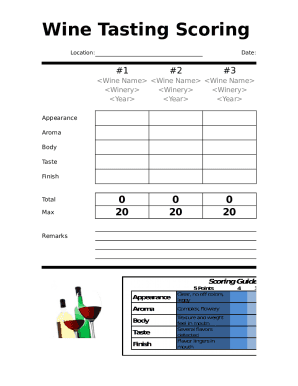
Log-log Calibration Linear Curve
What is Log-log Calibration Linear Curve?
A Log-log Calibration Linear Curve is a method used to analyze data where both the x and y-axis are logarithmically scaled. This technique is commonly used in scientific research and data analysis to represent complex relationships in a simplified manner.
What are the types of Log-log Calibration Linear Curve?
There are two main types of Log-log Calibration Linear Curves: 1. Direct Log-log Calibration Curve - where the relationship between variables is linear on both axes. 2. Indirect Log-log Calibration Curve - where the relationship between variables is linear only when one axis is a log scale.
How to complete Log-log Calibration Linear Curve
Completing a Log-log Calibration Linear Curve requires the following steps: 1. Collect relevant data points. 2. Plot the data points on a graph with logarithmic scales on both axes. 3. Fit a straight line to the data points using linear regression. 4. Evaluate the goodness of fit and adjust if necessary.
pdfFiller empowers users to create, edit, and share documents online. Offering unlimited fillable templates and powerful editing tools, pdfFiller is the only PDF editor users need to get their documents done.