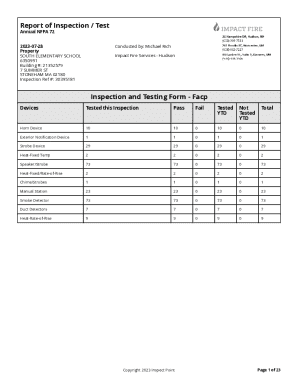
Get the free Inbreeding and selection on the X chromosome in domestic ...
Get, Create, Make and Sign inbreeding and selection on

How to edit inbreeding and selection on online
Uncompromising security for your PDF editing and eSignature needs
How to fill out inbreeding and selection on
How to fill out inbreeding and selection on
Who needs inbreeding and selection on?
Inbreeding and selection on form: A comprehensive guide
Understanding inbreeding in farm animals
Inbreeding, defined as the mating of individuals who are closely related genetically, plays a critical role in the genetics of farm animals. It often occurs within a breed, enhancing certain characteristics but simultaneously raising concerns about health and genetic diversity. Historically, selective breeding programs have utilized inbreeding to stabilize desirable traits, such as milk production in dairy cows or size in beef cattle. However, the consequences can extend beyond mere traits, impacting the overall genetic health of animal populations.
The importance of studying inbreeding cannot be overstated; it directly influences genetic diversity, health, and agricultural productivity. With modern farming demanding high-quality livestock, understanding inbreeding's effects becomes essential for sustainable livestock management. Issues like inbreeding depression—reduced fitness in a given population due to breeding from closely related individuals—can result in severe repercussions, making knowledge of inbreeding practices vital for farmers and breeders.
The biological relationships between animals
To grasp the concept of inbreeding, one must first recognize the genetic connections among animals. These relationships fluctuate in form, with types including parent-offspring and sibling relationships. A fundamental tool in this understanding is the Punnett square, which illustrates the probability of inheriting certain traits based on genetic combinations. For breeders, these connections are essential in predicting how desired traits will be passed on to progeny.
Moreover, evaluating genetic relationships has become more efficient with advanced tools and technologies. Modern software can analyze animal genetics, allowing breeders to make informed decisions rapidly. Resources such as genomic markers provide insights into inheritance patterns, making it easier for individuals managing animal breeding programs to select appropriate mates based on their genetic backgrounds.
Measurement of degree of biological relationship
The coefficient of relationship quantifies how closely related two individuals are, which is crucial in animal breeding. This coefficient ranges from 0 (no relation) to 1 (identical twins), providing context for selecting mates within a breeding program. Understanding this measure can greatly affect the genetic diversity within livestock populations and help breeders make decisions that either preserve or diversify genetic traits.
Several methods exist to calculate genetic relationships, including statistical models and software tools that analyze pedigree data. For instance, tools may employ algorithms that assess generations of lineage, thus creating a robust genetic profile for each animal. Practical exercises along with these calculations can provide hands-on experience for breeders, ensuring they understand and apply this knowledge effectively in their selection processes.
Usefulness of coefficient of relationship information
The coefficient of relationship serves a crucial function in breeding programs, directly impacting breeding decisions and overall success. This metric guides breeders in selecting the most compatible mates to enhance favorable traits while minimizing the risks of inbreeding depression. In cases where genetic health is monitored, case studies illustrate effective use of this data to improve livestock outputs by maintaining diversity within breeding populations.
Maintaining genetic health is paramount to livestock sustainability. Implementing strategies such as rotating breeding pairs and avoiding closely related individuals in mating selections can mitigate genetic homogenization, ensuring that populations remain robust and capable of adapting to environmental changes.
Measurement of the degree of inbreeding
Inbreeding coefficients show the probability that two alleles at a locus in an individual are identical by descent. These coefficients can be calculated based on pedigree data and indicate the level of inbreeding in a population. For livestock, understanding these coefficients provides insights into potential health issues arising from selected inbreeding strategies.
Interpreting inbreeding levels is critical, as varying levels can significantly impact animal health. For instance, coefficients above 0.10 often signal a heightened risk of inherited disorders and reduced fertility rates. Providing breeders with clear guidance on acceptable inbreeding levels helps them establish breeding protocols that safeguard animal welfare and maintain productivity.
Genetic consequences of inbreeding
Inbreeding has a well-documented effect on the physical traits of animals, particularly when it comes to defined aesthetic features or productive capabilities. Specific genes within a breed can become fixed, leading to a narrow phenotypic range, which might be desirable in some cases but detrimental in others. Understanding these impacts helps breeders select traits judiciously.
Health consequences frequently associated with inbreeding include genetic predispositions to diseases, reduced immune function, and lower fertility rates. For instance, breeds with high inbreeding coefficients often exhibit traits such as poor growth rates, increased vulnerability to infections, and overall reduced lifespans. Recognizing these patterns allows breeders to balance selection for desirable traits while ensuring genetic health.
Reasons for inbreeding in animal breeding
Deliberate inbreeding programs occur when breeders aim to enhance specific traits, aiming to produce offspring with high-quality characteristics, such as rapid growth rates or increased milk production. In some instances, a controlled, inbreeding strategy may yield immediate benefits for livestock performance and economic viability.
However, uncontrolled inbreeding poses significant risks. Ignoring genetic diversity often leads to a decrease in the general health of animal populations, increasing vulnerability to diseases and decreasing adaptability to environmental conditions. Ensuring that inbreeding is done with a clear focus on genetic diversity and health is crucial to sustainable animal husbandry.
Selection on form in inbreeding practices
Selection based on physical form is pivotal in breeding programs, as specific traits can significantly influence productivity. Breeders often focus on selecting for certain features like size, muscle definition, or even specific adaptations to climate. However, while focusing on desirable physical characteristics, the challenges of maintaining genetic health must not be overlooked.
Achieving a balance between form and genetic health can be accomplished through strategies such as inclusive selective breeding, where traits are evaluated holistically, encompassing both phenotypic appearance and genetic diversity metrics. This holistic approach ensures desired traits are enhanced while safeguarding the long-term viability of breed populations.
Practical tools and approaches for managing inbreeding
Today, interactive tools designed for managing breeding records can significantly streamline the breeding process. Platforms like pdfFiller empower users to document breeding plans efficiently, enabling effective tracking of genetic information, relationships, and inbreeding coefficients. Utilizing these tools not only simplifies documentation but also enhances decision-making in breeding choices.
By following a structured approach using tools like pdfFiller, individuals can access all relevant documents for managing breeding programs from anywhere, ensuring informed decision-making in the context of inbreeding and selection on form.
Summary of key concepts
Examining the multifaceted nature of inbreeding and selection on form reveals critical insights for livestock management. Understanding the genetic implications of inbreeding, along with relevant measures like coefficients, informs responsible breeding practices while optimizing genetic diversity. Tools and resources offer significant support to breeders, equipping them with the knowledge necessary to navigate the complexities of modern animal husbandry.
In conclusion, the careful interplay between genetic management and physical trait enhancement shapes the future of animal breeding. Utilizing modern tools and maintaining a focus on genetic health ensures that breeders can achieve success across generations, creating a sustainable approach to livestock production.






For pdfFiller’s FAQs
Below is a list of the most common customer questions. If you can’t find an answer to your question, please don’t hesitate to reach out to us.
How do I execute inbreeding and selection on online?
How do I make edits in inbreeding and selection on without leaving Chrome?
How do I complete inbreeding and selection on on an Android device?
What is inbreeding and selection on?
Who is required to file inbreeding and selection on?
How to fill out inbreeding and selection on?
What is the purpose of inbreeding and selection on?
What information must be reported on inbreeding and selection on?
pdfFiller is an end-to-end solution for managing, creating, and editing documents and forms in the cloud. Save time and hassle by preparing your tax forms online.