Periodic Table Of The Elements With Ionization Energies - Page 2
What is the Periodic Table Of The Elements With Ionization Energies?
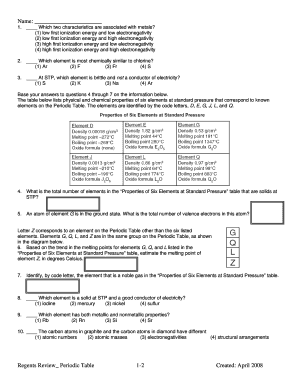
The Periodic Table Of The Elements With Ionization Energies is a comprehensive tool used in chemistry to organize and display the chemical elements in a structured manner. It provides essential information about the elements, including their atomic number, symbol, atomic weight, electron configuration, and ionization energies. Ionization energy is the amount of energy required to remove an electron from an atom or ion in its gaseous state. By studying the ionization energies of elements, scientists can gain valuable insights into their reactivity and chemical properties.
What are the types of Periodic Table Of The Elements With Ionization Energies?
There are several types of Periodic Table Of The Elements With Ionization Energies. The most common ones include:
How to complete Periodic Table Of The Elements With Ionization Energies
Completing the Periodic Table Of The Elements With Ionization Energies requires careful research and data compilation. Here are the steps to follow:
By following these steps, you can create a comprehensive Periodic Table Of The Elements With Ionization Energies that will serve as a valuable reference tool for chemistry students and professionals alike.