hence, auditors must navigate these disruptions while maintaining high-quality reporting standards.
Tools for creating an auditor’s report
Modern auditors can utilize various tools to streamline the creation of auditor’s reports. One notable option is pdfFiller, a versatile cloud-based platform that simplifies document management. pdfFiller offers functionalities such as interactive document creation, easy editing, digital signing, and seamless collaboration, all crucial for creating professional auditor’s reports.
Additionally, cloud-based solutions allow for the convenient storage and retrieval of documents, ensuring that auditors can access necessary files from anywhere. These features significantly enhance efficiency and accuracy in the reporting process, supporting auditors in meeting their deadlines while upholding quality.
Enhancing accessibility of the auditor's report
The accessibility of an auditor’s report is critical, not only for regulatory compliance but also for stakeholder engagement. Using clear, concise language in reports allows a broader audience to understand the findings without specialized financial knowledge. Effectively communicating results involves tailoring presentations to meet stakeholder needs and ensuring relevant information is prioritized.
Incorporating digital tools to distribute reports can also enhance accessibility, as stakeholders increasingly rely on technology to consume information. By optimizing reports for digital platforms, auditors can improve engagement and foster greater transparency between companies and their financial stakeholders.
Best practices for the preparation and review of auditor’s reports
To ensure the success of auditor’s reports, established best practices should be followed throughout each stage of preparation and review. A systematic approach encompasses a step-by-step process, beginning from comprehending the scope of the audit to the final issuance of the report. Auditors should engage in thorough reviews and quality control measures, ensuring reports are not only accurate but also reflect the findings comprehensively.
Additionally, involving stakeholders in the review process can enhance the integrity and acceptance of the report. Regular updates and opportunities for feedback allow auditors to address concerns proactively and maintain relationships grounded in trust and transparency.
Future trends in auditing and reporting
The auditing landscape continues to evolve, influenced by shifting standards and expectations from stakeholders. Increasing regulatory scrutiny is placing higher demands on auditors to be more thorough and transparent in their reporting. Technology’s role is also expanding, with tools like advanced data analytics, artificial intelligence, and machine learning reshaping how audits are performed.
As these trends materialize, the future of auditor’s reporting in Australia will likely see increased automation, enhancing efficiencies while providing deeper insights into financial operations. Auditors who embrace these innovations will be better equipped to navigate the complexities inherent in financial reporting.
Frequently asked questions about auditor's reports
Understanding auditor's reports can often raise questions, especially for those unfamiliar with auditing practices. Common questions include clarifications about the report's structure, the meaning of different opinions, and the audit process itself. For instance, individuals may wonder about the implications of a qualified opinion versus an unmodified opinion and how these should influence decision-making.
Additionally, many seek guidance on how to interpret findings in relation to their specific circumstances. Providing clear, actionable responses to these inquiries aligns with the goal of enhancing transparency and usability of auditor’s reports, ensuring stakeholders can confidently engage with financial documentation.






For pdfFiller’s FAQs
Below is a list of the most common customer questions. If you can’t find an answer to your question, please don’t hesitate to reach out to us.
How can I edit auditors report for australian from Google Drive?
How do I edit auditors report for australian online?
Can I create an electronic signature for signing my auditors report for australian in Gmail?
What is auditors report for australian?
Who is required to file auditors report for australian?
How to fill out auditors report for australian?
What is the purpose of auditors report for australian?
What information must be reported on auditors report for australian?
pdfFiller is an end-to-end solution for managing, creating, and editing documents and forms in the cloud. Save time and hassle by preparing your tax forms online.






















