Get the free Compressed sensing MRI: a review of the clinical literature
Get, Create, Make and Sign compressed sensing mri a



How to edit compressed sensing mri a online
Uncompromising security for your PDF editing and eSignature needs
How to fill out compressed sensing mri a

How to fill out compressed sensing mri a
Who needs compressed sensing mri a?
Compressed Sensing MRI: A Comprehensive How-To Guide
Understanding compressed sensing in MRI
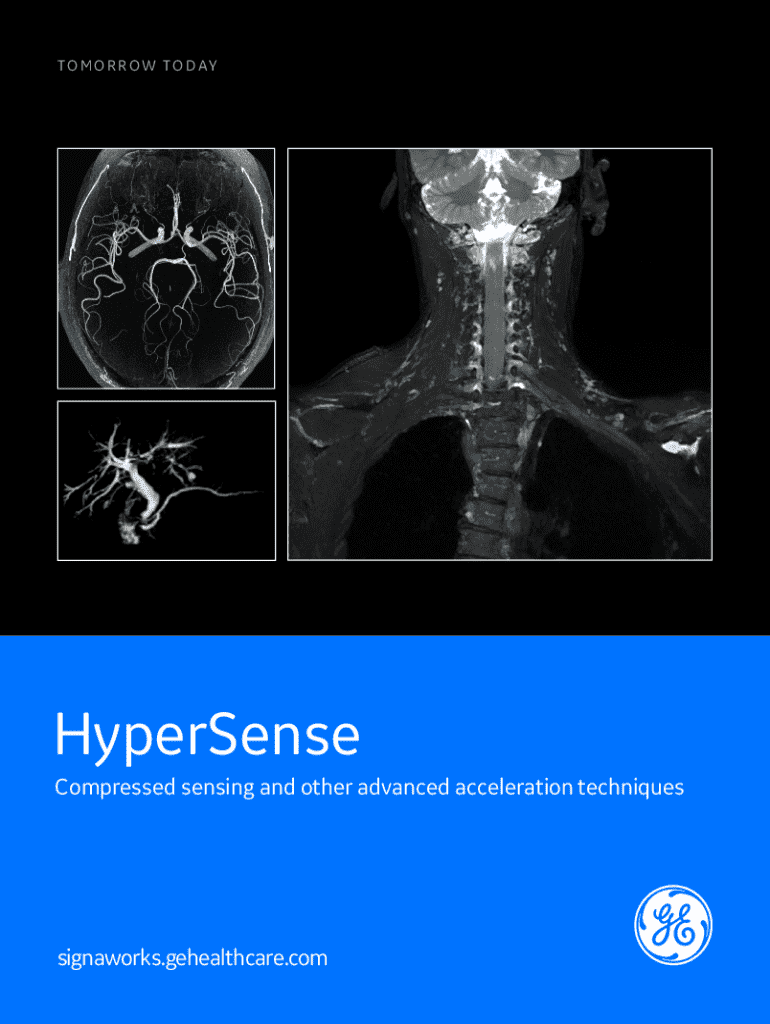
Compressed sensing is an innovative signal processing technique that captures and reconstructs signals with fewer samples than traditionally required. In the context of MRI, this means obtaining high-quality images while significantly reducing scan times. This revolutionary approach addresses critical challenges in medical imaging, enhancing both efficiency and patient experience.
The importance of compressed sensing in MRI cannot be overstated. In a clinical setting, longer scan times often lead to patient discomfort and increased chances of motion artifacts in images, which may compromise diagnostic accuracy. By leveraging sparse representation, compressed sensing empowers MRI systems to produce high-resolution images with reduced data acquisition, thus streamlining the imaging process.
The role of compressed sensing in MRI
The integration of compressed sensing in medical imaging brings numerous benefits. One of the most significant advantages is the reduction of scan times, enabling faster patient throughput in busy clinical settings. This is particularly beneficial for patients who may feel anxious or uncomfortable during lengthy procedures.
Additionally, compressed sensing elevates image quality by facilitating noise reduction and improving the clarity of anatomical structures. However, while the techniques promise multiple benefits, some limitations persist. These include challenges in the reconstruction algorithms and potential artifacts from insufficient sampling. Ongoing research aims to address these drawbacks, focusing on fine-tuning the methods to enhance reliability.
Overview of methodologies in compressed sensing MRI
The effectiveness of compressed sensing MRI largely hinges on the methodologies employed for image reconstruction. Fundamental techniques include iterative reconstruction methods, wherein images are progressively refined through multiple iterations, and Total Variation (TV) minimization, which emphasizes edges in images while promoting sparsity.
In addition to traditional approaches, innovative methods continue to emerge. Edge-preserving total variation-based methods focus on maintaining sharp features in images, essential for accurate diagnostics. Moreover, the integration of deep learning algorithms in reconstruction processes is transforming compressed sensing MRI, enhancing precision and decreasing computational complexity.
Applications of compressed sensing MRI across specialties
Compressed sensing MRI has found applications across various medical specialties due to its ability to enhance imaging efficiency and precision. In neuroscience, it proves indispensable for brain imaging, where high-resolution images are crucial for evaluating conditions such as tumors and neurodegenerative diseases.
In cardiovascular imaging, the rapid acquisition of images afforded by compressed sensing leads to improved visualization of the heart's anatomy and function, facilitating earlier diagnosis of cardiac conditions. Furthermore, musculoskeletal imaging benefits significantly, as it enables detailed evaluation of joints and soft tissues, essential for sports medicine and orthopedics.
How to implement compressed sensing MRI in practice
Implementing compressed sensing MRI effectively requires careful preparation and attention to detail. Clinicians must ensure they have the appropriate equipment and software, which typically includes advanced MRI scanners capable of supporting compressed sensing techniques. Additionally, patient preparation is vital; considerations such as positioning help optimize imaging outcomes.
Performing the scan necessitates selecting the right sequences and parameters. MR technicians should be adept at making real-time adjustments during scanning to adapt to patient needs and ensure the best result. Post-processing techniques are equally important, with several tools available for image reconstruction and optimization that enhance the final images produced.
Collaborative approaches and future directions
Advancements in compressed sensing MRI heavily depend on interdisciplinary collaboration among radiologists, technologists, and data scientists. This collaborative approach fosters innovation, as teams can brainstorm solutions to enhance imaging techniques and patient outcomes.
Emerging trends indicate a growing integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning within compressed sensing frameworks. Such innovations may soon allow for even more rapid and accurate image reconstruction, while potential future applications might extend to unexplored clinical practices, enhancing diagnostic capabilities.
Case studies and success stories
Real-world applications of compressed sensing MRI illustrate its transformative potential. Various hospitals and academic institutions report improved patient outcomes due to faster scan times and better image clarity. Case studies highlight instances where compressed sensing has facilitated timely diagnoses, particularly in emergency settings.
Patient testimonials further bolster the success narrative, where individuals express appreciation for the reduced scanning burden and enhanced comfort. These examples collectively underscore the real-life benefits of compressed sensing MRI, solidifying its role in modern medical practice.
Challenges and considerations
Implementing compressed sensing MRI is not without its challenges. Institutional barriers, such as the need for specialized training and potential budget constraints for advanced equipment, can complicate adoption. To maximize the technology's benefits, institutions must invest in staff education and infrastructural support.
Ethical considerations also arise within the realm of advanced imaging techniques. Patient consent for data usage, privacy, and data management become paramount as technologies evolve. Moreover, maintaining quality assurance and adherence to standards is essential to ensuring the ongoing reliability of compressed sensing MRI applications in clinical workflows.
Interactive tools and resources
The integration of interactive tools such as PDF documentation solutions enhances the workflow involved in managing MRI reports. Using tools like those offered by pdfFiller, radiologists can efficiently draft, edit, and manage MRI documentation. This contributes to streamlining processes, enabling effective collaboration among healthcare professionals.
Best practices for document management in radiology emphasize the importance of organizing and storing compressed sensing MRI reports. By leveraging cloud-based solutions, healthcare teams can access documents from anywhere, ensuring timely sharing and collaboration while maintaining data integrity.






For pdfFiller’s FAQs
Below is a list of the most common customer questions. If you can’t find an answer to your question, please don’t hesitate to reach out to us.
How do I modify my compressed sensing mri a in Gmail?
How can I send compressed sensing mri a to be eSigned by others?
How do I make edits in compressed sensing mri a without leaving Chrome?
What is compressed sensing mri a?
Who is required to file compressed sensing mri a?
How to fill out compressed sensing mri a?
What is the purpose of compressed sensing mri a?
What information must be reported on compressed sensing mri a?
pdfFiller is an end-to-end solution for managing, creating, and editing documents and forms in the cloud. Save time and hassle by preparing your tax forms online.















