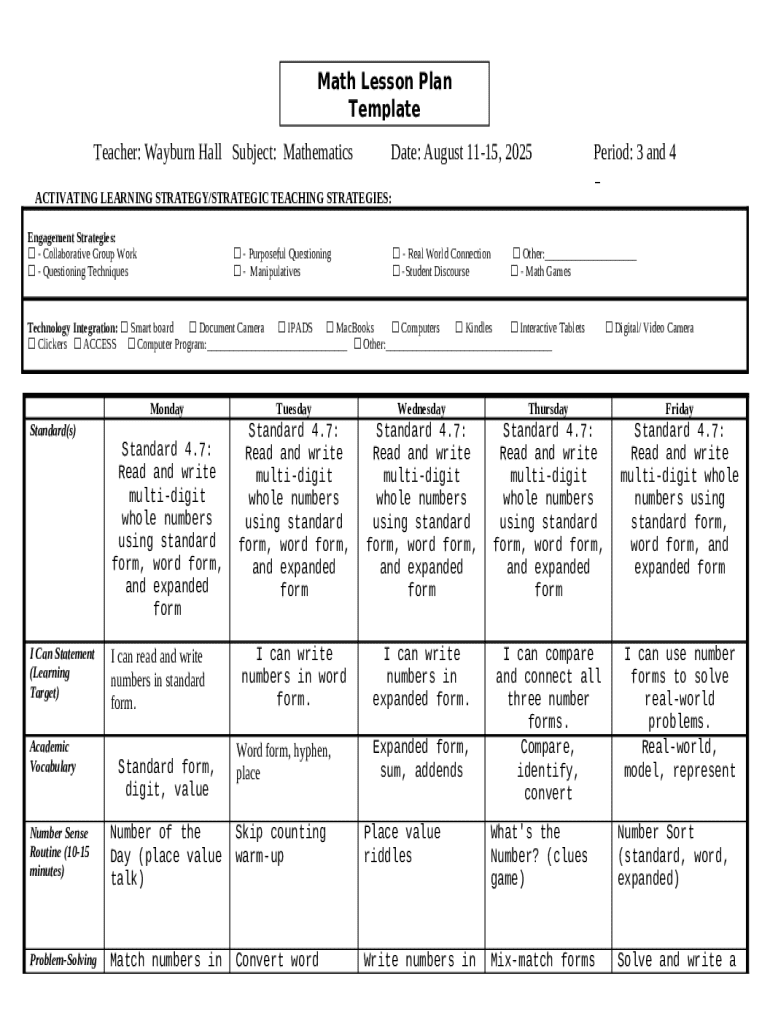
Understanding Multi-Digit Whole Numbers Form
Understanding multi-digit whole numbers
Multi-digit whole numbers are essential in everyday life, serving as the foundation for most mathematical operations. These numbers consist of two or more digits and can represent any whole value, from the number of apples in a basket to an account balance. Recognizing and working with multi-digit whole numbers is fundamental for both academic success and real-world applications.
Their significance becomes apparent when we consider budgeting, calculating distances, or determining quantities in various contexts. Students, including those being homeschooled, must grasp the structure and manipulation of these numbers to enhance their overall mathematical understanding.
The role of place value
Place value refers to the value assigned to a digit based on its position within a number. For instance, in the number 345, the digit '3' is in the hundreds place, thus representing 300, while '4' is in the tens place and represents 40. Understanding this concept is imperative for students, as it ensures clarity while performing addition, subtraction, and more complex operations.
Each digit's position impacts its value dramatically, making the mastery of place value concepts a crucial building block in mathematics. Whether teachers are using a place value chart in the classroom or parents are guiding their children at home, visual aids can greatly enhance understanding.
Place value breakdown
Identifying place values in multi-digit whole numbers begins with breaking down numbers into their respective categories. These include units, tens, hundreds, thousands, and even higher places depending on the number's magnitude. For example, the number 1,236 can be dissected to reveal that it comprises 1 thousand (1,000), 2 hundreds (200), 3 tens (30), and 6 units (6).
Using a place value chart can serve as a powerful visual tool to reinforce these concepts. Students can fill out sheets that depict each place in a number, thereby gaining a clearer understanding of how numbers are structured.
The first position in a multi-digit number, representing individual units.
The second position representing a group of ten units.
The third position, denoting a group of one hundred.
The fourth position, indicating a group of one thousand.
Hands-on activities can reinforce these concepts. For example, students could use physical objects like blocks to represent different place values, or engage with interactive software tools that allow them to manipulate numbers directly.
The various forms of multi-digit whole numbers
Multi-digit whole numbers can be represented in several forms, including standard form, expanded form, and word form, each serving a unique purpose in learning and application.
Standard form
Standard form is the simplest representation of a number, such as 1,254 or 5,678. It's what we typically use in everyday circumstances as well as in basic arithmetic operations.
Expanded form
Expanded form breaks down a number into the sum of its parts, showcasing the value of each digit. For example, 1,254 can be expressed as 1,000 + 200 + 50 + 4. This breakdown not only reinforces understanding of place value but also assists younger students in mastering addition algorithms while avoiding common pitfalls.
Word form
Word form requires writing the number out in words. For instance, 3,482 becomes 'three thousand four hundred eighty-two.' This practice is particularly beneficial for children, as it builds vocabulary and comprehension skills.
Practice exercises that transition between these forms can enhance students’ understanding, while also allowing them to see the interconnectedness of numerical representations.
Comparing multi-digit whole numbers
Understanding how to compare multi-digit whole numbers is an important skill. Students must learn to use the symbols for greater than (>), less than (<), and equals (=). This comparison facilitates numerous operations, including ordering numbers for addition or identifying larger quantities in real-life applications.
To compare numbers effectively, students can follow these techniques: first, examine the digit in the highest place value to determine which number is larger. If the highest digits are the same, proceed to the next place value until a difference is found.
Identify the highest place value in both numbers.
Compare the digits in that place value.
If digits are the same, move to the next place value and repeat.
Declare the relationship using the appropriate symbol.
Engaging students with games that involve number comparisons can reinforce their learning. By using objects or digital tools, they can practice these concepts in an enjoyable way.
Rounding multi-digit whole numbers
Rounding is a crucial skill that allows students to estimate values quickly. To round a multi-digit whole number, one must consider the digit to the immediate right of the target rounding position. If this digit is 5 or greater, you round up; if it's less than 5, you round down.
For instance, if rounding the number 3,764 to the nearest hundred, you look at the '7' in the tens place. The rounded number would then be 3,800. Emphasizing rounding techniques in practical scenarios, like estimating costs in budgeting, makes learning more relevant and engaging for students.
Identify the place value you need to round to.
Look at the digit to the right.
Decide whether to round up or down.
Rewrite the number with zeroes replacing the digits to the right of the rounded position.
Interactive exercises or worksheets can provide invaluable practice for students, enhancing their rounding abilities while providing a clearer picture of its real-life applications.
Application of multi-digit whole numbers
Mastering addition and subtraction involving multi-digit whole numbers is fundamental for students. Whether calculating expenses or summarizing data, these operations form the basis of more complex mathematics. While performing addition, it is vital to line up the numbers correctly according to their place values, as this ensures accuracy in calculations.
A step-by-step strategy for addition might involve: first writing the numbers vertically, then starting from the rightmost column, adding each digit, carrying over as needed, and finally writing the sum beneath. Common pitfalls include misalignment and forgetting to carry over, which can be easily avoided with regular practice.
Align the numbers by their rightmost digits.
Add each column starting from the right.
Carry over if the sum exceeds 9.
For real-world applications, consider projects such as budgeting for a class event or measuring supplies in a science fair. These practical situations help reinforce understanding, enabling students to visualize their skills in use.
Teaching multi-digit whole numbers
For educators, adopting effective strategies for teaching multi-digit concepts is crucial. It's essential to connect with students through various learning styles by incorporating visual, auditory, and kinesthetic methods. For example, using place value charts can help visual learners, while hands-on activities can support kinesthetic learners.
Resources for classroom use include interactive digital tools that allow students to manipulate numbers digitally, enhancing their understanding of place value and operations. Fostering a collaborative learning environment, where students can work in pairs or small groups, can also solidify their grasp of these concepts.
Engaging students with interactive content
Integrating technology in the classroom can further increase student engagement. Platforms that provide interactive activities or gamified lessons can transform the learning experience, making complex concepts more accessible and enjoyable.
By creating an engaging atmosphere where students feel comfortable exploring numbers, educators can nurture a lifelong interest in mathematics.
Fun activities and games
Incorporating games in learning about multi-digit whole numbers creates an enjoyable and stimulating environment. There are numerous resources available that introduce fun, interactive games specifically designed to reinforce these mathematical concepts. Games such as comparing numbers or estimating sums can be valuable tools for practice and mastery.
For competitive learning, educators or parents can structure activities as competitions, allowing students to test their skills against their peers. This can foster a motivating atmosphere, where students are encouraged to excel in their understanding of numbers.
Students compete to see who can accurately compare numbers the fastest.
Students search for multi-digit numbers hidden around the classroom or home.
Digital platforms with quizzes designed to reinforce understanding in a fun way.
Conclusion: The importance of mastery
Mastering multi-digit whole numbers is paramount, as it lays the groundwork for advanced mathematics. Understanding how to identify, manipulate, and apply these numbers equips students—whether in a classroom or a homeschooling environment—with essential skills for both academic success and daily life.
Continual learning and practice are vital to cement these concepts in students’ minds. With ongoing reinforcement from resources, engaging activities, and interactive tools, educators and parents alike can foster a strong foundation in the understanding of multi-digit whole numbers.
Additional insights
Looking forward, the trends in number education are shifting toward more interactive and technology-driven methods. Innovative applications and platforms are emerging to enhance learning, making the understanding of multi-digit whole numbers more accessible and enjoyable.
Utilizing technology can empower both students and educators. By embracing these advancements, educational experiences can be redefined, allowing learners to explore mathematical concepts in dynamic and engaging ways.