Smith Chart - Page 2
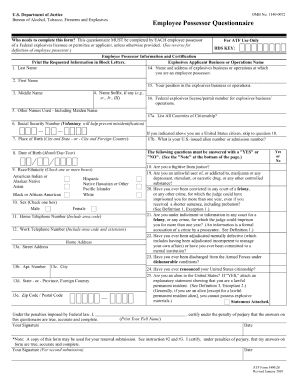
What is Smith Chart?
The Smith Chart is a graphical tool used in RF microwave engineering to assist with the analysis and design of transmission line circuits. It was invented by Phillip H. Smith in 1939 and has since become an indispensable tool for engineers working in the field. The Smith Chart allows engineers to easily visualize complex impedance values, match impedance between different components, and optimize the performance of transmission line circuits.
What are the types of Smith Chart?
There are mainly two types of Smith Charts: the Rectangular Smith Chart and the Polar Smith Chart. The Rectangular Smith Chart displays impedance values in terms of resistance and reactance, while the Polar Smith Chart represents impedance values in terms of magnitude and phase angle. Both types of Smith Charts offer their own advantages and are used depending on the specific requirements of the transmission line circuit being analyzed or designed.
How to complete Smith Chart
To complete a Smith Chart, follow these steps:
pdfFiller empowers users to create, edit, and share documents online. Offering unlimited fillable templates and powerful editing tools, pdfFiller is the only PDF editor users need to get their documents done.