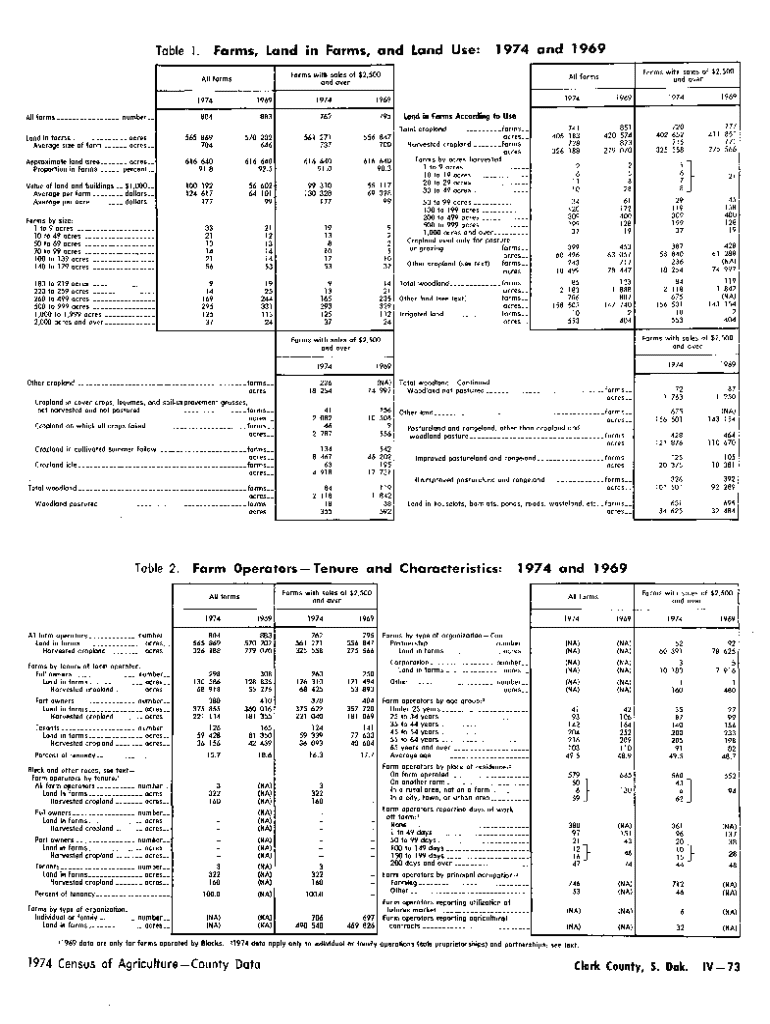
Get the free All farms ------ number -
Get, Create, Make and Sign all farms ------ number



How to edit all farms ------ number online
Uncompromising security for your PDF editing and eSignature needs
How to fill out all farms ------ number

How to fill out all farms ------ number
Who needs all farms ------ number?
A Comprehensive Guide to All Farms - Understanding the Basics
Overview of what you will learn
This guide explores the various aspects of farming, covering types of farms, the farming process, legal considerations, economic aspects, and modern agricultural technologies, particularly highlighting how pdfFiller can assist in streamlining document management.
Quick navigation links to key sections
Understanding farms
Farms are defined as plots of land dedicated to the cultivation of plants and animals for food, fiber, and other products. The diversity of farming embraces several types: crop farms focus on growing crops like fruits, grains, or vegetables; livestock farms raise animals such as cattle, sheep, and pigs; mixed farms combine both crops and livestock; and specialty farms concentrate on high-value products, such as organic produce or herbs. Each type plays a significant role in our economy and food supply, ensuring food security and providing livelihoods.
Farming is not just a source of food; it contributes significantly to the economy. For example, according to the USDA, the agriculture sector represents a considerable share of the U.S. GDP. Farms provide jobs in rural areas, create economic opportunities, and manage valuable natural resources. Understanding the multifaceted nature of farms helps stakeholders appreciate their contributions and the importance of sustainable practices.
Types of farms
Farming covers a wide spectrum, ranging from traditional crop and livestock methods to innovative modern practices. Here’s a closer look at the primary types of farms:
Each type of farm requires specific knowledge, resources, and management techniques, which vary widely depending on geographical location, market demand, and local climate conditions.
The farming process
The farming process unfolds in several distinct stages, each critical for successful yield management. These stages encompass preparation, planting, maintenance, harvesting, and post-harvest processing.
Utilizing effective tools and equipment at each stage can impact the overall success of a farm. From tractors and tillers to irrigation systems and harvesters, regular best practices in operation not only increase efficiency but also promote environmental sustainability.
Legal and compliance considerations
Farms operate under a myriad of regulations that govern everything from safe labor practices to environmental standards. Understanding these compliance requirements is essential to avoid penalties and ensure smooth operations. Regulations can vary by region or type of farming.
Utilizing tools such as pdfFiller can assist farmers in efficiently managing and filing necessary forms, ensuring compliance with evolving regulations without the stress.
Economic aspects of farming
The economic viability of farms hinges on understanding various costs associated with them. This includes both initial setup costs and ongoing operational expenses.
Accessing funding and grants is vital for many farmers, allowing them to invest in their farms and improve profitability. Various government programs, agricultural associations, and financial institutions offer funding based on program eligibility criteria.
Understanding market strategies and profitability assessments are essential. Farmers must analyze trends and adapt to consumer demands to remain competitive.
Technology in agriculture
Modern farming technologies are transforming agricultural practices, making them more efficient and sustainable. Precision agriculture focuses on monitoring and managing field variability to optimize yields.
Moreover, pdfFiller plays an essential role in farm documentation by enabling easy editing, managing forms, and digitally signing documents. This streamlines the often-complicated paperwork associated with farming.
Resources for farmers
Various resources are available to help farmers improve their operations and access crucial support. Farming associations offer networking opportunities, while funding resources provide financial aid for new and existing farmers.
Related forms and documentation
A variety of forms are essential for starting and managing a farm, and knowing how to navigate through these documents can save considerable time and stress.
Using proper tools like pdfFiller simplifies filling out essential forms, allowing farmers to complete and submit documentation seamlessly and conveniently.
Finding local support centers
Accessing support centers can significantly benefit farmers looking for localized resources and guidance. Many organizations provide assistance tailored to specific regions and needs.
FAQs related to farms
Frequently asked questions about farming practices shed light on common challenges and best practices within the industry.
Interactive tools for farmers
Utilizing interactive tools can greatly enhance farming operations and decision-making processes. Budgeting calculators and planning tools help farmers manage their resources effectively.
Leveraging technology allows farmers to maximize productivity, ensure compliance, and adapt quickly to market changes, thereby enhancing sustainability and growth.






For pdfFiller’s FAQs
Below is a list of the most common customer questions. If you can’t find an answer to your question, please don’t hesitate to reach out to us.
How can I send all farms ------ number to be eSigned by others?
How do I make changes in all farms ------ number?
How do I fill out the all farms ------ number form on my smartphone?
What is all farms ------ number?
Who is required to file all farms ------ number?
How to fill out all farms ------ number?
What is the purpose of all farms ------ number?
What information must be reported on all farms ------ number?
pdfFiller is an end-to-end solution for managing, creating, and editing documents and forms in the cloud. Save time and hassle by preparing your tax forms online.

























