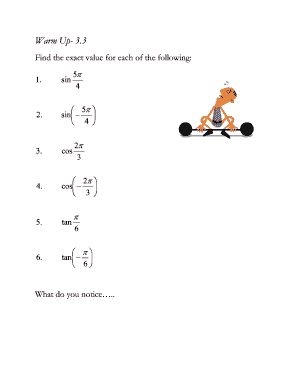Angles And Radians Of A Unit Circle
What is Angles And Radians Of A Unit Circle?
Angles and radians of a unit circle refer to the measurements used to describe the position of a point on the circle. An angle is the amount of rotation needed to move from one point to another on the circle. Radians, on the other hand, are a unit of measurement used for angles, defined as the ratio of the length of an arc on the unit circle to the radius of the circle.
What are the types of Angles And Radians Of A Unit Circle?
There are several types of angles and radians of a unit circle. These include:
Acute angles: These angles measure less than 90 degrees in the coordinate system of a unit circle.
Right angles: These angles measure exactly 90 degrees, forming a quarter of the unit circle.
Obtuse angles: These angles measure between 90 and 180 degrees in the coordinate system of a unit circle.
Straight angles: These angles measure exactly 180 degrees, forming a half circle.
Reflex angles: These angles measure between 180 and 360 degrees in the coordinate system of a unit circle.
How to complete Angles And Radians Of A Unit Circle
To complete angles and radians of a unit circle, follow these steps:
01
Identify the given angle or radian measure.
02
Determine the type of angle or radian measure based on its measurement.
03
Plot the angle or radian measure on the unit circle.
04
Label or mark the point corresponding to the angle or radian measure.
05
Use the coordinates of the marked point to determine its position in the coordinate system.
06
Repeat the process for any additional angles or radian measures.
pdfFiller empowers users to create, edit, and share documents online. Offering unlimited fillable templates and powerful editing tools, pdfFiller is the only PDF editor users need to get their documents done.
Video Tutorial How to Fill Out Angles And Radians Of A Unit Circle
Thousands of positive reviews can’t be wrong
Read more or give pdfFiller a try to experience the benefits for yourself
Questions & answers
How do you find the radian measure of an angle on a unit circle?
In any circle of radius r, the ratio of the arc length ℓ to the circumference equals the ratio of the angle θ subtended by the arc at the centre and the angle in one revolution. Thus, measuring the angles in radians, ℓ2πr=θ2π⟹ ℓ=rθ.
What is the easiest way to remember the radians on the unit circle?
0:05 7:18 ❖ A Way to remember the Entire Unit Circle for Trigonometry ❖ - YouTube YouTube Start of suggested clip End of suggested clip And remember that the circumference of a circle is 2 pi times its radius well the unit circle hasMoreAnd remember that the circumference of a circle is 2 pi times its radius well the unit circle has radius 1. So we'll just get 2 pi times 1 or simply 2 pi.
How do you find the reference angle in radians?
How do I calculate the reference angle in radians? 0 to π/2 — First quadrant, so reference angle = angle . π/2 to π — Second quadrant, so reference angle = π - angle . π to 3π/2 — Third quadrant, so reference angle = angle - π . and. 3π/2 to 2π — Fourth quadrant, so reference angle = 2π - angle .
Related templates