Get the free Fiduciary Tax FAQs - Missouri Department of Revenue - dor mo
Get, Create, Make and Sign fiduciary tax faqs



Editing fiduciary tax faqs online
Uncompromising security for your PDF editing and eSignature needs
How to fill out fiduciary tax faqs

How to fill out fiduciary tax faqs
Who needs fiduciary tax faqs?
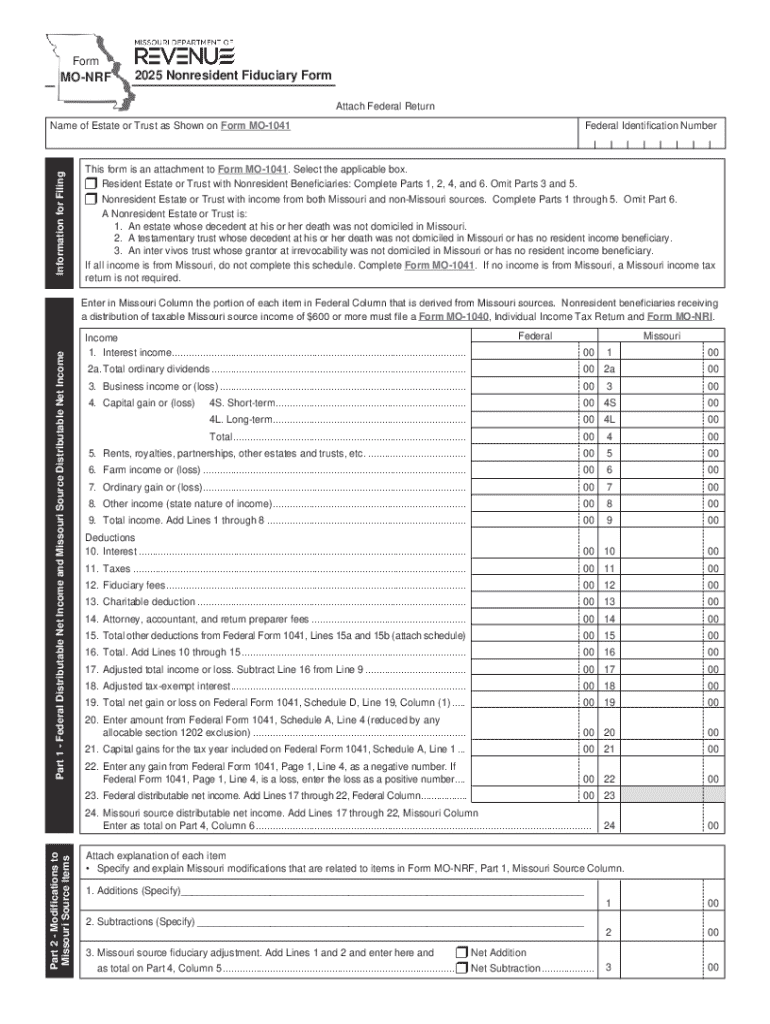
Comprehensive Guide to Fiduciary Tax FAQs Form
Understanding fiduciary tax
Fiduciary tax plays a pivotal role in the management of estates and trusts, where a fiduciary is responsible for handling the tax affairs of the estate or trust in accordance with the law. This type of tax ensures that any income generated from estate or trust assets is accurately reported and taxed at the appropriate rate, thus fulfilling legal obligations and protecting the interests of beneficiaries.
A fiduciary must understand key terminology associated with fiduciary tax, as clear definitions lay the groundwork for proper management. Terms such as fiduciary, beneficiary, estate, and trust are essential to comprehend the responsibilities and expectations placed on those managing such entities. The fiduciary's role in tax filings is crucial; they must ensure that all relevant income—such as interest, dividends, and rental income—is reported accurately, while also tracking allowable deductions.
Fiduciary tax and its implications
Understanding who needs to file fiduciary taxes is foundational for compliance. Generally, individuals acting as fiduciaries—trustees, executors, or personal representatives—are responsible for filing tax returns for estates and trusts. Entities such as trusts and estates that generate income during the taxable year also fall under this category, necessitating the timely filing of Form 1041, U.S. Income Tax Return for Estates and Trusts.
There are several misconceptions about fiduciary tax that can cause confusion. A common misunderstanding is the belief that fiduciary tax is synonymous with personal income tax. In reality, fiduciary tax applies to the income generated by an estate or trust, distinct from an individual's personal income. Additionally, many are unaware of how to accurately compute taxable income for estates and trusts, which can differ significantly from personal income calculations, leading to potential issues with compliance.
The fiduciary tax filing process
The fiduciary tax filing process begins with an understanding of the filing requirements. Form 1041 is essential for estates and trusts that have gross income over a specified threshold. This form requires clear documentation of the estate or trust’s income sources, deductions, and distributions to beneficiaries. Educational resources are available to guide fiduciaries through the process, ensuring compliance with IRS regulations.
Completing Form 1041 involves several key steps: First, collect necessary documents such as bank statements, investment income records, and any relevant deductions. Next, accurately input income sources, including dividends and interest earned. It's also crucial to report distributions made to beneficiaries on Schedule K-1, ensuring each recipient receives their portion in compliance with tax regulations. Common pitfalls include failing to report all income or miscalculating deductions, which can lead to costly errors and penalties.
State-specific fiduciary tax considerations
Fiduciary tax laws can vary significantly between states, reflecting each state’s unique legal framework. For example, some states impose taxes on fiduciary income that might not be taxable at the federal level, while others may have different reporting requirements and thresholds. Understanding state-specific regulations is essential for fiduciaries to ensure compliance and avoid unexpected tax liabilities.
In states like California, fiduciary taxes must be filed in conjunction with state-specific forms, affecting how income from estates and trusts is reported. Conversely, states such as Florida do not impose a state income tax, which simplifies the filing process for fiduciaries operating there. Furthermore, managing fiduciary tax obligations across multiple states can present challenges. It is advisable to keep meticulous records and consult a tax professional to navigate these complexities.
Managing estates and trusts for tax efficiency
Tax efficiency is essential for fiduciaries overseeing estates and trusts. Best practices include maintaining robust record-keeping systems that document income and distributions. Keeping detailed records not only aids in accurate tax reporting but also ensures transparency for beneficiaries, which is crucial for maintaining trust and clarity. Tracking income and distributions meticulously can also highlight opportunities for tax optimization.
Tax planning strategies are critical to minimizing fiduciary tax liability. For instance, exploring the timing of distributions and understanding the tax implications can lower overall tax burdens. Consider asset allocation strategies that might enhance tax efficiency or employing tax-exempt investments within trusts. Being proactive in tax planning can significantly impact the net value passed on to beneficiaries, preserving the estate's wealth effectively.
Resources for fiduciaries
For fiduciaries navigating the complexities of fiduciary tax, several resources can prove invaluable. Tools and templates available on pdfFiller empower users to create, edit, and manage fiduciary tax-related documents efficiently. From interactive forms to digital signing solutions, pdfFiller facilitates seamless document management, allowing fiduciaries to focus more on compliance and less on paperwork.
Learning opportunities such as webinars, forums, and guides provide insights into best practices for fiduciaries. Engaging with these resources can enhance understanding of fiduciary responsibilities and tax obligations. However, recognizing when to seek professional help is also key. Consultations with tax professionals or legal counsel specializing in estate planning are crucial when complexities arise or when significant tax implications are at stake.
Frequently asked questions
Several common questions arise regarding fiduciary tax that can help clarify the overall process. For instance, many fiduciaries ask about the distinction between taxable and non-taxable income for trusts. It’s vital to understand that while most income generated by an estate or trust is taxable, certain exemptions may apply depending on the nature of the income and state laws.
Additionally, fiduciaries may encounter issues such as mistakes on Form 1041 or questions about filing status. It’s advisable to conduct a thorough review of all submissions prior to filing. Should problems arise, developing a systematic troubleshooting approach can mitigate potential issues, ensuring compliance and accuracy. Being proactive in addressing these challenges can save time and resources down the line.






For pdfFiller’s FAQs
Below is a list of the most common customer questions. If you can’t find an answer to your question, please don’t hesitate to reach out to us.
How can I send fiduciary tax faqs for eSignature?
How do I make changes in fiduciary tax faqs?
Can I edit fiduciary tax faqs on an Android device?
What is fiduciary tax faqs?
Who is required to file fiduciary tax faqs?
How to fill out fiduciary tax faqs?
What is the purpose of fiduciary tax faqs?
What information must be reported on fiduciary tax faqs?
pdfFiller is an end-to-end solution for managing, creating, and editing documents and forms in the cloud. Save time and hassle by preparing your tax forms online.

























