Get the free Confidence Intervals for Population Mean: Videos & Practice ...
Get, Create, Make and Sign confidence intervals for population



How to edit confidence intervals for population online
Uncompromising security for your PDF editing and eSignature needs
How to fill out confidence intervals for population

How to fill out confidence intervals for population
Who needs confidence intervals for population?
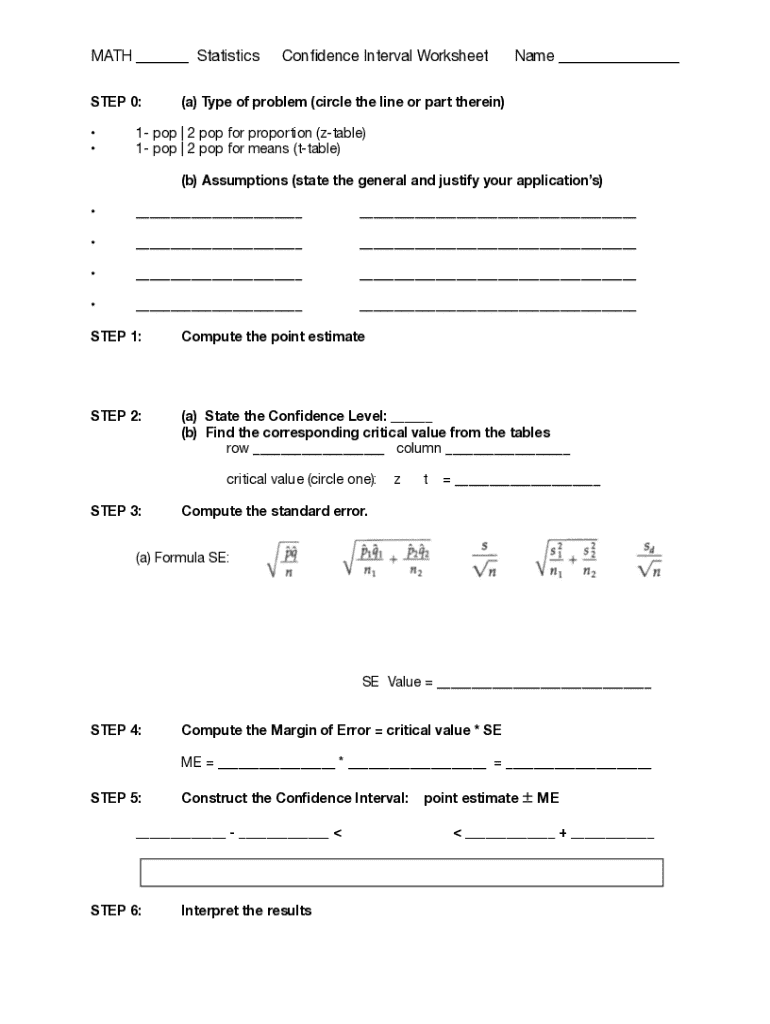
Confidence intervals for population form
Understanding the concept of confidence intervals
Confidence intervals are a fundamental concept in statistical analysis used to estimate the uncertainty surrounding a population parameter. By applying statistical methods to sample data, researchers can establish a range of plausible values for populations based on observed data. A confidence interval provides not only an estimate of a parameter but also an insight into the reliability of that estimate.
The importance of confidence intervals in statistical analysis cannot be overstated. They allow researchers to quantify the uncertainty inherent in sample estimates, enabling better decision-making across a variety of fields, from healthcare to market research. A strong confidence interval reflects the accuracy of the inference drawn from the sample to the population at large.
In real-world applications, confidence intervals are pivotal. For instance, in clinical trials, a new medication's effectiveness is evaluated by computing confidence intervals for improvement rates, which helps determine its viability. Similarly, businesses analyze consumer preferences through confidence intervals to make strategic decisions based on market trends.
Key terms related to confidence intervals
Understanding confidence intervals requires familiarity with several key terms. The first is the distinction between population and sample; a population includes all subjects of interest, while a sample is a subset used to gain insights about the population. Additionally, the confidence level is the probability that the interval produced will capture the actual population parameter, commonly expressed as 90%, 95%, or 99%.
The margin of error is another crucial component, representing the range of values above and below the sample estimate. Additionally, the critical value refers to a statistical constant derived from the probability distribution that determines how far away from the sample mean the true population parameter is expected to be.
Types of confidence intervals
There are primarily two types of confidence intervals that statisticians calculate: those for population means and those for population proportions. Confidence intervals for population means are employed when the goal is to estimate the average value of a certain characteristic within a population. This is particularly common in fields such as psychology and medicine.
On the other hand, confidence intervals for population proportions are used when researchers want to estimate the proportion of a population that possesses a certain characteristic. For instance, this type of interval is relevant in polling data and demographic studies. Understanding the differences between these types can improve the accuracy of statistical inferences and lead to better-informed conclusions.
Calculating the margin of error
Margin of error is crucial in constructing a confidence interval as it quantifies the extent of uncertainty associated with the sample estimate. The formula for calculating the margin of error is as follows: Margin of Error = Critical Value × Standard Error. Here, the critical value is obtained from Z or t-distribution tables, while the standard error measures variability of the sample mean or proportion.
Several factors influence the margin of error, including the sample size and the chosen confidence level. Larger sample sizes tend to yield smaller margins of error due to more representative data, while increasing the confidence level results in a broader range, thereby increasing the margin of error.
Constructing confidence intervals
Constructing confidence intervals requires a systematic approach. For population means, the first step is to identify sample data, followed by determining the appropriate confidence level. Next, calculate the margin of error using the previously discussed formula, and finally formulate the confidence interval using the sample mean along with the margin of error.
For population proportions, similar steps apply—begin by identifying your sample data, select the desired confidence level, and compute the margin of error. Then, construct the confidence interval by using the sample proportion and its associated margin of error to delineate the valid bounds of your estimate.
Practical examples of confidence intervals
Let's explore a practical example for a population mean: Suppose a survey of 100 households reveals an average monthly expenditure of $2,500 with a standard deviation of $300. Using a 95% confidence level with a critical value of 1.96: Margin of Error = 1.96 × (300/√100) = $58.80, resulting in a confidence interval of ($2,441.20, $2,558.80). This means we can say with 95% confidence that the average monthly expenditure for all households is between these values.
For a population proportion example, consider a survey indicating that 60 out of 100 individuals prefer product A over product B. The sample proportion (p) here is 0.60. With a 95% confidence level, the critical value remains 1.96. The margin of error, in this case, would be: Margin of Error = 1.96 × √(0.60 × 0.40 / 100) = 0.096. Thus, the confidence interval for the proportion is (0.504, 0.696), indicating that between 50.4% and 69.6% of the population prefers product A.
Visual representation can solidify understanding, such as plotting both results on a bar graph, illustrating the ranges and emphasizing the expected certainty of results.
Interactive tools for creating confidence intervals
In today's digital age, many tools can assist users in calculating and visualizing confidence intervals for population forms. At pdfFiller, users can access a wide range of interactive tools, including a confidence interval calculator that simplifies these calculations. This platform allows seamless document creation, editing, signing, and management of forms, providing users with powerful document solutions.
Using the confidence interval calculator involves entering your sample data, selecting the desired confidence level, and letting the tool calculate the margin of error and resulting confidence interval. This user-friendly interface ensures that anyone, regardless of statistical expertise, can confidently engage with statistical analysis.
Common misunderstandings about confidence intervals
Confusion often arises when interpreting the confidence level associated with an interval. A confidence level of 95% implies that if we were to take 100 samples, we would expect about 95 of them to produce intervals that contain the true population parameter. It does not imply that there is a 95% chance the true parameter lies within any specific calculated interval.
Another common misunderstanding is confusing confidence intervals with prediction intervals. While confidence intervals provide a range for parameters based on sample estimates, prediction intervals predict individual outcomes based on the model, which is generally wider due to greater uncertainty. Several case studies can often highlight these misinterpretations, leading to flawed conclusions.
Advanced topics in confidence intervals
As statistical methodologies evolve, confidence intervals are being adapted for more complex data scenarios. For non-normal distributions, techniques such as bootstrapping offer a means to approximate confidence intervals without relying on traditional parametric assumptions. This method enhances robustness, especially in cases of skewed data.
Additionally, the debate between Bayesian and frequentist approaches in statistics has implications for confidence intervals. Bayesian methods incorporate prior knowledge to refine estimates, while frequentist approaches rely solely on the data at hand. These advanced methods ensure that users can select the best approach depending on the nature of the analysis and the specific needs of research.
Practical tips for effective usage
When utilizing confidence intervals, it is crucial to select the appropriate confidence level that aligns with the objectives of the study. For higher stakes research, a 99% confidence level may be warranted, while exploratory studies may suffice with a 90% level. It's equally vital to consider the sample size, as larger samples yield more reliable results, effectively reducing the margin of error.
In reporting confidence intervals, clarity is key. Clearly state the interval range alongside the context of the findings to provide a complete picture of what the data indicates. Transparency in methodology enhances trustworthiness in research outputs.
Conclusion and next steps
In conclusion, understanding confidence intervals for population forms is crucial for making informed decisions based on statistical analysis. A solid grasp of the underlying principles, combined with practical examples and advanced methodologies, equips researchers and analysts to draw accurate inferences from data.
Utilizing tools like pdfFiller not only streamlines the document creation process but also enhances efficiency in managing various forms necessary for statistical reporting. Engage with these resources to elevate your statistical practice and deepen your understanding of more complex statistical topics.






For pdfFiller’s FAQs
Below is a list of the most common customer questions. If you can’t find an answer to your question, please don’t hesitate to reach out to us.
Can I create an electronic signature for signing my confidence intervals for population in Gmail?
How do I edit confidence intervals for population on an iOS device?
How do I fill out confidence intervals for population on an Android device?
What is confidence intervals for population?
Who is required to file confidence intervals for population?
How to fill out confidence intervals for population?
What is the purpose of confidence intervals for population?
What information must be reported on confidence intervals for population?
pdfFiller is an end-to-end solution for managing, creating, and editing documents and forms in the cloud. Save time and hassle by preparing your tax forms online.















