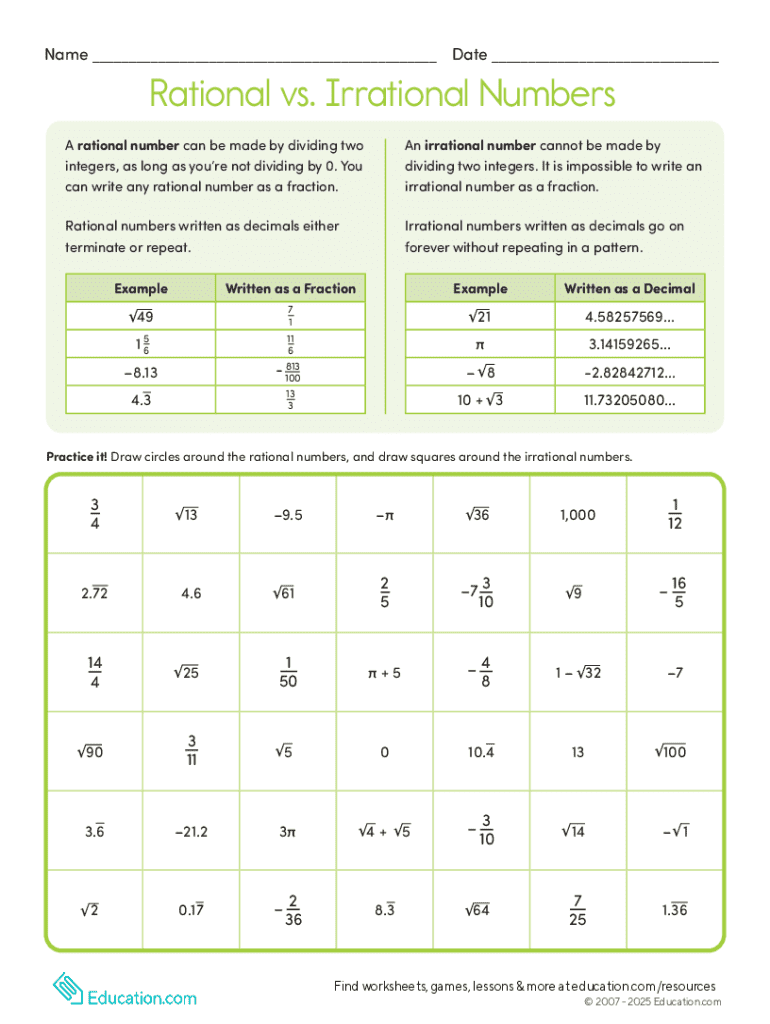
Get the free Comparing Rational And Irrational Numbers Worksheet ...
Get, Create, Make and Sign comparing rational and irrational



How to edit comparing rational and irrational online
Uncompromising security for your PDF editing and eSignature needs
How to fill out comparing rational and irrational

How to fill out comparing rational and irrational
Who needs comparing rational and irrational?
Comparing Rational and Irrational Form
Understanding the basics of rational and irrational numbers
Rational numbers are defined as numbers that can be expressed in the form of a fraction where both the numerator (p) and denominator (q) are integers, with the denominator not equal to zero. For instance, the numbers 1/2, -3, and 4.0 are all rational. When you break them down, you realize they can be represented as a ratio of two integers: 1/2 is 1 divided by 2, while -3 can be expressed as -3/1.
On the other hand, irrational numbers cannot be expressed as simple fractions. They are non-repeating, non-terminating decimals, making them impossible to represent fully in a finite decimal or fraction format. Well-known examples of irrational numbers include the square root of 2 (√2), the mathematical constant π (pi), and e (Euler's number). These numbers have decimal representations that stretch infinitely without repeating patterns, providing a stark contrast to their rational counterparts.
How to classify rational and irrational numbers
Classifying numbers as rational or irrational hinges on understanding their unique characteristics. Rational numbers must meet specific criteria: they can always be expressed as p/q, where p and q are integers and q ≠ 0. This also allows them to include integers like 4, which can be expressed as 4/1 or even fractions like 2/3 or -5/2.
Conversely, irrational numbers lack such a representation. Their decimal expansions are infinitely long and do not form repeating sequences, making classification straightforward as well; simply check for repeating or terminating behavior. For practical classification, visual examples can be incredibly useful. Interactive tools, such as those available on pdfFiller, can assist in visually identifying rational versus irrational numbers through graphing techniques.
Key differences between rational and irrational numbers
The most prominent difference lies in the structural representation of these numbers. Rational numbers can be neatly arranged in the form a/b, where a and b are integers, allowing for straightforward mathematical operations. In contrast, irrational numbers are often presented in forms such as √2 or π, inherently indicating their non-terminating nature. This difference in structure plays a crucial role in how they interact within mathematical operations.
When it comes to addition or multiplication, rational numbers yield rational results, while the interaction with irrational numbers can lead to both rational and irrational outcomes. For example, adding a rational number like 1/2 to an irrational number like √2 yields the sum as an irrational number (1/2 + √2 ≠ p/q). Visual aids, like Venn diagrams, help illustrate these differences, showing that while all integers can be classified under rational numbers, the world of irrationals exists outside this realm.
Real-world applications
Rational numbers find utility in various aspects of our daily lives. They are fundamental in financial calculations, where transactions occur in fractional values, and statistics where averages and ratios are key. For example, a person might need to calculate the interest rate on a loan as a fraction, such as 3/100 or 0.03. Rational numbers simplify these computations.
In contrast, irrational numbers are prominent in geometry and natural phenomena. For instance, π is crucial for calculating the circumference of circles, while the constant e is vital in exponential growth equations. The seamless integration of both types often emerges in mathematical problem solving. A physical construction project may require both the exact measurements (rational) and the calculation of materials (irrational) like the area derived from π.
Interactive examples and practice problems
When seeking to identify rational numbers within a set, a useful approach involves analyzing their expressions. For example, determining if numbers like 2/3, 5, and √4 fit within this category requires understanding the representation of each number as a fraction. Rational numbers can always be represented in fractional form, making it easier to identify them amidst potential candidates.
To identify irrational numbers, one should look for non-terminating and non-repeating decimal behavior. An example is evaluating 0.101001000100001..., which extends infinitely without a pattern, making it irrational. Engaging with practice questions tailored to both types of numbers not only solidifies understanding but allows learners to apply the theory in various contexts. Solutions that mix rational and irrational numbers further enhance this learning process.
Properties of rational and irrational numbers
Rational numbers exhibit several common properties worth noting. They are closed under addition and multiplication, meaning adding or multiplying any two rational numbers will yield a rational result. This property serves as a cornerstone in arithmetic and algebra, providing a reliable framework for calculations involving these numbers. Another important aspect is their density; between any two rational numbers, there are infinitely many others, allowing them to fill the number line densely.
In contrast, the properties of irrational numbers stand out due to their unique nature. They also exhibit density, with irrational numbers distributed throughout the rational numbers. However, they cannot be closed under addition; for example, the sum of two irrational numbers is not guaranteed to be irrational. This interplay between rational and irrational numbers is crucial for understanding how both forms coexist, enhancing the richness of the number system.
Frequently asked questions (FAQs)
Common misconceptions abound regarding rational and irrational numbers. A frequent question arises about whether 0.333... is a rational number. Indeed, it is, as it can be represented as the fraction 1/3. Some users may wonder how rational numbers function in real-world situations, where examples abound in finance, statistics, and measurement. The questions of representation lead to an interesting discussion about whether any irrational number can be expressed as a fraction — to which the answer remains a firm no, as their very definition prohibits such representation.
Comparing rational and irrational numbers
Rational and irrational numbers might seem distinct, yet they compliment each other within the number system. They serve critical roles in advanced mathematics, particularly in calculus and number theory where understanding limits and sequences becomes vital. For example, in calculus, the concept of limits often involves approaching a rational number through irrational values, illustrating the interplay between these two forms.
Real-life examples abound where both types of numbers work in tandem. In engineering, calculations related to the design of structures must incorporate both rational measurements and irrational constants like π. Understanding this synergy is not just an academic exercise; it is essential for practical problem-solving across various fields. By mastering the nuances of both rational and irrational forms, one can effectively tackle complex mathematical challenges with confidence.
Summary of key concepts
The exploration of rational and irrational numbers unveils a world of numerical relationships that underpin much of mathematics. Definitions, classifications, and applications highlight the critical roles that both forms play in our understanding of mathematics. Rational numbers, easily represented and manipulated, offer simplicity in everyday calculations, while irrational numbers expand our comprehension of the numerical continuum.
Mastering both forms is essential for mathematical literacy. As we engage with problems involving both types, we appreciate their unique properties and coexistence within the broader numerical landscape, allowing for a well-rounded mathematical education that is both practical and theoretical. Tools like pdfFiller enhance this learning experience, offering interactive platforms for practicing and applying these concepts effectively.
Additional learning tools
To enhance your learning further, exploring interactive tutorials on pdfFiller allows users to practice with both rational and irrational numbers expertly. By utilizing editing tools, individuals can create personalized worksheets that cater to their unique learning needs. This systematic approach to document creation makes mastering the nuances of these two forms both accessible and engaging, fostering a deeper understanding of their properties and applications.






For pdfFiller’s FAQs
Below is a list of the most common customer questions. If you can’t find an answer to your question, please don’t hesitate to reach out to us.
How do I modify my comparing rational and irrational in Gmail?
Can I create an eSignature for the comparing rational and irrational in Gmail?
How can I fill out comparing rational and irrational on an iOS device?
What is comparing rational and irrational?
Who is required to file comparing rational and irrational?
How to fill out comparing rational and irrational?
What is the purpose of comparing rational and irrational?
What information must be reported on comparing rational and irrational?
pdfFiller is an end-to-end solution for managing, creating, and editing documents and forms in the cloud. Save time and hassle by preparing your tax forms online.















