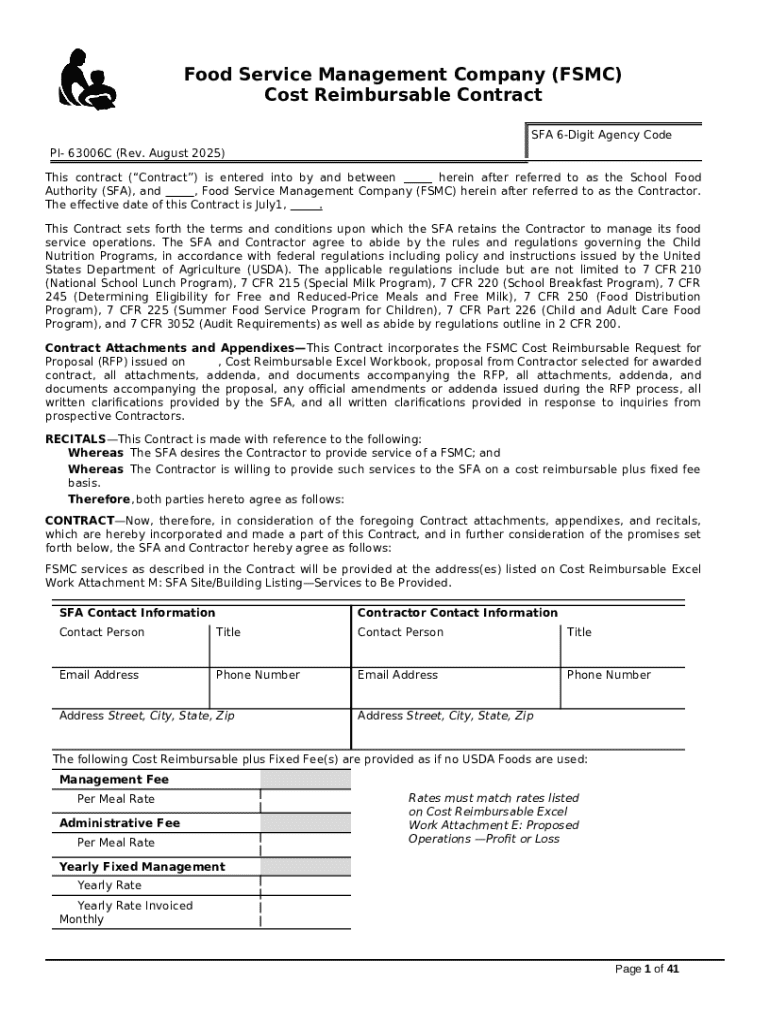
Understanding the Cost Reimbursable Contract Form
Understanding cost reimbursable contracts
A cost reimbursable contract is a type of agreement where the contractor is paid for their incurred expenses, plus an additional amount for profit. This form of contract is particularly advantageous when the full scope of work cannot be defined at the outset, allowing flexibility to adjust as the project evolves.
Key characteristics of cost reimbursable contracts include the reimbursement of actual costs and an understanding of various expense categories. Here are some features central to this type of contract:
Cost reimbursement basis: Payments are made based on actual costs incurred.
Types of reimbursable expenses: Can include labor, materials, and overhead costs.
When to use a cost reimbursable contract
Cost reimbursable contracts are ideal in situations where project complexity demands flexibility. They adapt well to environments where risks and uncertainties prevail, ensuring that costs related to unforeseen circumstances are adequately managed. Examples of ideal scenarios include research and development projects, and projects where the final deliverables and scope are evolving.
In contrast to fixed-price contracts, which set a predetermined price, cost reimbursable contracts focus on covering the actual expenses incurred. This comparison highlights several project-specific applications, particularly in industries like construction, IT, and government contracts, where precise scope cannot be established upfront.
Essential components of a cost reimbursable contract
A well-structured cost reimbursable contract lays a strong foundation for project success. Critical components to include are a clear scope of work, which outlines what is expected of the contractor, and cost baselines, which provide reference points for budgeting. Establishing allowable costs is essential for clarifying what can be reimbursed; this typically includes labor costs, materials, and necessary overheads.
Clear scope of work: Precise definitions of tasks ensure that all parties understand expectations.
Cost baselines and estimates: Establishing what is expected helps manage project budgets effectively.
Types of allowable costs: Clarity on reimbursable types aids financial transparency.
Developing a cost reimbursable contract form
Drafting a cost reimbursable contract form involves several systematic steps. The first step is to identify all parties involved, ensuring clarity on roles and responsibilities from the outset. The next step is outlining the scope of work, which should detail specific deliverables and timelines.
Next, specify payment terms, including how and when reimbursements are processed. Detailing reporting and documentation requirements is also critical to ensure compliance and effective tracking of costs. Utilizing interactive tools can simplify this process, allowing for efficient completion of the form.
Identify parties involved: Clearly define the roles of each stakeholder.
Outline the scope of work: Detail deliverables and timelines for clarity.
Specify payment terms: State how reimbursements will be processed.
Detail reporting and documentation requirements: Set guidelines for financial transparency.
Types of cost reimbursable contracts
Several types of cost reimbursable contracts exist, each tailored to specific needs and project parameters. The Cost-Plus Fixed Fee (CPFF) is one of the most common, providing a set fee in addition to reimbursed costs. In contrast, the Cost-Plus Incentive Fee (CPIF) rewards efficiency, offering a bonus for keeping costs below a predetermined threshold.
Another variation is the Cost-Plus Award Fee (CPAF), designed to motivate contractors based on performance, while the Cost-Plus Percentage of Costs (CPPC) compensates contractors based on a percentage of total costs. Each type has its advantages and disadvantages, impacting how risks and rewards are allocated.
Cost-Plus Fixed Fee (CPFF): Provides a guaranteed fee.
Cost-Plus Incentive Fee (CPIF): Encourages cost efficiency.
Cost-Plus Award Fee (CPAF): Incentivizes high performance.
Cost-Plus Percentage of Costs (CPPC): Compensates based on a percentage of total costs.
Financial management within cost reimbursable contracts
Effective financial management is crucial when handling cost reimbursable contracts. Establishing clear budgets enables project teams to monitor expenses closely and ensure they adhere to agreed-upon financial frameworks. Regular expense tracking is necessary, relying on real-time reporting to detect discrepancies or potential overruns early on.
Reporting requirements should be well-defined, ensuring that stakeholders have access to timely and accurate financial data to inform decision-making. An organized approach to financial management not only allows for project adjustments when needed but also enhances accountability among all involved parties.
Compliance and regulatory considerations
Compliance with regulatory frameworks is non-negotiable in cost reimbursable contracts. In the U.S., the Federal Acquisition Regulation (FAR) governs these agreements, establishing guidelines for managing contract costs and ensuring fairness in public procurement. Familiarity with FAR Subpart 16.3 is essential for compliance, especially for government contractors.
Common pitfalls include neglecting to document costs properly or misunderstanding the limits on allowable expenses. Awareness of these guidelines and maintaining diligent records is vital in protecting all parties' interests and avoiding costly disputes.
Clauses and terms to include in the contract
Incorporating precise clauses within a cost reimbursable contract can prevent misinterpretations and disputes. Essential clauses include termination clauses, which outline conditions for ending the contract, and change management processes that allow for adaptability in the face of project changes.
Another crucial aspect is specifying a dispute resolution mechanism, providing a recourse for conflict. By prioritizing specificity in the language used for these clauses, both parties can establish mutual understanding and a clear path for any unforeseen circumstances.
Termination clauses: Define conditions under which the contract can be ended.
Change management processes: Establish how adjustments to the scope are handled.
Dispute resolution: Set clear procedures for resolving conflicts.
Practical examples and case studies
Examining real-world applications of cost reimbursable contracts can provide invaluable insights. One illustrative example is a large-scale construction project where initial estimates fluctuated due to unforeseen site conditions. A cost reimbursable contract allowed the contractor to efficiently manage these unexpected expenses, keeping the project on track.
A successful case study might explore how a project team effectively utilized a CPFF contract to deliver high-quality results by remaining transparent about cost management. The emphasis on documentation and clear communication fostered an environment where lessons were learned and a project was completed under budget and ahead of schedule.
Creating instant reports and documentation
In today’s fast-paced project environments, having the ability to generate immediate reports is invaluable. When working with cost reimbursable contracts, look for document management solutions that allow for real-time report generation and comprehensive tracking of expenses. Interactive tools can significantly bridge the gap between data entry and reporting, enabling teams to maintain accurate records effortlessly.
Maintaining detailed documentation is crucial, as this supports compliance and financial oversight. Thanks to the functionalities provided by platforms like pdfFiller, managing documentation becomes streamlined, promoting efficiency across all project stages.
Advanced management strategies
Advanced approaches can significantly enhance the efficacy of cost reimbursable contracts. Tips such as fostering effective collaboration among teams will streamline communication, ultimately reducing the risk of misunderstandings related to cost and scope. Cloud-based platforms like pdfFiller enhance accessibility; users can quickly access documents from anywhere, elevating project management capabilities.
Integrating tools specifically designed for agile communication maintains momentum, especially regarding fast-paced projects. These strategies not only enhance the efficiency of contract management but also encourage a culture of transparency and collaboration among all parties involved.
Frequently asked questions (FAQs)
Cost reimbursable contracts often raise numerous queries. Common questions include how to determine what expenses are reimbursable and the implications of changes in project scope. Answering these queries involves clarifying the nuances of contract language and compliance requirements.
Addressing misconceptions about cost risk and overall management can foster clearer expectations. Strategies for overcoming common challenges include prioritizing documentation and transparent communication, which are essential to the successful execution of cost reimbursable agreements.