How To Write A Budget Proposal For A Project
What is how to write a budget proposal for a project?
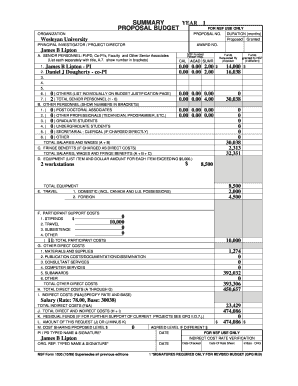
When creating a budget proposal for a project, it is essential to outline the costs associated with the project, including materials, labor, and any other expenses. The proposal should clearly define the scope of the project and provide a breakdown of the anticipated costs. It is crucial to be detail-oriented and realistic when estimating the budget for a project.
What are the types of how to write a budget proposal for a project?
There are several types of budget proposals that can be used when outlining the financial aspects of a project. Some common types include:
How to complete how to write a budget proposal for a project
Completing a budget proposal for a project involves several key steps to ensure accuracy and effectiveness. Here are some tips to help you complete a budget proposal successfully:
pdfFiller empowers users to create, edit, and share documents online. Offering unlimited fillable templates and powerful editing tools, pdfFiller is the only PDF editor users need to get their documents done.