Get the free Filamentous Algae, Including Colonial Forms. This is a comprehensive guide and overv...
Get, Create, Make and Sign filamentous algae including colonial



How to edit filamentous algae including colonial online
Uncompromising security for your PDF editing and eSignature needs
How to fill out filamentous algae including colonial

How to fill out filamentous algae including colonial
Who needs filamentous algae including colonial?
Filamentous algae including colonial forms: A comprehensive guide
Understanding filamentous algae
Filamentous algae are unique and diverse organisms that thrive in various aquatic environments. These organisms are primarily characterized by their thread-like structures that can form extensive mats or colonies, often giving them a significant presence in both freshwater and marine ecosystems. Key distinguishing features include their filamentous growth forms, which allow them to capture sunlight efficiently and perform photosynthesis. Unlike other algae that may exist as singles cells, filamentous algae can form intertwined filaments, emphasizing their communal aspect.
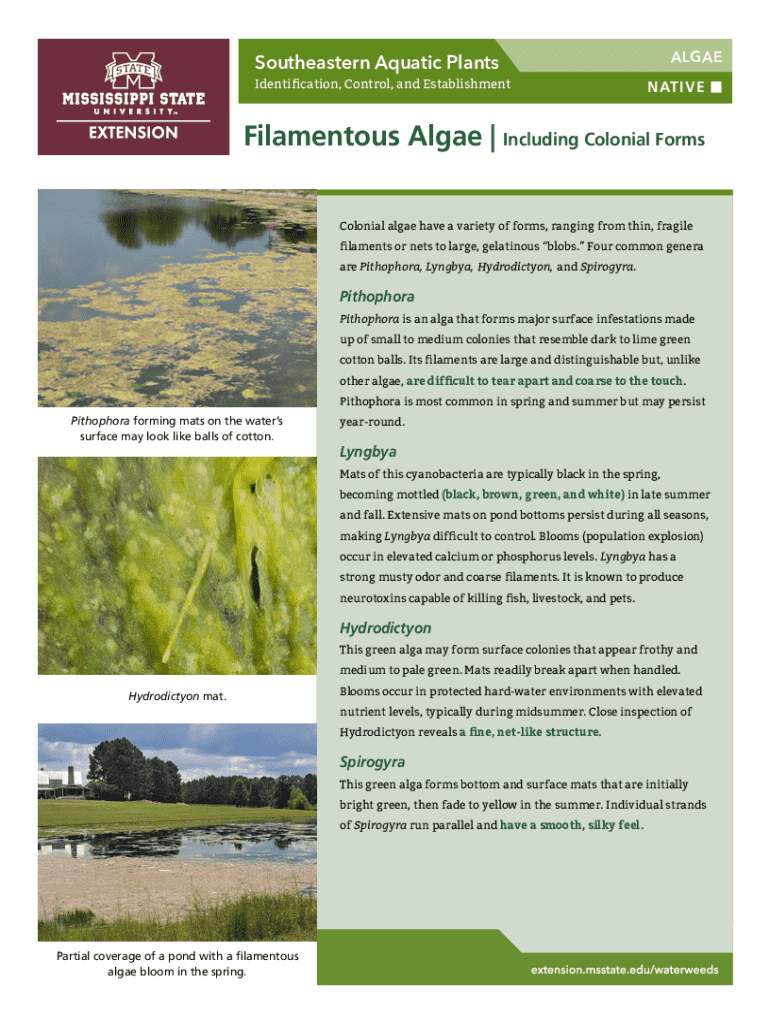
Types of filamentous algae include genera such as **Pithophora**, **Lyngbya**, and **Hydrodictyon**, each possessing unique traits. **Pithophora**, for example, forms dense mats that can significantly alter local ecosystems. **Lyngbya** is notable for its ability to produce toxins that can affect aquatic life and human health. On the other hand, **Hydrodictyon** will form net-like structures on the water's surface that are visible from afar, marking its distinct colonial form.
The role of filamentous algae in ecosystems
In aquatic ecosystems, filamentous algae play an essential ecological role. They serve as primary producers, forming the basis of many food webs. Through photosynthesis, these algae convert sunlight into energy, supporting various herbivorous organisms such as zooplankton, which in turn serve as food for larger species, including fish. Their presence can significantly enhance biodiversity by providing habitats and food sources for numerous aquatic organisms.
Filamentous algae also establish symbiotic relationships, particularly with certain invertebrates, and bacteria, aiding in nutrient cycling. However, the growth of these algae can sometimes lead to negative impacts, such as the reduction of light penetration in water, which affects other aquatic flora and fauna. Their place in the food chain makes them vital, but their unchecked growth can disrupt ecological balance and biodiversity.
Urban and agricultural environments
Filamentous algae favor nutrient-rich environments, meaning they often thrive in urban and agricultural settings due to runoff that contains fertilizers and other nutrients. These conditions create ideal growth environments for filamentous algae, leading to the rapid development of colonies, which can be observed as surface mats or blobs on water bodies. Factors influencing their growth rates include temperature, light availability, and nutrient concentrations.
While filamentous algae can help purify water and provide oxygen, their overgrowth can lead to eutrophication, resulting in excessive nutrients, decreased water quality, and hypoxic conditions for aquatic life. Hence, while beneficial in moderate amounts, they pose challenges when left unchecked. Sustainable water management practices need to be implemented to balance these benefits against the potential drawbacks of algal blooms.
Identifying and classifying colonial forms
Identifying various colonial forms of filamentous algae can be accomplished through careful observation and recognition techniques. Cyclindrical filaments may indicate the presence of **Lyngbya**, while a mesh-like structure suggests **Hydrodictyon**. Observing growth patterns, texture, and color can further aid identification efforts. For instance, surface infestations often appear as green or brownish mats, while **Pithophora** colonies can resemble cotton balls interspersed in water.
Key features to observe include the color variations, the texture of the filaments, and the arrangement of the filaments themselves. Different colonial forms can drastically impact their environments—such as forming barriers to sunlight or altering local nutrient cycling, thus influencing broader ecological interactions.
Management of filamentous algae in various settings
Effective management of filamentous algae involves monitoring growth and implementing control measures. Regular monitoring can be achieved using tools such as water quality testing kits, visual assessments, and aerial surveys, especially for larger water bodies. By observing signs of excessive growth—such as surface mats, floating blobs, or drastic discoloration—stakeholders can determine potential pollution indicators and make informed management decisions.
Control measures can include biological options, such as introducing herbivorous fish that consume algae, or chemical treatments to alleviate overgrowth. Best practices in prevention involve maintaining balanced nutrient levels, reducing runoff, and implementing sustainable landscaping practices. For aquaculture farms and ponds, routine maintenance activities and timely interventions are crucial to prevent filamentous algae expansion.
Interactive tools and resources
Utilizing tools like **pdfFiller** can greatly assist in documenting and reporting on filamentous algae management. This versatile platform allows users to create, edit, and sign PDF reports with ease, offering a systematic approach for individuals and teams working on algae research and management projects. Users can efficiently fill out assessments, edit findings, and generate clear documentation that helps in tracking management efforts.
Collaboration features in pdfFiller also ensure that team members can access and contribute to shared documents, streamlining communication. With cloud-based storage, users can access their documents from anywhere, making it easier to work on research projects involving filamentous algae or share updates on algae management initiatives.
Case studies and real-world applications
Successful management of filamentous algae can be observed in various regions around the world. For instance, in some lakes of North America, community-driven initiatives have effectively reduced the overgrowth of filamentous algae through a combination of biological controls and sustainable land use practices. These examples illustrate how localized efforts can combat algal blooms and restore ecosystem balance.
Collaborative research also plays a critical role in understanding filamentous algae. Many studies involve partnerships among universities, governmental agencies, and environmental organizations, focusing on the ecology and management of algae. These efforts consistently yield new methods and insights that help in devising innovative control measures and preventative strategies.
Future directions in filamentous algae research
Emerging trends in filamentous algae research highlight the potential for technological advancements to enhance management strategies. Recent developments include the utilization of drones for aerial monitoring of algal blooms and advancements in molecular biology to understand the genetic makeup of specific algae species. These innovations are paving the way for more effective monitoring and control techniques.
Community involvement continues to be crucial, as public education initiatives can foster awareness and proactive measures towards algae management. Engaging local communities in monitoring efforts, promoting education around sustainable practices, and encouraging participation in research can significantly enhance the understanding and control of filamentous algae, ensuring healthier aquatic ecosystems.
Integrating your findings
Documenting and sharing discoveries regarding filamentous algae is essential for effective management and collaboration across various stakeholders. Best practices for thorough documentation include maintaining clear and detailed reports on algae growth, management actions taken, and outcomes observed. Using platforms like pdfFiller facilitates creating comprehensive reports that are easily shareable and adaptable, crucial for collaborative environments.
Leveraging features of pdfFiller can enhance the organization and sharing of insights on filamentous algae. Users can utilize functionalities such as version control and collaborative commenting to enrich their documentation processes, making it easier to convey findings back to stakeholders and contribute to the collective knowledge surrounding filamentous algae management.






For pdfFiller’s FAQs
Below is a list of the most common customer questions. If you can’t find an answer to your question, please don’t hesitate to reach out to us.
How can I send filamentous algae including colonial for eSignature?
How do I edit filamentous algae including colonial online?
Can I create an electronic signature for the filamentous algae including colonial in Chrome?
What is filamentous algae including colonial?
Who is required to file filamentous algae including colonial?
How to fill out filamentous algae including colonial?
What is the purpose of filamentous algae including colonial?
What information must be reported on filamentous algae including colonial?
pdfFiller is an end-to-end solution for managing, creating, and editing documents and forms in the cloud. Save time and hassle by preparing your tax forms online.