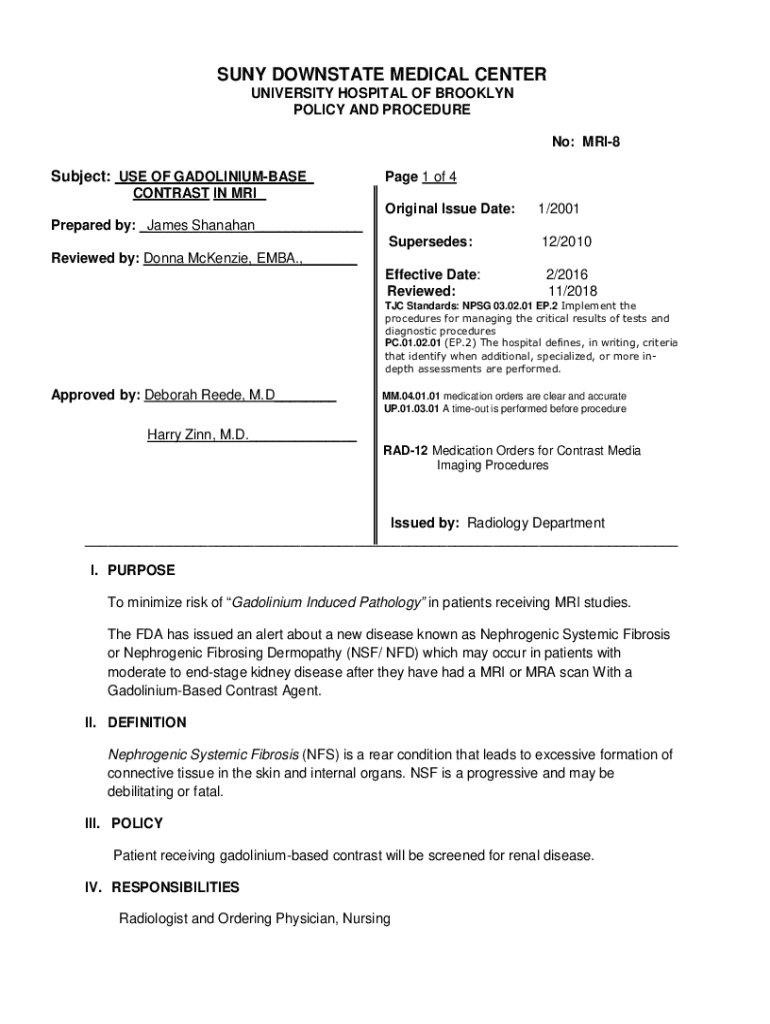
Get the free Mri-8 Use of Gadolinium-based Contrast in Mri
Get, Create, Make and Sign mri-8 use of gadolinium-based



How to edit mri-8 use of gadolinium-based online
Uncompromising security for your PDF editing and eSignature needs
How to fill out mri-8 use of gadolinium-based

How to fill out mri-8 use of gadolinium-based
Who needs mri-8 use of gadolinium-based?
MRI-8 use of gadolinium-based form: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding gadolinium-based contrast agents (GBCAs)
Gadolinium-based contrast agents (GBCAs) are specialized pharmaceutical formulations used in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to enhance the visibility of internal structures. These agents improve the differentiation of tissues based on their magnetic properties, making diagnoses more accurate. They are crucial for visualizing blood vessels, tumors, and any pathological changes within organs.
The primary types of GBCAs include linear and macrocyclic agents, categorized by their chemical structure. Linear agents are older and less stable, potentially leading to higher risks of gadolinium retention in the body, whereas macrocyclic agents have a more stable structure that mitigates this risk. Notable examples include Gadobutrol and Gadopentetate dimeglumine, widely used in clinical practice.
The mechanism of action revolves around gadolinium's paramagnetic properties. When GBCAs are injected into the body, they alter the relaxation times of nearby hydrogen atoms in the MRI scanner's magnetic field. This alteration results in improved contrast and clarity of the images captured, allowing healthcare professionals to assess conditions more effectively.
Indications for gadolinium use in MRI
GBCAs are indicated in various clinical scenarios, primarily when enhanced imaging is necessary to identify abnormalities. Common situations include evaluating tumors, assessing stroke risks, or examining the vascular system for anomalies. They are also employed in neurological evaluations to distinguish between healthy and diseased tissue in conditions such as multiple sclerosis.
By providing enhanced diagnostic imagery, Gadolinium usage significantly improves diagnostic accuracy. For instance, its role in detecting and characterizing brain lesions has transformed treatment approaches. In this way, GBCAs facilitate timely interventions, which are critical in conditions that necessitate sooner therapeutics.
Gadolinium administration guidelines
When administering GBCAs, several guidelines must be adhered to maintain patient safety and imaging efficacy. Dosage typically depends on the patient's age, weight, and the clinical indication. Generally, adult dosages range from 0.1 to 0.3 mmol/kg of body weight, adjusted for specific imaging needs.
Preparation for the MRI scan includes the patient's thorough medical history evaluation, particularly assessing for previous allergic reactions to contrast agents. Special populations such as children, pregnant women, and the elderly may require modifications in administration due to altered physiological responses or increased susceptibility to potential side effects.
Safety considerations and risk assessment
While GBCAs are generally safe, risks are associated with their use, particularly in patients with compromised renal function. Nephrogenic Systemic Fibrosis (NSF) is a severe condition linked to the use of gadolinium in patients with severe renal impairment. Furthermore, Gadolinium Deposition Disease (GDD) has emerged as a concern, involving various long-term effects due to gadolinium retention in the body.
Evaluating kidney function before administration is critical, primarily through the estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate (eGFR) calculation. Ensuring that eGFR is above the threshold for safe gadolinium administration is essential. Additionally, protocols must incorporate routine creatinine testing to manage patients' safety effectively.
Navigating the gadolinium administrative process
A well-structured process is integral when integrating GBCAs into MRI protocols. The initial step involves a thorough pre-imaging assessment. This includes a complete medical history review to identify any contraindications, allergies, or history of adverse reactions.
Following this, healthcare providers must be adept at gadolinium administration techniques, ensuring proper intravenous access and timely delivery of the contrast agent. Post-scan, patient care protocols include monitoring for any signs of discomfort or side effects, reinforcing the importance of patient education alongside consent, where patients are informed of the procedure, potential risks, and benefits.
Innovations and the future of gadolinium-enhanced imaging
The future of gadolinium-enhanced imaging is progressing rapidly, with innovations such as new contrast agents that aim to reduce associated risks. Emerging alternatives, like iron-based contrast agents and other non-gadolinium options, are being investigated for their safety and efficacy profile.
Artificial intelligence is also becoming integral in enhancing the safety of gadolinium use. AI’s evolving role in radiology can assist in real-time monitoring for adverse reactions while ensuring that only necessary contrast is administered based on the specific imaging requirements.
Interactive tools and resources on gadolinium use
Healthcare providers can improve patient safety and understanding through interactive tools available on websites like pdfFiller. Online risk assessment tools can gauge a patient's suitability for GBCA use, ensuring better patient outcomes.
Additionally, templates for documenting patient consent and educational materials can streamline the process of educating patients on gadolinium use. These tools promote transparency, allowing healthcare professionals to maintain open lines of communication with their patients.
Common questions and misconceptions about GBCAs
Patients often have concerns about gadolinium safety, fueled by misconceptions and media reports on its long-term effects. One common myth is that all GBCAs are unsafe. However, when used properly and in appropriate patients, these agents have been shown to be safe and effective.
Clearly educating patients about their specific type of GBCA, the procedures involved, and actual risk statistics is critical in alleviating fears. This engagement fosters a setting where patients can voice their concerns, leading to a more collaborative and reassuring experience.
Case studies and clinical outcomes
Recent studies showcase the efficacy of GBCAs in clinical outcomes. Research has demonstrated that utilizing gadolinium significantly enhances the detection rates of tumors, leading to timely interventions that improve patient prognosis.
Notably, one study indicated that patients with suspicious brain lesions showed improved diagnostic outcomes when gadolinium was used, reducing false-negative rates. Such evidence supports the integration of GBCAs into routine MRI protocols, given their capability to influence treatment strategies positively.
Practical advice for patients undergoing MRI with gadolinium
Preparing for an MRI with gadolinium includes understanding the requirements and what to expect. Patients should arrive at the facility well-hydrated and communicate any medications they are taking or previous reactions to contrast agents.
Encouraging open communication with healthcare providers helps in addressing any concerns or questions, ensuring that patients feel informed and comfortable with the procedure. Being fully prepared can enhance the overall experience and reduce anxiety associated with the scan.
Importance of continuous monitoring and research
Continuous research on gadolinium safety and efficacy is crucial, especially as new GBCAs enter the market. Ongoing studies will help us understand the long-term implications of gadolinium exposure, guiding best practices in its administration.
Healthcare institutions play a pivotal role in ensuring patient safety by adopting updated protocols and engaging in continuous education regarding the use of GBCAs. This commitment will promote safer imaging practices and improve overall patient outcomes.
Integrating gadolinium forms into workflow for healthcare providers
Streamlining administrative processes can significantly enhance the efficiency of using GBCAs in MRI workflows. Healthcare providers can leverage document creation solutions such as those offered by pdfFiller, enabling the seamless management of patient records related to gadolinium use.
Utilizing PDF tools to manage patient documents ensures that vital information is readily accessible, reducing the risks of miscommunication, improving documentation accuracy, and enhancing patient safety with gadolinium.
Patient-centric approaches to gadolinium administration
A patient-centric approach must be emphasized in gadolinium use, tailoring administration based on individual patient history and risk factors. This strategy enhances the safety and efficacy of imaging procedures by prioritizing patient needs and responses.
Encouraging shared decision-making in choosing to use gadolinium allows patients to feel more involved in their care, fostering trust and improving overall satisfaction with the imaging process. Effective communication bridges the gap between healthcare providers and patients, ensuring optimal outcomes.






For pdfFiller’s FAQs
Below is a list of the most common customer questions. If you can’t find an answer to your question, please don’t hesitate to reach out to us.
How do I make changes in mri-8 use of gadolinium-based?
Can I create an eSignature for the mri-8 use of gadolinium-based in Gmail?
How can I edit mri-8 use of gadolinium-based on a smartphone?
What is mri-8 use of gadolinium-based?
Who is required to file mri-8 use of gadolinium-based?
How to fill out mri-8 use of gadolinium-based?
What is the purpose of mri-8 use of gadolinium-based?
What information must be reported on mri-8 use of gadolinium-based?
pdfFiller is an end-to-end solution for managing, creating, and editing documents and forms in the cloud. Save time and hassle by preparing your tax forms online.















