2 Sample T Test Conditions
What is 2 sample t test conditions?
The 2 sample t test conditions are statistical assumptions that need to be met in order to perform a two-sample t test. This test is used to determine if there is a significant difference between the means of two independent groups. There are two main conditions that must be satisfied for the 2 sample t test:
What are the types of 2 sample t test conditions?
The types of 2 sample t test conditions are as follows:
Independence: The observations in each group must be independent of each other. This means that the values in one group should not be influenced by the values in the other group.
Normality: The data in each group should be approximately normally distributed. This can be checked using statistical tests or by visual inspection of histograms or normal probability plots.
How to complete 2 sample t test conditions
To complete the 2 sample t test conditions, follow these steps:
01
Gather the data for the two groups you want to compare.
02
Check for independence by ensuring that the observations in each group are not influenced by the other group.
03
Check for normality by using statistical tests or visually inspecting the data distribution in each group.
04
If the conditions are met, proceed with conducting the two-sample t test to assess the difference between the means of the two groups.
pdfFiller empowers users to create, edit, and share documents online. Offering unlimited fillable templates and powerful editing tools, pdfFiller is the only PDF editor users need to get their documents done.
Thousands of positive reviews can’t be wrong
Read more or give pdfFiller a try to experience the benefits for yourself
Questions & answers
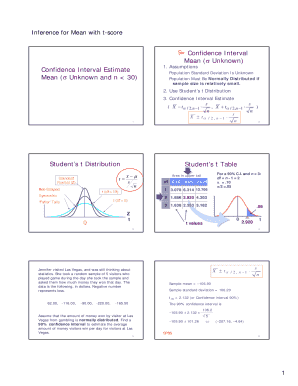
What is a two-sample t-test?
The two-sample t-test (Snedecor and Cochran, 1989) is used to determine if two population means are equal. A common application is to test if a new process or treatment is superior to a current process or treatment. There are several variations on this test. The data may either be paired or not paired.
What is the T value in a 2 sample t test?
The t-test produces two values as its output: t-value and degrees of freedom. The t-value, or t-score, is a ratio of the difference between the mean of the two sample sets and the variation that exists within the sample sets. The numerator value is the difference between the mean of the two sample sets.
What are the conditions for a 2 sample t-test?
Two-sample t-test assumptions Data values must be independent. Data in each group must be obtained via a random sample from the population. Data in each group are normally distributed. Data values are continuous. The variances for the two independent groups are equal.
How do you do a two sample t test?
Steps to Calculate Two Sample T Hypothesis Test (Unequal Variance): Step 1 – Calculate mean (X̅) of each sample. X̅ = (x1 + x2 + …. Step 2 – Calculate variance (S2) of each sample. Step 3 – Calculate t value. Step 4 – Calculate degrees of freedom (DF) Step 5 – Compare t-calc with critical value in the t-distribution table.
What are the 2 types of two sample t tests?
Independent two-sample t-test. Paired sample t-test.
What are the conditions for using t-test?
The conditions required to conduct a t-test include the measured values in ratio scale or interval scale, simple random extraction, homogeneity of variance, appropriate sample size, and normal distribution of data.
Related templates